Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Cell-free protein synthesizers
2360
Both instruments shown were developed by CellFree Sciences of Yokohama, Japan. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaStatistical cartography
2331
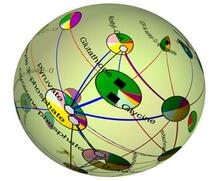
Like a world of its own, this sphere represents all the known chemical reactions in the E. coli bacterium. Luis A. Nunes Amaral, Northwestern University View MediaLily mitosis 07
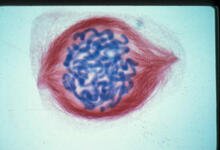
1017
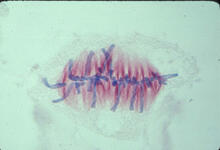
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
3739
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaBiopixels
3266
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. This image shows a small chip with about 500 blinking bacterial colonies or biopixels. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaHeart muscle with reprogrammed skin cells
3273
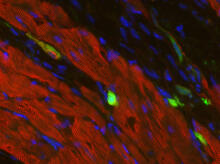
Skins cells were reprogrammed into heart muscle cells. The cells highlighted in green are remaining skin cells. Red indicates a protein that is unique to heart muscle. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, via CIRM View MediaYeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
6772
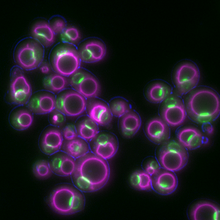
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaMap of protein structures 01
2365
A global "map of the protein structure universe." The Berkeley Structural Genomics Center has developed a method to visualize the vast universe of protein structures in which proteins of similar struc Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaLarvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
3627
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 2
6588
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
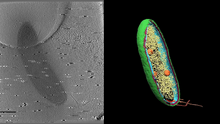
6569
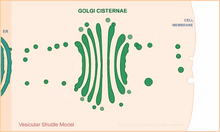
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaVesicular shuttle model
1306
Animation for the vesicular shuttle model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaYeast cells entering mitosis
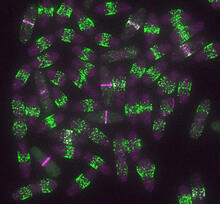
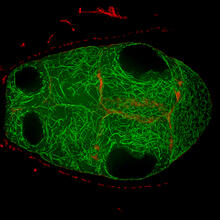
6791
Yeast cells entering mitosis, also known as cell division. The green and magenta dots are two proteins that play important roles in mitosis. They show where the cells will split. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaCircadian rhythm
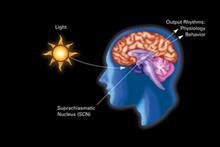
2841
The human body keeps time with a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. Crabtree + Company View MediaCircadian rhythm neurons in the fruit fly brain
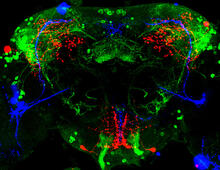
3754
Some nerve cells (neurons) in the brain keep track of the daily cycle. This time-keeping mechanism, called the circadian clock, is found in all animals including us. Justin Blau, New York University View MediaImmune cell attacks cell infected with a retrovirus
2489
T cells engulf and digest cells displaying markers (or antigens) for retroviruses, such as HIV. Kristy Whitehouse, science illustrator View MediaVDAC-1 (4)
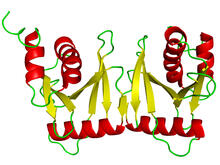
2495
The structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaNormal vascular development in frog embryos
3404
In vivo vascular development in kdr:GFP frogs. Related to images 3403 and 3405. Hye Ji Cha, University of Texas at Austin View MediaEpithelial cell migration
6899
High-resolution time lapse of epithelial (skin) cell migration and wound healing. It shows an image taken every 13 seconds over the course of almost 14 minutes. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaUbiquitin-fold modifier 1 from C. elegans
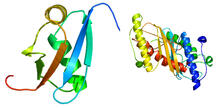
2388
Solution NMR structure of protein target WR41 (left) from C. elegans. Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium View MediaMouse heart muscle cells
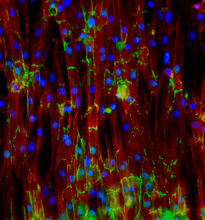
3282
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaHuman fibroblast undergoing cell division
6519
During cell division, cells physically divide after separating their genetic material to create two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Nilay Taneja, Vanderbilt University, and Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaHydra 05
2441
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaThree neurons and human ES cells
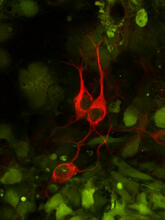
3290
The three neurons (red) visible in this image were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Undifferentiated stem cells are green here. Anirvan Ghosh lab, University of California, San Diego, via CIRM View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaNatcher Building 08
1088
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaColorful communication
2313
The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi glows when near its kind. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaSea urchin embryo 01
1047
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediatRNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans
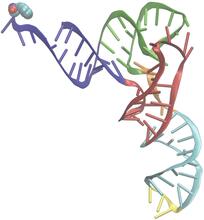
2351
An NMR solution structure model of the transfer RNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans (subunit Sen15). This represents the first structure of a eukaryotic tRNA splicing endonuclease subunit. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaStructure of heme, side view
3540
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaPeripheral nerve cell derived from ES cells
3264
A peripheral nerve cell made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
3597
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaLily mitosis 05
1015
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaFruit fly egg chamber
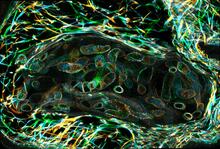
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaNatcher Building 05
1085
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaTiny points of light in a quantum dot
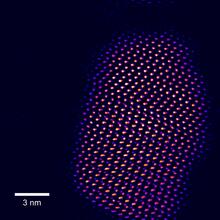
2332
This fingertip-shaped group of lights is a microscopic crystal called a quantum dot. About 10,000 times thinner than a sheet of paper, the dot radiates brilliant colors under ultraviolet light. Sandra Rosenthal and James McBride, Vanderbilt University, and Stephen Pennycook, Oak Ridge National Laboratory View MediaScanning electron microscopy of collagen fibers
3735
This image shows collagen, a fibrous protein that's the main component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen is a strong, ropelike molecule that forms stretch-resistant fibers. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
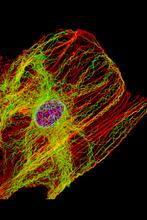
3617
This image shows a normal fibroblast, a type of cell that is common in connective tissue and frequently studied in research labs. James J. Faust and David G. Capco, Arizona State University View MediaChromosome inside nucleus (with labels)
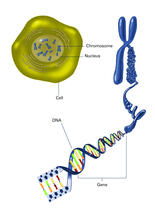
2540
The long, stringy DNA that makes up genes is spooled within chromosomes inside the nucleus of a cell. Crabtree + Company View MediaCell cycle wheel
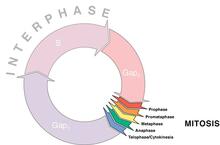
1310
A typical animal cell cycle lasts roughly 24 hours, but depending on the type of cell, it can vary in length from less than 8 hours to more than a year. Most of the variability occurs in Gap1. Judith Stoffer View MediaPathways: What is It? | Why Scientists Study Cells
6540
Learn how curiosity about the world and our cells is key to scientific discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaThe 26S proteasome engages with a protein substrate
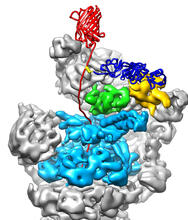
3763
The proteasome is a critical multiprotein complex in the cell that breaks down and recycles proteins that have become damaged or are no longer needed. Andreas Martin, HHMI View MediaMyelinated axons 2
3397
Top view of myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaLipid raft
1285
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. Judith Stoffer View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
6789
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaHen egg lysozyme (1)
2396
Crystals of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaA Bacillus subtilis biofilm grown in a Petri dish
3718
Bacterial biofilms are tightly knit communities of bacterial cells growing on, for example, solid surfaces, such as in water pipes or on teeth. Gürol Süel, UCSD View MediaGenetic patchworks
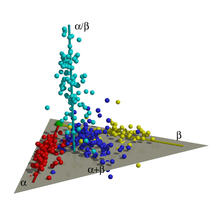
2588
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University View MediaPhenylalanine tRNA molecule
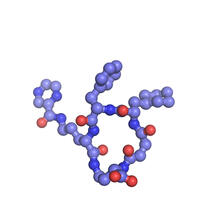
3406
Phenylalanine tRNA showing the anticodon (yellow) and the amino acid, phenylalanine (blue and red spheres). Patrick O'Donoghue and Dieter Soll, Yale University View MediaSerratezomine A
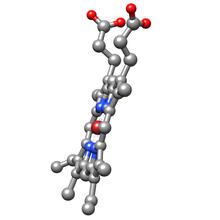
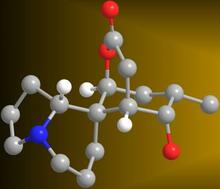
2687
A 3-D model of the alkaloid serratezomine A shows the molecule's complex ring structure. View Media