Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
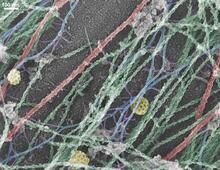
Sea urchin embryo 06
1052
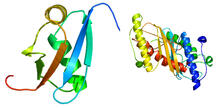
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaUbiquitin-fold modifier 1 from C. elegans
2388
Solution NMR structure of protein target WR41 (left) from C. elegans. Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium View MediaCell Nucleus and Lipid Droplets
6547
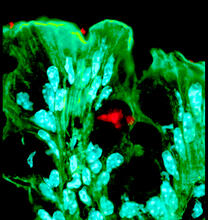
A cell nucleus (blue) surrounded by lipid droplets (yellow). James Olzmann, University of California, Berkeley View MediaBacteria in the mouse colon
3527
Image of the colon of a mouse mono-colonized with Bacteroides fragilis (red) residing within the crypt channel. The red staining is due to an antibody to B. Sarkis K. Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells
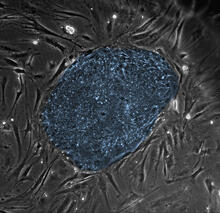
2608
The center cluster of cells, colored blue, shows a colony of human embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaCellular polarity
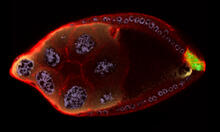
2309
As an egg cell develops, a process called polarization controls what parts ultimately become the embryo's head and tail. This picture shows an egg of the fruit fly Drosophila. Wu-Min Deng, Florida State University View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated
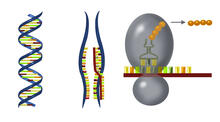
2547
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaVideo of Calling Cards in a mouse brain
6781
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. NIH Director's Blog View MediaZebrafish head vasculature video
6933
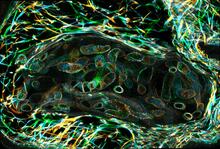
Various views of a zebrafish head with blood vessels shown in purple. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaCells lining the blood vessel walls
3633
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School. View MediaStem cell differentiation
1294
Undifferentiated embryonic stem cells cease to exist a few days after conception. In this image, ES cells are shown to differentiate into sperm, muscle fiber, hair cells, nerve cells, and cone cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
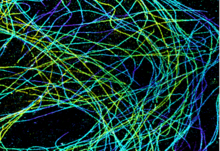
6891
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
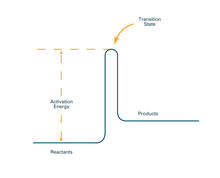
2526
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaVDAC video 02
2571
This video shows the structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaMouse heart fibroblasts
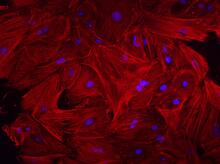
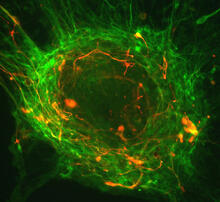
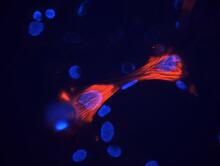
3281
This image shows mouse fetal heart fibroblast cells. The muscle protein actin is stained red, and the cell nuclei are stained blue. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaGlowing bacteria make a pretty postcard
3492
This tropical scene, reminiscent of a postcard from Key West, is actually a petri dish containing an artistic arrangement of genetically engineered bacteria. Nathan C. Shaner, The Scintillon Institute View MediaGolgi
1275
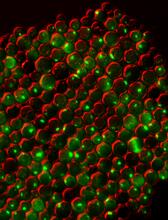
The Golgi complex, also called the Golgi apparatus or, simply, the Golgi. Judith Stoffer View MediaProtein clumping in zinc-deficient yeast cells
3550
The green spots in this image are clumps of protein inside yeast cells that are deficient in both zinc and a protein called Tsa1 that prevents clumping. Colin MacDiarmid and David Eide, University of Wisconsin--Madison View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--gradient background
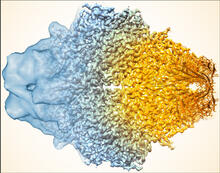
5883
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaAging book of life
1334
Damage to each person's genome, often called the "Book of Life," accumulates with time. Judith Stoffer View MediaHuman ES cells differentiating into neurons
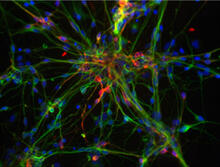
3276
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
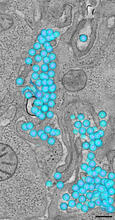
3571
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaNatcher Building 08
1088
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaDopaminergic neurons from ES cells
3270
Human embryonic stem cells differentiated into dopaminergic neurons, the type that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Image courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Jeannie Liu, Lab of Jan Nolta, University of California, Davis, via CIRM View MediaBody toxins (with labels)
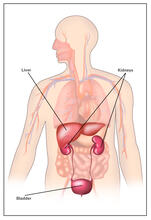
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaAdult and juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squids
7010
An adult Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, (~4 cm) surrounded by newly hatched juveniles (~2 mm) in a bowl of seawater.Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View Media
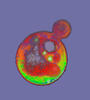
Multinucleated cancer cell
6967
A cancer cell with three nuclei, shown in turquoise. The abnormal number of nuclei indicates that the cell failed to go through cell division, probably more than once. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaLife of an AIDS virus (with labels and stages)
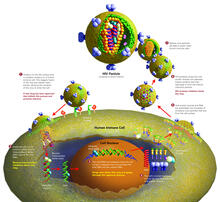
2515
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaEpigenetic code (with labels)
2563
The "epigenetic code" controls gene activity with chemical tags that mark DNA (purple diamonds) and the "tails" of histone proteins (purple triangles). Crabtree + Company View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 1
3730
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaSmooth muscle from mouse stem cells
3289
These smooth muscle cells were derived from mouse neural crest stem cells. Red indicates smooth muscle proteins, blue indicates nuclei. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institutes, via CIRM View MediaAtomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
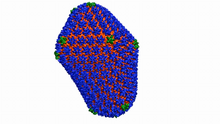
6601
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaLarvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
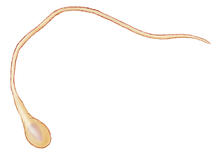
3627
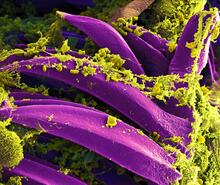
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner View MediaBubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
3576
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. NIAID View MediaHuman fibroblast undergoing cell division
6519
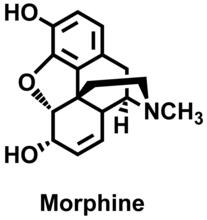
During cell division, cells physically divide after separating their genetic material to create two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Nilay Taneja, Vanderbilt University, and Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaMorphine Structure
3438
The chemical structure of the morphine molecule Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 1)
6553
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi (red) and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 48 hours on 1% agar surface from a sma L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaHimastatin
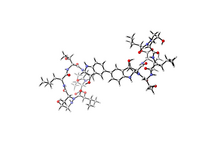
6848
A model of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaNatural nanomachine in action
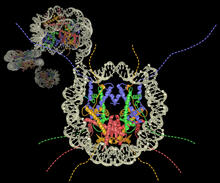
2336
Using a supercomputer to simulate the movement of atoms in a ribosome, researchers looked into the core of this protein-making nanomachine and took snapshots. Kevin Sanbonmatsu, Los Alamos National Laboratory View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaNucleosome
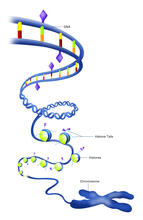
2741
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaFruit fly retina 01
2430
Image showing rhabdomeres (red), the light-sensitive structures in the fruit fly retina, and rhodopsin-4 (blue), a light-sensing molecule. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773
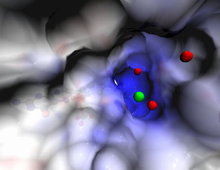
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
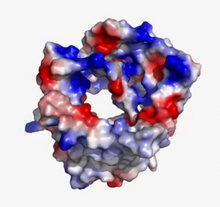
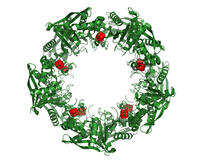
3720
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaCells use bubble-like structures called vesicles to transport cargo
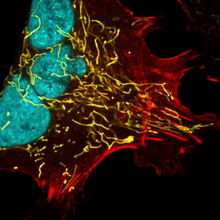
3634
Cells use bubble-like structures called vesicles (yellow) to import, transport, and export cargo and in cellular communication. A single cell may be filled with thousands of moving vesicles.Tatyana Svitkina, University of Pennsylvania View Media
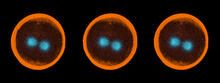
Sea urchin embryo 04
1050
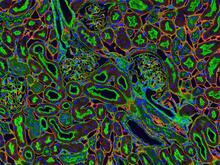
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaNCMIR kidney-1
3675
Stained kidney tissue. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View Media