Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
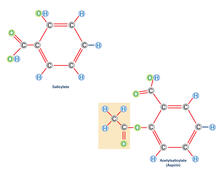
Aspirin (with labels)
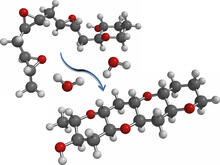
2530
Acetylsalicylate (bottom) is the aspirin of today. Crabtree + Company View MediaTracking cells in a gastrulating zebrafish embryo
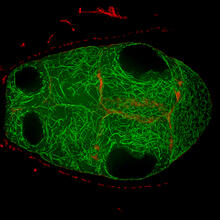
6776
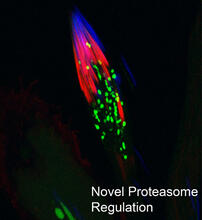
During development, a zebrafish embryo is transformed from a ball of cells into a recognizable body plan by sweeping convergence and extension cell movements. This process is called gastrulation. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaProteasome
3451
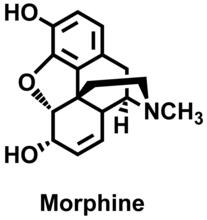
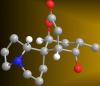
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaMorphine Structure
3438
The chemical structure of the morphine molecule Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaSea urchin embryo 01
1047
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 2
5856
Three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular matrix in a thin section of the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum between the plasma membranes of the cell. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaBlood clots show their flex
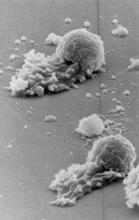
2450
Blood clots stop bleeding, but they also can cause heart attacks and strokes. Eric Lee, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaDopaminergic neurons from ES cells
3270
Human embryonic stem cells differentiated into dopaminergic neurons, the type that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Image courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Jeannie Liu, Lab of Jan Nolta, University of California, Davis, via CIRM View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaMandelate racemase from B. subtilis
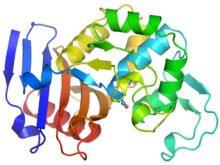
2350
Model of the mandelate racemase enzyme from Bacillus subtilis, a bacterium commonly found in soil. New York Structural GenomiX Research Consortium, PSI View MediamDia1 antibody staining- 02
3331
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaSpreading Cells- 02
3329
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaMapping disease spread
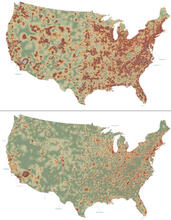
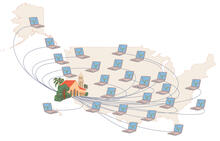
2320
How far and fast an infectious disease spreads across a community depends on many factors, including transportation. These U.S. David Chrest, RTI International View MediaFocal adhesions (with labels)
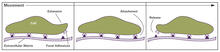
2503
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaInduced pluripotent stem cells from skin
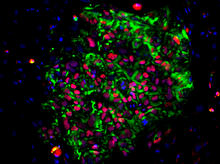
3278
These induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) were derived from a woman's skin. Green and red indicate proteins found in reprogrammed cells but not in skin cells (TRA1-62 and NANOG). Kathrin Plath lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaRecombinant DNA
2564
To splice a human gene into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. coli bacterium, cut the plasmid with a restriction enzyme, and splice in human DNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaStress Response in Cells
6570
Two highly stressed osteosarcoma cells are shown with a set of green droplet-like structures followed by a second set of magenta droplets. Julia F. Riley and Carlos A. Castañeda, Syracuse University View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 3
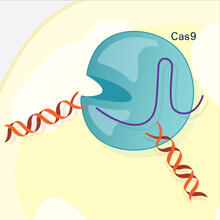
6487
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaFruit fly egg chamber
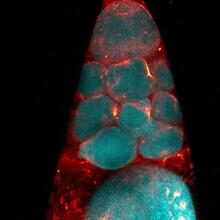
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaFruit fly nurse cells during egg development
6753
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaDicer generates microRNAs (with labels)
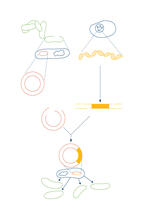
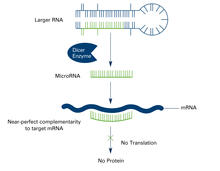
2557
The enzyme Dicer generates microRNAs by chopping larger RNA molecules into tiny Velcro®-like pieces. MicroRNAs stick to mRNA molecules and prevent the mRNAs from being made into proteins. Crabtree + Company View MediaRibbon diagram of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6766
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
3414
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaTFIID complex binds DNA to start gene transcription
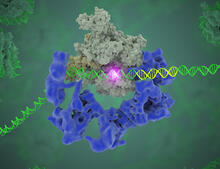
3766
Gene transcription is a process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaKinases (with labels)
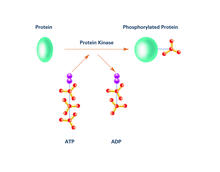
2535
Kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups (red-yellow structures) to proteins (green), assigning the proteins a code. Crabtree + Company View MediaC. elegans with blue and yellow lights in the background
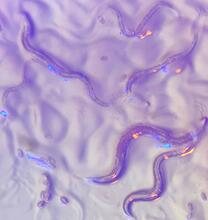
6750
These microscopic roundworms, called Caenorhabditis elegans, lack eyes and the opsin proteins used by visual systems to detect colors. H. Robert Horvitz and Dipon Ghosh, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaDNase
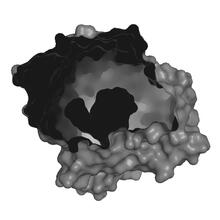
2410
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaThermotoga maritima and its metabolic network
2702
A combination of protein structures determined experimentally and computationally shows us the complete metabolic network of a heat-loving bacterium. View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 1
3730
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaMitosis - interphase
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaDiversity oriented synthesis: generating skeletal diversity using folding processes
3327
This 1 1/2-minute video animation was produced for chemical biologist Stuart Schreiber's lab page. The animation shows how diverse chemical structures can be produced in the lab. Eric Keller View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaCell division with late aligning chromosomes
2747
This video shows an instance of abnormal mitosis where chromosomes are late to align. Gary Gorbsky, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation View MediaTransmission electron microscopy showing cross-section of the node of Ranvier
3740
Nodes of Ranvier are short gaps in the myelin sheath surrounding myelinated nerve cells (axons). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse embryo showing Smad4 protein
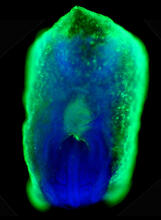
2607
This eerily glowing blob isn't an alien or a creature from the deep sea--it's a mouse embryo just eight and a half days old. The green shell and core show a protein called Smad4. Kenneth Zaret, Fox Chase Cancer Center View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
3739
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaTEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
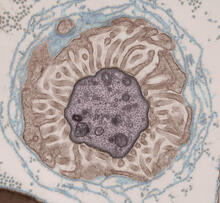
5759
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaSea urchin embryo 02
1048
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaSecreted protein from Mycobacteria
2379
Model of a major secreted protein of unknown function, which is only found in mycobacteria, the class of bacteria that causes tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaNatcher Building 10
1090
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaFolding@Home
1276
Stanford University scientist Vijay Pande decided to couple the power of computers with the help of the public. Judith Stoffer View MediaWorm sperm
3489
To develop a system for studying cell motility in unnatrual conditions -- a microscope slide instead of the body -- Tom Roberts and Katsuya Shimabukuro at Florida State University disassembled and rec Tom Roberts, Florida State University View MediaCascade reaction promoted by water
2490
This illustration of an epoxide-opening cascade promoted by water emulates the proposed biosynthesis of some of the Red Tide toxins. Tim Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaGenetic patchworks
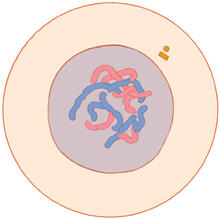
2588
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University View MediaAldolase
6350
2.5Å resolution reconstruction of rabbit muscle aldolase collected on a FEI/Thermo Fisher Titan Krios with energy filter and image corrector. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaZ rings in bacterial division
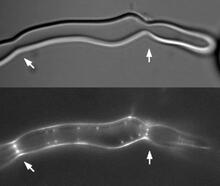
2456
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). Masaki Osawa, Duke University View Media