Image Gallery: Histone deacetylases
ID
7001
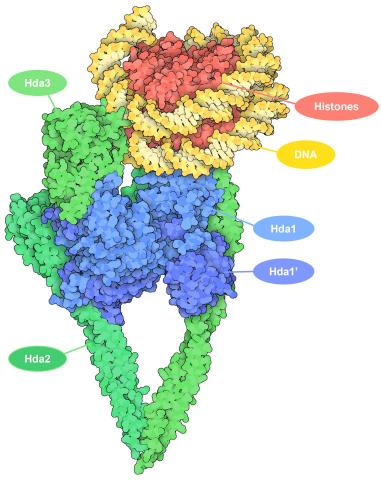
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Access to DNA is controlled, in part, by how tightly it’s wrapped around proteins called histones to form nucleosomes. The complex shown here, from yeast cells (PDB entry 6Z6P), includes several histone deacetylase (HDAC) enzymes (green and blue) bound to a nucleosome (histone proteins in red; DNA in yellow). The yeast HDAC enzymes are similar to the human enzymes. Two enzymes form a V-shaped clamp (green) that holds the other others, a dimer of the Hda1 enzymes (blue). In this assembly, Hda1 is activated and positioned to remove acetyl groups from histone tails.
Source
Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank.
Topics