Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Superconducting magnet
1120
Superconducting magnet for NMR research, from the February 2003 profile of Dorothee Kern in Findings. Mike Lovett View MediaEnzymes convert subtrates into products
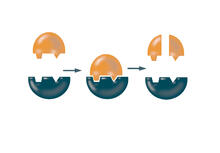
2521
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2522 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaMicrofluidic chip
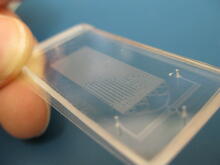
3265
Microfluidic chips have many uses in biology labs. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaYeast cells with nuclei and contractile rings
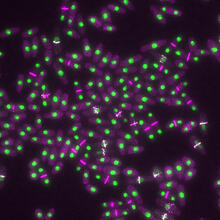
6792
Yeast cells with nuclei shown in green and contractile rings shown in magenta. Nuclei store DNA, and contractile rings help cells divide. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
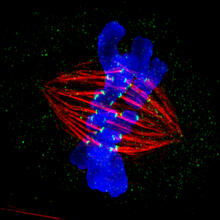
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
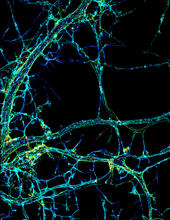
3678
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaDicty fruit
2684
Dictyostelium discoideum is a microscopic amoeba. A group of 100,000 form a mound as big as a grain of sand. Featured in The New Genetics. View MediaCrane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
6898
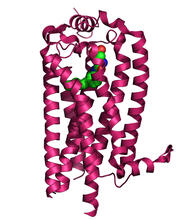
A crane fly spermatocyte during metaphase of meiosis-I, a step in the production of sperm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaSphingolipid S1P1 receptor
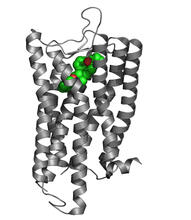
3362
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, ML056. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaDolly the sheep
2690
Scientists in Scotland were the first to clone an animal, this sheep named Dolly. She later gave birth to Bonnie, the lamb next to her. View MediaTracking embryonic zebrafish cells
6775
To better understand cell movements in developing embryos, researchers isolated cells from early zebrafish embryos and grew them as clusters. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaV. Cholerae Biofilm
3580
Industrious V. cholerae bacteria (yellow) tend to thrive in denser biofilms (left) while moochers (red) thrive in weaker biofilms (right). View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (White Background)
6534
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaCapillary protein crystallization robot
2357
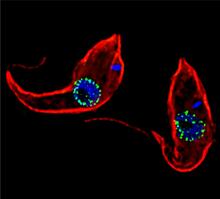
This ACAPELLA robot for capillary protein crystallization grows protein crystals, freezes them, and centers them without manual intervention. Structural Genomics of Pathogenic Protozoa Consortium View MediaTrypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
3765
Trypanosoma brucei is a single-cell parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans. Michael Rout, Rockefeller University View MediaFly cells live
2315
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaCalcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
3449
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaCultured cells
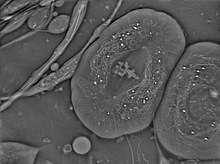
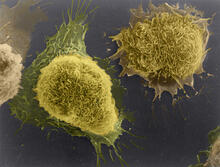
1178
This image of laboratory-grown cells was taken with the help of a scanning electron microscope, which yields detailed images of cell surfaces. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaWhite Poppy
3424
A white poppy. View cropped image of a poppy here 3423. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaMouse brain 1
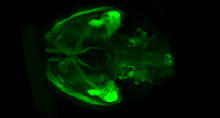
6929
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaPrecise development in the fruit fly embryo
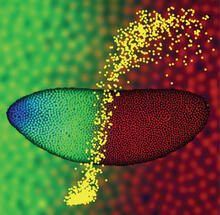
2593
This 2-hour-old fly embryo already has a blueprint for its formation, and the process for following it is so precise that the difference of just a few key molecules can change the plans. Thomas Gregor, Princeton University View MediaCluster analysis of mysterious protein
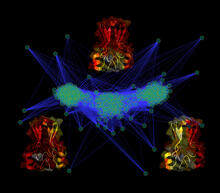
3295
Researchers use cluster analysis to study protein shape and function. Each green circle represents one potential shape of the protein mitoNEET. Patricia Jennings and Elizabeth Baxter, University of California, San Diego View MediaColorful communication
2313
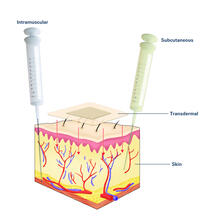
The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi glows when near its kind. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaDrugs enter skin (with labels)
2532
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2531 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaActivation energy
2525
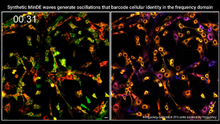
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2526 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaGolden gene chips
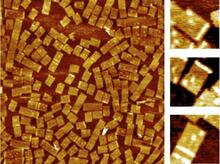
2455
A team of chemists and physicists used nanotechnology and DNA's ability to self-assemble with matching RNA to create a new kind of chip for measuring gene activity. Hao Yan and Yonggang Ke, Arizona State University View MediaNatcher Building 06
1086
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaIntroduction to Genome Editing Using CRISPR/Cas9
5815
Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9 is a rapidly expanding field of scientific research with emerging applications in disease treatment, medical therapeutics and bioenergy, just to name a few. Janet Iwasa View MediaFruit fly larvae brains showing tubulin
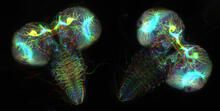
6808
Two fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) larvae brains with neurons expressing fluorescently tagged tubulin protein. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaSea urchin embryo 06
1052
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaNociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide opioid receptor
3364
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, compound-24 Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaAging book of life
1334
Damage to each person's genome, often called the "Book of Life," accumulates with time. Judith Stoffer View MediaBuilding blocks and folding of proteins
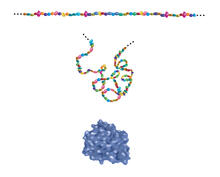
2508
Proteins are made of amino acids hooked end-to-end like beads on a necklace. To become active, proteins must twist and fold into their final, or "native," conformation. Crabtree + Company View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
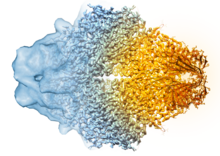
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View Media