Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
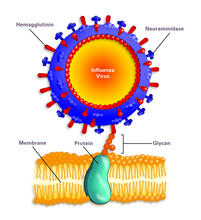
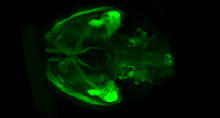
Influenza virus attaches to host membrane (with labels)
2505
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View MediaDynamin Fission
3448
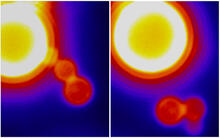
Time lapse series shows short dynamin assemblies (not visible) constricting a lipid tube to make a "beads on a string" appearance, then cutting off one of the beads i.e., catalyzing membrane fission). Ramachandran, Pucadyil et al. , The Scripps Research Institute View MediaBond types
2519
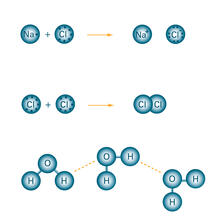
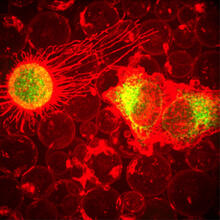
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaFruit fly sperm cells
2433
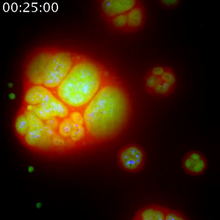
Developing fruit fly spermatids require caspase activity (green) for the elimination of unwanted organelles and cytoplasm via apoptosis. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaAnglerfish ovary cross-section
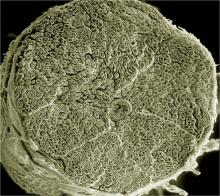
3620
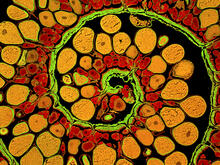
This image captures the spiral-shaped ovary of an anglerfish in cross-section. Once matured, these eggs will be released in a gelatinous, floating mass. James E. Hayden, The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, Pa. View MediaCryo-ET cell cross-section visualizing insulin vesicles
6607
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a color-coded, 3D version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaFly by night
2417
This fruit fly expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the same pattern as the period gene, a gene that regulates circadian rhythm and is expressed in all sensory neurons on the surface of the fl Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia View MediaXenopus laevis embryos
2756
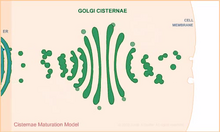
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a model organism for studying embryonic development. The frog embryo on the left lacks the developmental factor Sizzled. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaCisternae maturation model
1307
Animation for the cisternae maturation model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaFruit fly in the pink
2693
Fruit flies are a common model organism for basic medical research. Crabtree + Company View MediaNeutrophil-like cells migrating in a microfluidic chip
6886
Neutrophil-like cells (blue) in a microfluidic chip preferentially migrating toward LTB4 over fMLP. Caroline Jones, University of Texas at Dallas. View MediaCatalase diversity
7003
Catalases are some of the most efficient enzymes found in cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMouse liver labeled with fluorescent probe
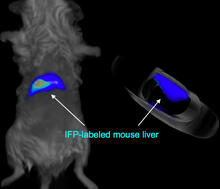
2601
A mouse liver glows after being tagged with specially designed infrared-fluorescent protein (IFP). Xiaokun Shu, University of California, San Diego View MediaChromosome inside nucleus
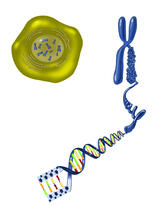
2539
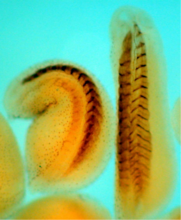
The long, stringy DNA that makes up genes is spooled within chromosomes inside the nucleus of a cell. Crabtree + Company View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
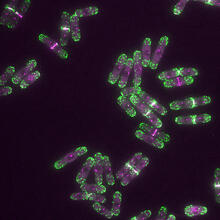
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaCytonemes in developing fruit fly cells
3574
Scientists have long known that multicellular organisms use biological molecules produced by one cell and sensed by another to transmit messages that, for instance, guide proper development of organs Sougata Roy, University of California, San Francisco View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
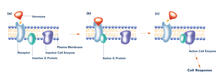
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaMouse heart muscle cells
3282
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaHeLa cells
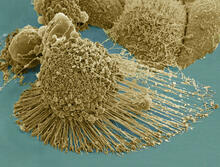
3519
Scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic HeLa cell. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaProteins related to myotonic dystrophy
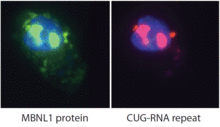
2727
Myotonic dystrophy is thought to be caused by the binding of a protein called Mbnl1 to abnormal RNA repeats. Manuel Ares, University of California, Santa Cruz View MediaCellular metropolis
2308
Like a major city, a cell teems with specialized workers that carry out its daily operations--making energy, moving proteins, or helping with other tasks. Kathryn Howell, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center View MediaIntroduction to Genome Editing Using CRISPR/Cas9
5815
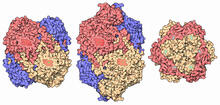
Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9 is a rapidly expanding field of scientific research with emerging applications in disease treatment, medical therapeutics and bioenergy, just to name a few. Janet Iwasa View MediaVDAC-1 (3)
2494
The structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaRespiratory droplet
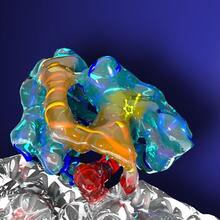
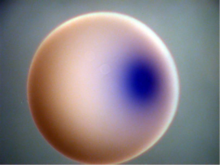
6994
This painting shows a cross section of a small respiratory droplet, like the ones that are thought to transmit SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaVDAC video 01
2570
This video shows the structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaKappa opioid receptor
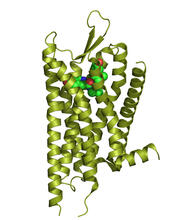
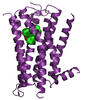
3359
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, JDTic. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediamDia1 antibody staining- 02
3331
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaYeast cells with endocytic actin patches
6793
Yeast cells with endocytic actin patches (green). These patches help cells take in outside material. When a cell is in interphase, patches concentrate at its ends. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaMouse brain 1
6929
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaiPS cell facility at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research
2723
This lab space was designed for work on the induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell collection, part of the NIGMS Human Genetic Cell Repository at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research. Courtney Sill, Coriell Institute for Medical Research View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaBody toxins (with labels)
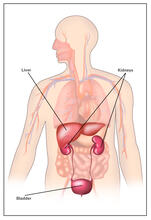
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaX-ray crystallography (with labels)
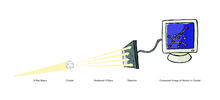
2512
X-ray crystallography allows researchers to see structures too small to be seen by even the most powerful microscopes. Crabtree + Company View MediaXenopus laevis egg
2753
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a model organism for studying embryonic development. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaCryogenic storage tanks at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research
2722
Established in 1953, the Coriell Institute for Medical Research distributes cell lines and DNA samples to researchers around the world. Courtney Sill, Coriell Institute for Medical Research View MediaSerratezomine A
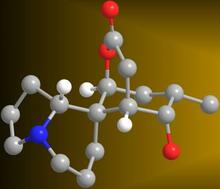
2687
A 3-D model of the alkaloid serratezomine A shows the molecule's complex ring structure. View MediaCells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
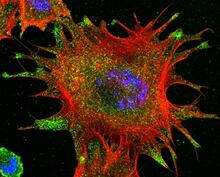
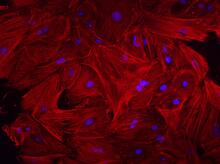
3617
This image shows a normal fibroblast, a type of cell that is common in connective tissue and frequently studied in research labs. James J. Faust and David G. Capco, Arizona State University View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
3488
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaAbnormal, spiky fibroblast
3613
This is a fibroblast, a connective tissue cell that plays an important role in wound healing. Normal fibroblasts have smooth edges. Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, Mo. View MediaPlasma-Derived Membrane Vesicles
5887
This fiery image doesn’t come from inside a bubbling volcano. Instead, it shows animal cells caught in the act of making bubbles, or blebbing. Jeanne Stachowiak, University of Texas at Austin View MediaMouse heart fibroblasts
3281
This image shows mouse fetal heart fibroblast cells. The muscle protein actin is stained red, and the cell nuclei are stained blue. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaNCMIR human spinal nerve
3387
Spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. They run within the spinal column to carry nerve signals to and from all parts of the body. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaEpigenetic code (with labels)
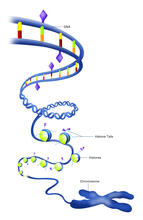
2563
The "epigenetic code" controls gene activity with chemical tags that mark DNA (purple diamonds) and the "tails" of histone proteins (purple triangles). Crabtree + Company View MediaSmooth ER
1292
The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two types: Rough ER is covered with ribosomes and prepares newly made proteins; smooth ER specializes in making lipids and breaking down toxic molecules. Judith Stoffer View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
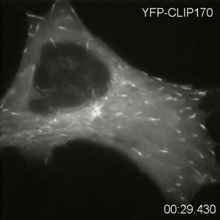
2784
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaHistone deacetylases
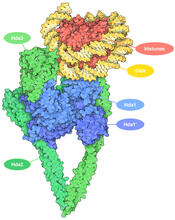
7001
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMouse mammary cells lacking anti-cancer protein
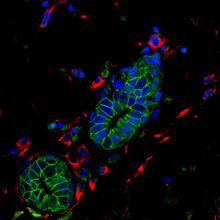
3432
Shortly after a pregnant woman gives birth, her breasts start to secrete milk. This process is triggered by hormonal and genetic cues, including the protein Elf5. Nature Cell Biology, November 2012, Volume 14 No 11 pp1113-1231 View MediaDisease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
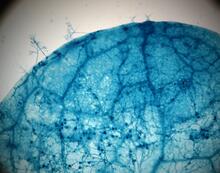
2782
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View Media