Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
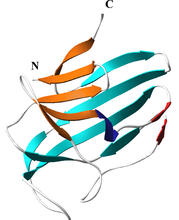
X-ray crystallography
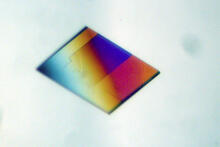
2511
X-ray crystallography allows researchers to see structures too small to be seen by even the most powerful microscopes. Crabtree + Company View MediaLarvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
3627
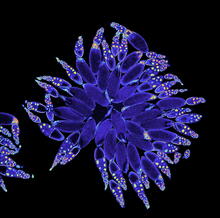
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner View MediaAntibiotic-surviving bacteria
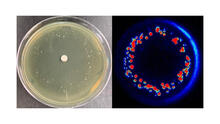
6802
Colonies of bacteria growing despite high concentrations of antibiotics. These colonies are visible both by eye, as seen on the left, and by bioluminescence imaging, as seen on the right. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaBacterial alpha amylase
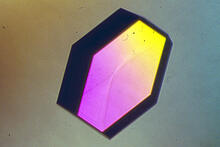
2401
A crystal of bacterial alpha amylase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaEnzymes convert subtrates into products
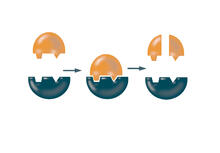
2521
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2522 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaBond types (with labels)
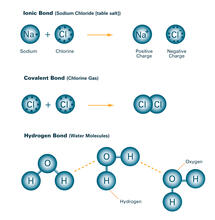
2520
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaEpithelial cells
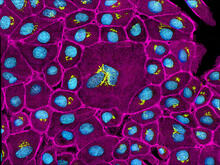
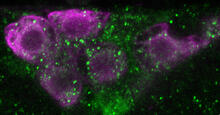
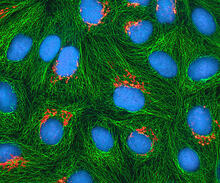
3647
This image mostly shows normal cultured epithelial cells expressing green fluorescent protein targeted to the Golgi apparatus (yellow-green) and stained for actin (magenta) and DNA (cyan). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
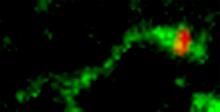
3488
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaNucleotides make up DNA (with labels)
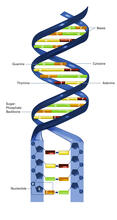
2542
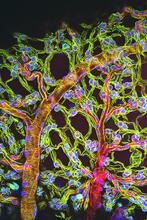
DNA consists of two long, twisted chains made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains one base, one phosphate molecule, and the sugar molecule deoxyribose. Crabtree + Company View MediaWeblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
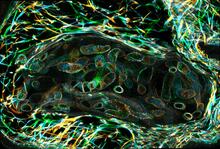
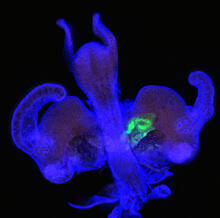
3616
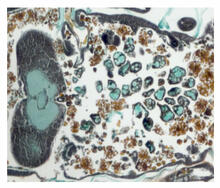
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University. View MediaHuman liver cell (hepatocyte)
3610
Hepatocytes, like the one shown here, are the most abundant type of cell in the human liver. Donna Beer Stolz, University of Pittsburgh View MediaMounting of protein crystals
2368
Automated methods using micromachined silicon are used at the Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics to mount protein crystals for X-ray crystallography. The Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaPlanarian stem cell colony
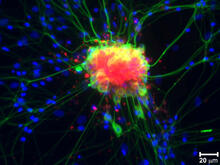
3306
Planarians are freshwater flatworms that have powerful abilities to regenerate their bodies, which would seem to make them natural model organisms in which to study stem cells. Peter Reddien, Whitehead Institute View MediaTelomeres on outer edge of nucleus during cell division
3484
New research shows telomeres moving to the outer edge of the nucleus after cell division, suggesting these caps that protect chromosomes also may play a role in organizing DNA. Laure Crabbe, Jamie Kasuboski and James Fitzpatrick, Salk Institute for Biological Studies View MediaSecreted protein from Mycobacteria
2379
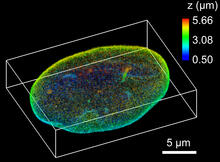
Model of a major secreted protein of unknown function, which is only found in mycobacteria, the class of bacteria that causes tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaNuclear Lamina
6572
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
6982
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaPlasma-Derived Membrane Vesicles
5887
This fiery image doesn’t come from inside a bubbling volcano. Instead, it shows animal cells caught in the act of making bubbles, or blebbing. Jeanne Stachowiak, University of Texas at Austin View MediaMyelinated axons 1
3396
Myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaStreptococcus bacteria
1157
Image of Streptococcus, a type (genus) of spherical bacteria that can colonize the throat and back of the mouth. Stroptococci often occur in pairs or in chains, as shown here. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaBacterial cells aggregated above a light-organ pore of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
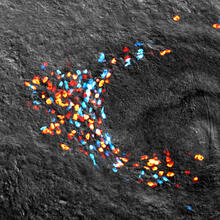
7019
The beating of cilia on the outside of the Hawaiian bobtail squid’s light organ concentrates Vibrio fischeri cells (green) present in the seawater into aggregates near the pore-containing tis Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaNerve ending
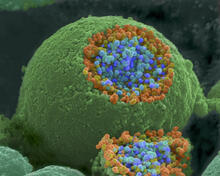
1244
A scanning electron microscope picture of a nerve ending. It has been broken open to reveal vesicles (orange and blue) containing chemicals used to pass messages in the nervous system. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaRed blood cells
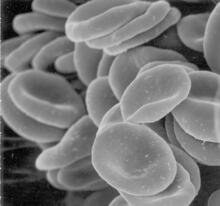
1101
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sa Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaZebrafish embryo
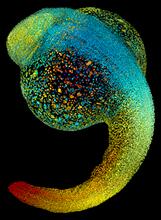
3644
Just 22 hours after fertilization, this zebrafish embryo is already taking shape. By 36 hours, all of the major organs will have started to form. Philipp Keller, Bill Lemon, Yinan Wan, and Kristin Branson, Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Va. View MediaNerve cell
1338
Nerve cells have long, invisibly thin fibers that carry electrical impulses throughout the body. Some of these fibers extend about 3 feet from the spinal cord to the toes. Judith Stoffer View MediaLily mitosis 12
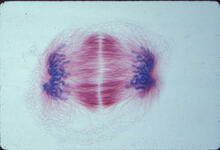
1018
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaFruit fly ovary
6522
In this image of a stained fruit fly ovary, the ovary is packed with immature eggs (with DNA stained blue). The cytoskeleton (in pink) is a collection of fibers that gives a cell shape and support. Crystal D. Rogers, Ph.D., University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine; and Mariano A. Loza-Coll, Ph.D., California State University, Northridge. View MediaHeLa cells
3522
Multiphoton fluorescence image of cultured HeLa cells with a fluorescent protein targeted to the Golgi apparatus (orange), microtubules (green) and counterstained for DNA (cyan). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaNatcher Building 07
1087
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaNCMIR Intestine-2
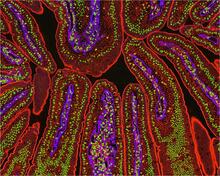
3390
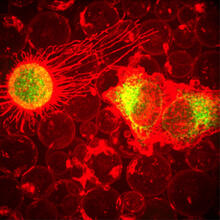
The small intestine is where most of our nutrients from the food we eat are absorbed into the bloodstream. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaARTS triggers apoptosis
2432
Cell showing overproduction of the ARTS protein (red). ARTS triggers apoptosis, as shown by the activation of caspase-3 (green) a key tool in the cell's destruction. The nucleus is shown in blue. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaResearch mentor and student
2767
A research mentor (Lori Eidson) and student (Nina Waldron, on the microscope) were 2009 members of the BRAIN (Behavioral Research Advancements In Neuroscience) program at Georgia State University in A Elizabeth Weaver, Georgia State University View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
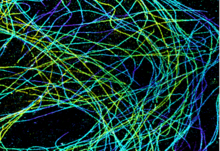
6891
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaMicrotubule breakdown
2321
Like a building supported by a steel frame, a cell contains its own sturdy internal scaffolding made up of proteins, including microtubules. Eva Nogales, University of California, Berkeley View MediaPlanting roots
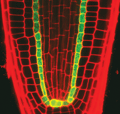
2329
At the root tips of the mustard plant Arabidopsis thaliana (red), two proteins work together to control the uptake of water and nutrients. Philip Benfey, Duke University View MediaYeast cells entering mitosis
6791
Yeast cells entering mitosis, also known as cell division. The green and magenta dots are two proteins that play important roles in mitosis. They show where the cells will split. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
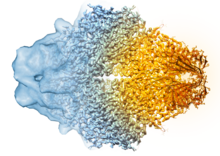
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
2406
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaMouse brain 1
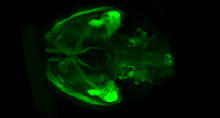
6929
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaPSI: from genes to structures
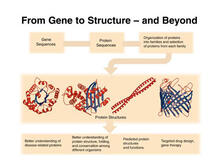
2363
The goal of the Protein Structure Initiative (PSI) is to determine the three-dimensional shapes of a wide range of proteins by solving the structures of representative members of each protein family f National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
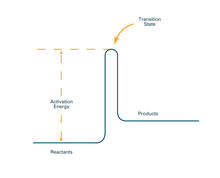
2526
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaSpinal nerve cells
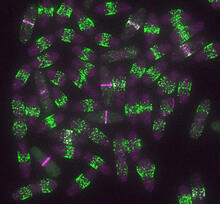
3251
Neurons (green) and glial cells from isolated dorsal root ganglia express COX-2 (red) after exposure to an inflammatory stimulus (cell nuclei are blue). Lawrence Marnett, Vanderbilt University View MediaThree neurons and human ES cells
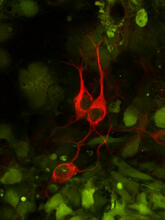
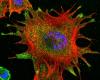
3290
The three neurons (red) visible in this image were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Undifferentiated stem cells are green here. Anirvan Ghosh lab, University of California, San Diego, via CIRM View MediaFruit fly ovary
3607
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaAssembly of the HIV capsid
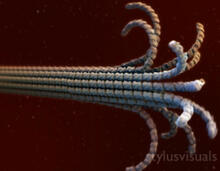
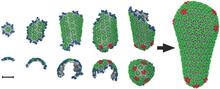
5729
The HIV capsid is a pear-shaped structure that is made of proteins the virus needs to mature and become infective. John Grime and Gregory Voth, The University of Chicago View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa lacking Draper
2759
In the absence of the engulfment receptor Draper, salivary gland cells (light blue) persist in the thorax of a developing Drosophila melanogaster pupa. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaBacterial symbionts colonizing the crypts of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid light organ
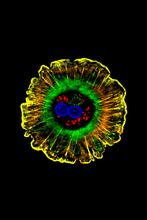
7020
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, stained blue. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaNMR spectrometer
2371
This photo shows a Varian Unity Inova 900 MHz, 21.1 T standard bore magnet Nuclear Magnetic Resonnance (NMR) spectrometer. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaSingle-cell “radios” image
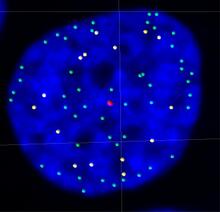
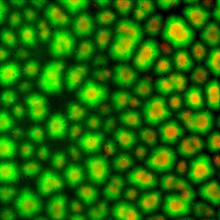
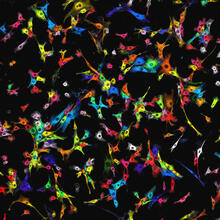
7021
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View Media