Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
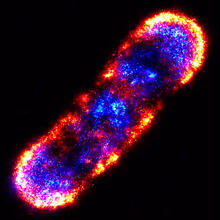
Retroviruses as fossils
2709
DNA doesn't leave a fossil record in stone, the way bones do. Instead, the DNA code itself holds the best evidence for organisms' genetic history. Emily Harrington, science illustrator View MediaProtein purification facility
2376
The Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics protein purification facility is responsible for purifying all recombinant proteins produced by the center. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaRNA folding in action
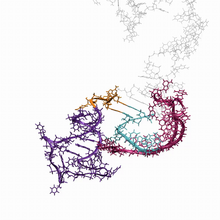
6625
An RNA molecule dynamically refolds itself as it is being synthesized. When the RNA is short, it ties itself into a “knot” (dark purple). Julius Lucks, Northwestern University View MediaInduced pluripotent stem cells from skin
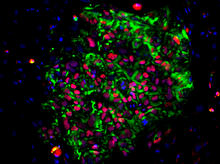
3278
These induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) were derived from a woman's skin. Green and red indicate proteins found in reprogrammed cells but not in skin cells (TRA1-62 and NANOG). Kathrin Plath lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaSee how immune cell acid destroys bacterial proteins
6602
This animation shows the effect of exposure to hypochlorous acid, which is found in certain types of immune cells, on bacterial proteins. American Chemistry Council View MediaLos ritmos circadianos y el núcleo supraquiasmático
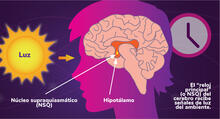
6614
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y de comportamiento que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaInsulin and protein interact in pancreatic beta cells
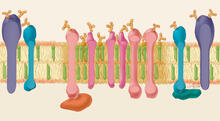
3546
A large number of proteins interact with the hormone insulin as it is produced in and secreted from the beta cells of the pancreas. William E. Balch, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMouse brain slice showing nerve cells
6901
A 20-µm thick section of mouse midbrain. The nerve cells are transparent and weren’t stained. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaGlycoproteins
1270
About half of all human proteins include chains of sugar molecules that are critical for the proteins to function properly. Appears in the NIGMS booklet Inside the Cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
6591
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaHydra 04
2440
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaLipid raft
1285
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. Judith Stoffer View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
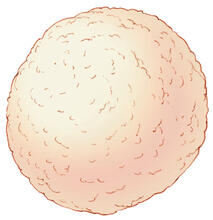
2406
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaThree muscle fibers; the middle has a defect found in some neuromuscular diseases
3630
Of the three muscle fibers shown here, the one on the right and the one on the left are normal. The middle fiber is deficient a large protein called nebulin (blue). Christopher Pappas and Carol Gregorio, University of Arizona View MediaQuartered torso
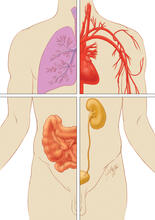
1280
Cells function within organs and tissues, such as the lungs, heart, intestines, and kidney. Judith Stoffer View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaMyelinated axons 1
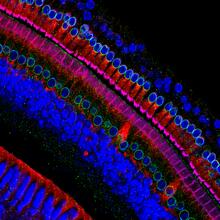
3396
Myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaIndependence Day
5888
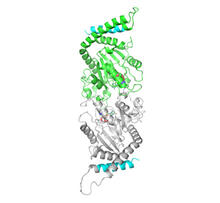
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaDynamin structure
2744
When a molecule arrives at a cell's outer membrane, the membrane creates a pouch around the molecule that protrudes inward. Josh Chappie, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH View MediaPig trypsin (3)
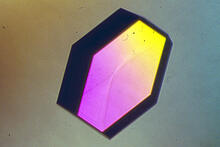
2414
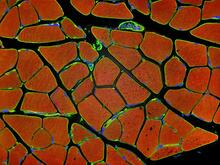
Crystals of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaHuman skeletal muscle
3677
Cross section of human skeletal muscle. Image taken with a confocal fluorescent light microscope. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaPathways: What's the Connection? | Different Jobs in a Science Lab
6541
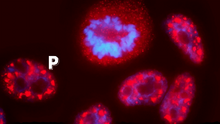
Learn about some of the different jobs in a scientific laboratory and how researchers work as a team to make discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 03
2605
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 24 hours
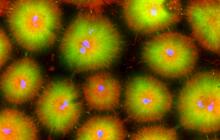
6557
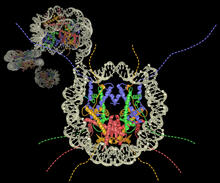
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface from a small L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
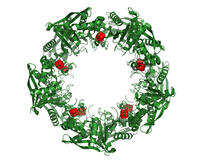
3720
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
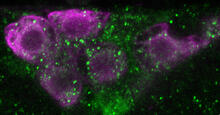
6982
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaStretch detectors
2714
Muscles stretch and contract when we walk, and skin splits open and knits back together when we get a paper cut. Christopher Chen, University of Pennsylvania View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
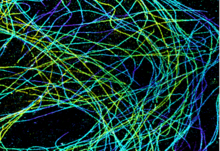
6891
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaCloseup of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
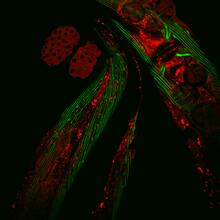
6583
Closeup of C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaSelf-organizing proteins
2771
Under the microscope, an E. coli cell lights up like a fireball. Each bright dot marks a surface protein that tells the bacteria to move toward or away from nearby food and toxins. View MediaBreast cancer cells change migration phenotypes
6986
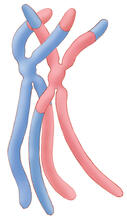
Cancer cells can change their migration phenotype, which includes their shape and the way that they move to invade different tissues. Bo Sun, Oregon State University. View MediaChromosomes after crossing over
1314
Duplicated pair of chromosomes have exchanged material. Judith Stoffer View MediaNucleosome
2741
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaCalcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
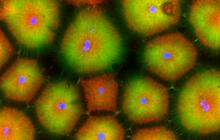
3449
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaTransient receptor potential channel TRPV5
6577
A 3D reconstruction of a transient receptor potential channel called TRPV5 that was created based on cryo-electron microscopy images. Vera Moiseenkova-Bell, University of Pennsylvania. View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 02
2791
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaNormal vascular development in frog embryos
3404
In vivo vascular development in kdr:GFP frogs. Related to images 3403 and 3405. Hye Ji Cha, University of Texas at Austin View MediaFruit fly nurse cells transporting their contents during egg development
6754
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaRegenerating lizard tail
6968
The interior of a regenerating lizard tail 14 days after the original tail was amputated. Thomas Lozito, University of Southern California. View MediaCultured cells
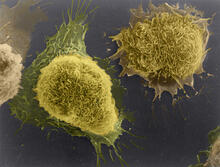
1178
This image of laboratory-grown cells was taken with the help of a scanning electron microscope, which yields detailed images of cell surfaces. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaHair cells: the sound-sensing cells in the ear
3618
These cells get their name from the hairlike structures that extend from them into the fluid-filled tube of the inner ear. Henning Horn, Brian Burke, and Colin Stewart, Institute of Medical Biology, Agency for Science, Technology, and Research, Singapore View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMicroarray 01
1070
Microarrays, also called gene chips, are tools that let scientists track the activity of hundreds or thousands of genes simultaneously. Maggie Werner-Washburne, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque View MediaStructure of a key antigen protein involved with Hepatitis C Virus infection
5866
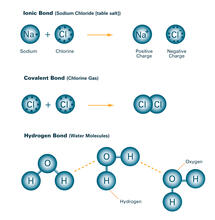
A three-dimensional representation of the structure of E2, a key antigen protein involved with hepatitis C virus infection. Mansun Law Associate Professor Department of Immunolgy and Microbial Science The Scripps Research Institute View MediaBond types (with labels)
2520
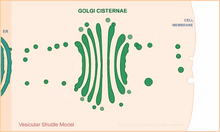
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaVesicular shuttle model
1306
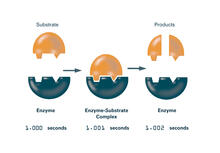
Animation for the vesicular shuttle model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaEnzymes convert subtrates into products (with labels)
2522
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2521 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View Media