Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Cell toxins
1312
A number of environmental factors cause DNA mutations that can lead to cancer: toxins in cigarette smoke, sunlight and other radiation, and some viruses. Judith Stoffer View MediaA mammalian eye has approximately 70 different cell types
3641
The incredible complexity of a mammalian eye (in this case from a mouse) is captured here. Each color represents a different type of cell. Bryan William Jones and Robert E. Marc, University of Utah View MediaCone cell
1271
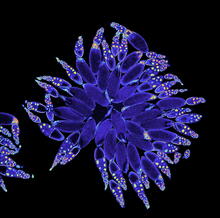
The cone cell of the eye allows you to see in color. Appears in the NIGMS booklet Inside the Cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaSponge
2728
Many of today's medicines come from products found in nature, such as this sponge found off the coast of Palau in the Pacific Ocean. Phil Baran, Scripps Research Institute View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared-labeled
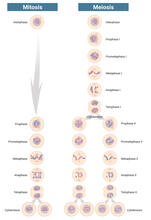
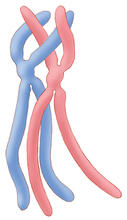
6788
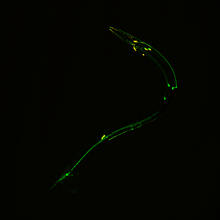
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaTEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
5759
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaCellular metropolis
2308
Like a major city, a cell teems with specialized workers that carry out its daily operations--making energy, moving proteins, or helping with other tasks. Kathryn Howell, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 2
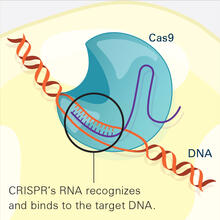
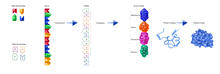
6486
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaInfluenza virus attaches to host membrane (with labels)
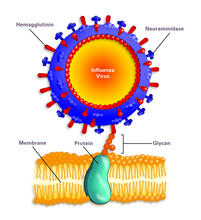
2505
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View MediaGroup of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
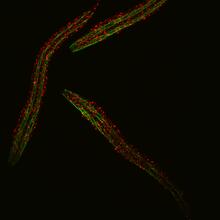
6582
Three C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaTetrapolar mitosis
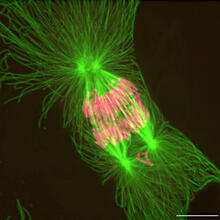
2739
This image shows an abnormal, tetrapolar mitosis. Chromosomes are highlighted pink. The cells shown are S3 tissue cultured cells from Xenopus laevis, African clawed frog. Gary Gorbsky, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation View MediaDynein moving along microtubules
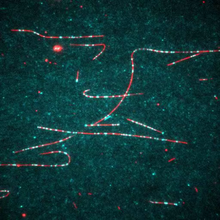
7023
Dynein (green) is a motor protein that “walks” along microtubules (red, part of the cytoskeleton) and carries its cargo along with it. This video was captured through fluorescence microscopy. Morgan DeSantis, University of Michigan. View MediaCryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
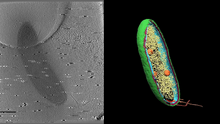
6569
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaBrain cells in the hippocampus
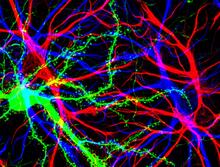
3688
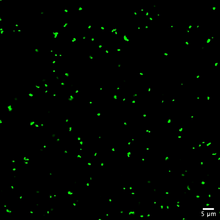
Hippocampal cells in culture with a neuron in green, showing hundreds of the small protrusions known as dendritic spines. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaFocal adhesions
2502
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaFrom DNA to Protein (labeled)
2510
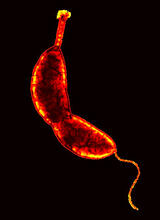
The genetic code in DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into proteins with specific sequences. Crabtree + Company View MediaTwo-headed Xenopus laevis tadpole
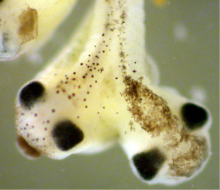
2755
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a research organism for studying embryonic development. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaSmall blood vessels in a mouse retina
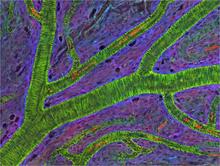
3400
Blood vessels at the back of the eye (retina) are used to diagnose glaucoma and diabetic eye disease. They also display characteristic changes in people with high blood pressure. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaChromosomes before crossing over
1315
Duplicated pair of chromosomes lined up and ready to cross over. Judith Stoffer View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
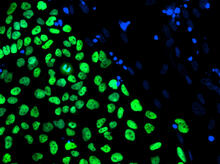
3275
The nuclei stained green highlight human embryonic stem cells grown under controlled conditions in a laboratory. Blue represents the DNA of surrounding, supportive feeder cells. Julie Baker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaSerratezomine A
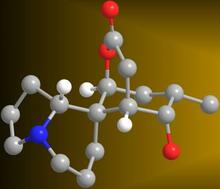
2687
A 3-D model of the alkaloid serratezomine A shows the molecule's complex ring structure. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
3414
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaYeast cell
1092
A whole yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell viewed by X-ray microscopy. Inside, the nucleus and a large vacuole (red) are visible. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaMap of protein structures 02
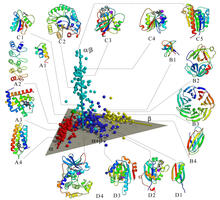
2367
A global "map of the protein structure universe" indicating the positions of specific proteins. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6887
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaLeading cells with light
2708
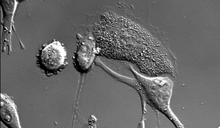
A blue laser beam turns on a protein that helps this human cancer cell move. Responding to the stimulus, the protein, called Rac1, first creates ruffles at the edge of the cell. Yi Wu, University of North Carolina View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 2
6588
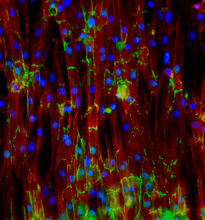
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMouse heart muscle cells
3282
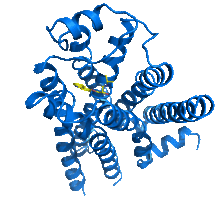
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaBeta2-adrenergic receptor protein
2337
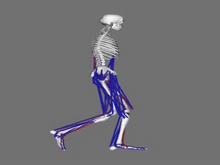
Crystal structure of the beta2-adrenergic receptor protein. The Stevens Laboratory, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaSimulation of leg muscles moving
6598
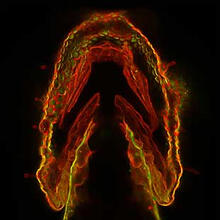
When we walk, muscles and nerves interact in intricate ways. This simulation, which is based on data from a six-foot-tall man, shows these interactions. Chand John and Eran Guendelman, Stanford University View MediaHydra 06
2442
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaPlasma membrane
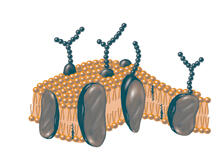
2523
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2524 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaSkin cell (keratinocyte)
3599
This normal human skin cell was treated with a growth factor that triggered the formation of specialized protein structures that enable the cell to move. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaDrosophila (fruit fly) myosin 1D motility assay
6562
Actin gliding powered by myosin 1D. Note the counterclockwise motion of the gliding actin filaments. Serapion Pyrpassopoulos and E. Michael Ostap, University of Pennsylvania View MediaAspirin (with labels)
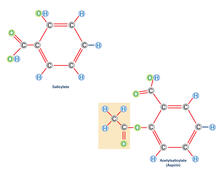
2530
Acetylsalicylate (bottom) is the aspirin of today. Crabtree + Company View MediaSea urchin embryo 01
1047
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaScientists display X-ray diffraction pattern obtained with split X-ray beamline
2384
Scientists from Argonne National Laboratory's Advanced Photon Source (APS) display the first X-ray diffraction pattern obtained from a protein crystal using a split X-ray beam, the first of its kind a GM/CA Collaborative Access Team View MediaSea urchin embryo 06
1052
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaNeural circuits in worms similar to those in humans
3252
Green and yellow fluorescence mark the processes and cell bodies of some C. elegans neurons. Shawn Xu, University of Michigan View MediaA bundle of myelinated peripheral nerve cells (axons)
3737
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaIntrons
2550
Genes are often interrupted by stretches of DNA (introns, blue) that do not contain instructions for making a protein. Crabtree + Company View MediaProteins related to myotonic dystrophy
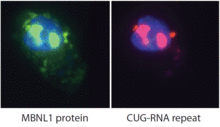
2727
Myotonic dystrophy is thought to be caused by the binding of a protein called Mbnl1 to abnormal RNA repeats. Manuel Ares, University of California, Santa Cruz View MediaFruit fly ovary
3607
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaGlowing glycans
2473
Sugars light up the cells in this jaw of a 3-day-old zebrafish embryo and highlight a scientific first: labeling and tracking the movements of sugar chains called glycans in a living organism. Carolyn Bertozzi, University of California, Berkeley View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaCaulobacter
3262
A study using Caulobacter crescentus showed that some bacteria use just-in-time processing, much like that used in industrial delivery, to make the glue that allows them to attach to surfaces, Yves Brun, Indiana University View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 04
2797
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaAldolase
6350
2.5Å resolution reconstruction of rabbit muscle aldolase collected on a FEI/Thermo Fisher Titan Krios with energy filter and image corrector. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View Media