Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
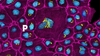
Mitochondria
1287
Bean-shaped mitochondria are cells' power plants. These organelles have their own DNA and replicate independently. The highly folded inner membranes are the site of energy generation. Judith Stoffer View MediaVesicle traffic
1283
This illustration shows vesicle traffic inside a cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaScanning electron microscopy of collagen fibers
3735
This image shows collagen, a fibrous protein that's the main component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen is a strong, ropelike molecule that forms stretch-resistant fibers. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 1
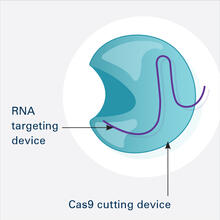
6465
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the first frame in a series of four. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaOligoendopeptidase F from B. stearothermophilus
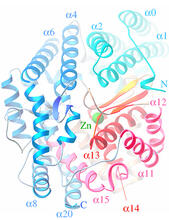
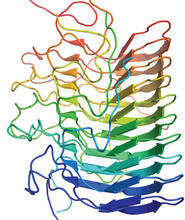
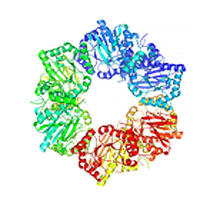
2373
Crystal structure of oligoendopeptidase F, a protein slicing enzyme from Bacillus stearothermophilus, a bacterium that can cause food products to spoil. Accelerated Technologies Center for Gene to 3D Structure/Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
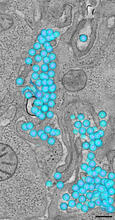
3571
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaV. Cholerae Biofilm
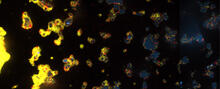
3580
Industrious V. cholerae bacteria (yellow) tend to thrive in denser biofilms (left) while moochers (red) thrive in weaker biofilms (right). View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
5874
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaFungal lipase (2)
2411
Crystals of fungal lipase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaTiny strands of tubulin, a protein in a cell's skeleton
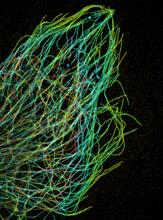
3611
Just as our bodies rely on bones for structural support, our cells rely on a cellular skeleton. Pakorn Kanchanawong, National University of Singapore and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health; and Clare Waterman, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells 02
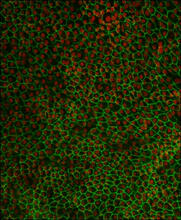
3287
This image shows a layer of retinal pigment epithelium cells derived from human embryonic stem cells, highlighting the nuclei (red) and cell surfaces (green). David Buckholz and Sherry Hikita, University of California, Santa Barbara, via CIRM View MediaNatcher Building 09
1089
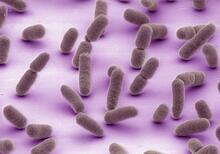
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaLeptospira bacteria
1166
Leptospira, shown here in green, is a type (genus) of elongated, spiral-shaped bacteria. Infection can cause Weil's disease, a kind of jaundice, in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaStructure of amyloid-forming prion protein
3542
This structure from an amyloid-forming prion protein shows one way beta sheets can stack. Douglas Fowler, University of Washington View MediaSmooth ER
1292
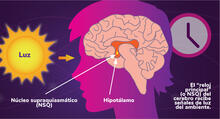
The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two types: Rough ER is covered with ribosomes and prepares newly made proteins; smooth ER specializes in making lipids and breaking down toxic molecules. Judith Stoffer View MediaLos ritmos circadianos y el núcleo supraquiasmático
6614
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y de comportamiento que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaCrawling cell
6964
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaSelf-organizing proteins
2771
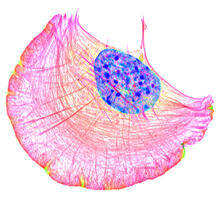
Under the microscope, an E. coli cell lights up like a fireball. Each bright dot marks a surface protein that tells the bacteria to move toward or away from nearby food and toxins. View MediaFruit fly ovary
6522
In this image of a stained fruit fly ovary, the ovary is packed with immature eggs (with DNA stained blue). The cytoskeleton (in pink) is a collection of fibers that gives a cell shape and support. Crystal D. Rogers, Ph.D., University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine; and Mariano A. Loza-Coll, Ph.D., California State University, Northridge. View MediaBiopixels
3266
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. This image shows a small chip with about 500 blinking bacterial colonies or biopixels. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaTranslation
1281
Ribosomes manufacture proteins based on mRNA instructions. Each ribosome reads mRNA, recruits tRNA molecules to fetch amino acids, and assembles the amino acids in the proper order. Judith Stoffer View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaPainted chromosomes
2764
Like a paint-by-numbers picture, painted probes tint individual human chromosomes by targeting specific DNA sequences. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaA panorama view of cells
5761
This photograph shows a panoramic view of HeLa cells, a cell line many researchers use to study a large variety of important research questions. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaAdult and juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squids
7010
An adult Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, (~4 cm) surrounded by newly hatched juveniles (~2 mm) in a bowl of seawater.Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View Media
Fruit fly egg chamber
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaSkin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
3628
This image shows the uncontrolled growth of cells in squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. If caught early, squamous cell carcinoma is usually not life-threatening. Markus Schober and Elaine Fuchs, The Rockefeller University View MediaMitosis - metaphase
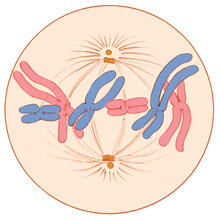
1329
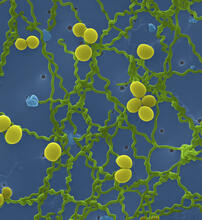
A cell in metaphase during mitosis: The copied chromosomes align in the middle of the spindle. Judith Stoffer View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaLab mice
1069
Many researchers use the mouse (Mus musculus) as a model organism to study mammalian biology. Bill Branson, National Institutes of Health View MediaTelomerase illustration
1335
Reactivating telomerase in our cells does not appear to be a good way to extend the human lifespan. Cancer cells reactivate telomerase. Judith Stoffer View MediaShiga toxin
6997
E. coli bacteria normally live harmlessly in our intestines, but some cause disease by making toxins. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaNicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase
2355
Model of the enzyme nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaDynamin Fission
3448
Time lapse series shows short dynamin assemblies (not visible) constricting a lipid tube to make a "beads on a string" appearance, then cutting off one of the beads i.e., catalyzing membrane fission). Ramachandran, Pucadyil et al. , The Scripps Research Institute View MediaHost infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. View MediaOptic nerve astrocytes
5852
Astrocytes in the cross section of a human optic nerve head Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
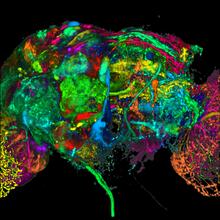
5868
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaDrosophila (fruit fly) myosin 1D motility assay
6562
Actin gliding powered by myosin 1D. Note the counterclockwise motion of the gliding actin filaments. Serapion Pyrpassopoulos and E. Michael Ostap, University of Pennsylvania View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaCarbon building blocks
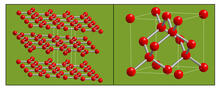
2506
The arrangement of identical molecular components can make a dramatic difference. For example, carbon atoms can be arranged into dull graphite (left) or sparkly diamonds (right). Crabtree + Company View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
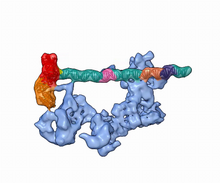
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
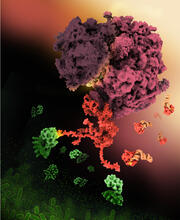
6799
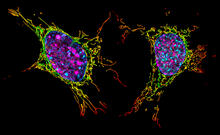
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
6789
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaHaplotypes
2566
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. Crabtree + Company View MediaSnowflake DNA origami
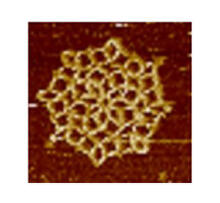
3724
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. The image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Images: A Holiday-Themed Collection. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaFruit fly ovaries
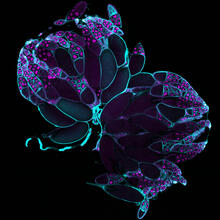
6807
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media
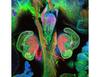
Master clock of the mouse brain
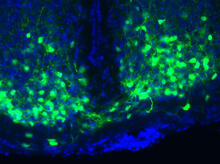
3547
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis View MediaNuclear Lamina – Three Views
6573
Three views of the entire nuclear lamina of a HeLa cell produced by tilted light sheet 3D single-molecule super-resolution imaging using a platform termed TILT3D. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View Media