Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
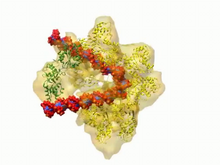
Computer sketch of bird-and-flower DNA origami
3689
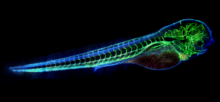
A computer-generated sketch of a DNA origami folded into a flower-and-bird structure. See also related image 3690. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
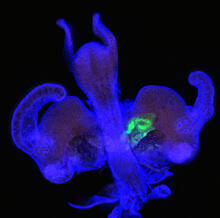
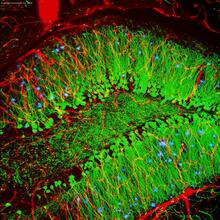
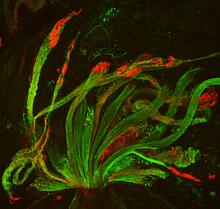
6661
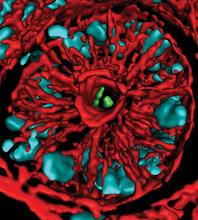
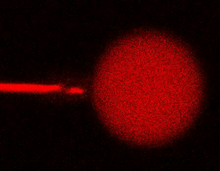
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaMouse colon with gut bacteria
3566
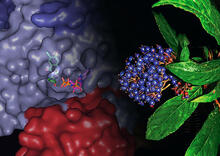
A section of mouse colon with gut bacteria (center, in green) residing within a protective pocket. Sarkis K. Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology View MediaChang Shan
3483
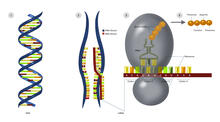
For thousands of years, Chinese herbalists have treated malaria using Chang Shan, a root extract from a type of hydrangea that grows in Tibet and Nepal. Paul Schimmel Lab, Scripps Research Institute View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated (with labels and numbers for stages)
2549
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
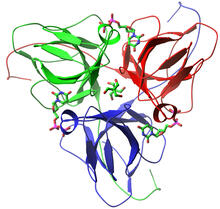
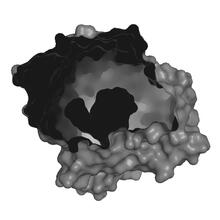
3307
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaHuman ES cells differentiating into neurons
3276
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaBacterial symbionts colonizing the crypts of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid light organ
7020
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, stained blue. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaHippocampal neuron in culture
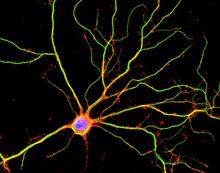
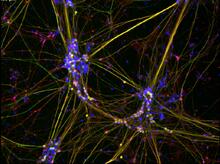
3687
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaTEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
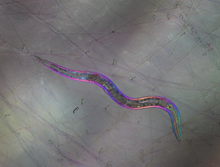
5759
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa lacking Draper
2759
In the absence of the engulfment receptor Draper, salivary gland cells (light blue) persist in the thorax of a developing Drosophila melanogaster pupa. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaSynapses in culture
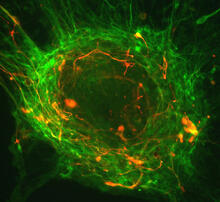
3399
Cultured hippocampal neurons grown on a substrate of glial cells (astrocytes). The glial cells form the pink/brown underlayment in this image. The tan threads are the neurons. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaIndependence Day
5888
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaActive site of sulfite oxidase
2746
Sulfite oxidase is an enzyme that is essential for normal neurological development in children. John Enemark, University of Arizona View MediaLorsch Swearing In
3530
Jon Lorsch at his swearing in as NIGMS director in August 2013. Also shown are Francis Collins, NIH Director, and Judith Greenberg, former NIGMS Acting Director. View MediaSnowflake DNA origami
3724
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. The image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Images: A Holiday-Themed Collection. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (2)
2404
Crystals of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaPathways: What's the Connection? | Different Jobs in a Science Lab
6541
Learn about some of the different jobs in a scientific laboratory and how researchers work as a team to make discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaC. elegans trapped by carnivorous fungus
6963
Real-time footage of Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm, trapped by a carnivorous fungus, Arthrobotrys dactyloides. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaNeural circuits in worms similar to those in humans
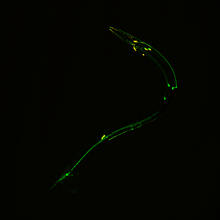
3252
Green and yellow fluorescence mark the processes and cell bodies of some C. elegans neurons. Shawn Xu, University of Michigan View MediaBacterial glucose isomerase
2409
A crystal of bacterial glucose isomerase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaBacteria working to eat
2304
Gram-negative bacteria perform molecular acrobatics just to eat. Because they're encased by two membranes, they must haul nutrients across both. Emad Tajkhorshid, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared-labeled
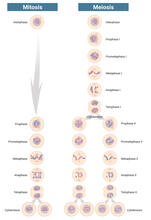
6788
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaBee venom toxin destroying a cell
3583
This video condenses 6.5 minutes into less than a minute to show how the toxin in bee venom, called melittin, destroys an animal or bacterial cell. Huey Huang, Rice University View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
6982
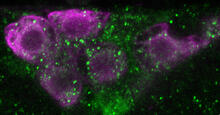
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaCryo-ET cross-section of the Golgi apparatus
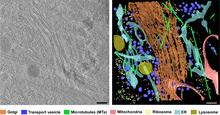
6606
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a 3D, color-coded version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaFruit fly spermatids
3590
Developing spermatids (precursors of mature sperm cells) begin as small, round cells and mature into long-tailed, tadpole-shaped ones. Lacramioara Fabian, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada View MediaBiofilm formed by a pathogen
6518
A biofilm is a highly organized community of microorganisms that develops naturally on certain surfaces. Scott Chimileski, Ph.D., and Roberto Kolter, Ph.D., Harvard Medical School. View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 1
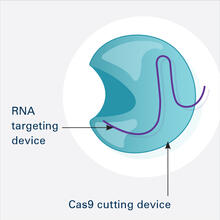
6465
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the first frame in a series of four. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaAntitoxin GhoS (Illustration 2)
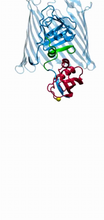
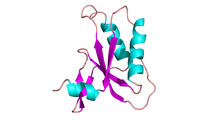
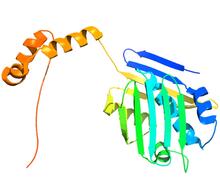
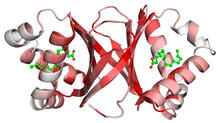
3428
Structure of the bacterial antitoxin protein GhoS. GhoS inhibits the production of a bacterial toxin, GhoT, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Rebecca Page and Wolfgang Peti, Brown University and Thomas K. Wood, Pennsylvania State University View MediaFinding one bug
2314
A nanometer-sized biosensor can detect a single deadly bacterium in tainted ground beef. How? Weihong Tan, University of Florida in Gainesville View MediaAutomated Worm Sorter - 4
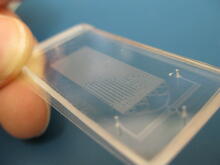
3475
Georgia Tech associate professor Hang Lu holds a microfluidic chip that is part of a system that uses artificial intelligence and cutting-edge image processing to automatically examine large number of Georgia Tech/Gary Meek View MediadUTP pyrophosphatase from M. tuberculosis
2381
Model of an enzyme, dUTP pyrophosphatase, from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Drugs targeted to this enzyme might inhibit the replication of the bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaFungal lipase (2)
2411
Crystals of fungal lipase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaSmooth muscle from mouse stem cells
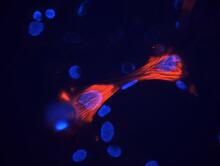
3289
These smooth muscle cells were derived from mouse neural crest stem cells. Red indicates smooth muscle proteins, blue indicates nuclei. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institutes, via CIRM View MediaHsp33 figure 2
3355
Featured in the March 15, 2012 issue of Biomedical Beat. Related to Hsp33 Figure 1, image 3354. Ursula Jakob and Dana Reichmann, University of Michigan View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell
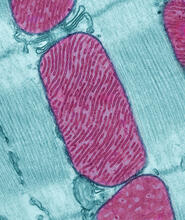
3661
These mitochondria (red) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaLipid raft
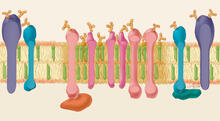
1285
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. Judith Stoffer View MediaPeripheral nerve cells derived from ES cells
3263
Peripheral nerve cells made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaLily mitosis 05
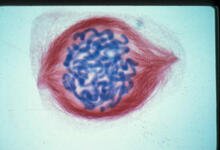
1015
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaCellular metropolis
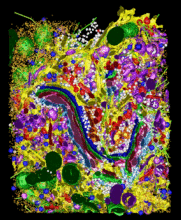
2308
Like a major city, a cell teems with specialized workers that carry out its daily operations--making energy, moving proteins, or helping with other tasks. Kathryn Howell, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center View MediaPodocytes from a chronically diseased kidney
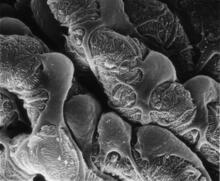
3565
This scanning electron microscope (SEM) image shows podocytes--cells in the kidney that play a vital role in filtering waste from the bloodstream--from a patient with chronic kidney disease. Olga Troyanskaya, Princeton University and Matthias Kretzler, University of Michigan View MediaDimeric ferredoxin-like protein from an unidentified marine microbe
2340
This is the first structure of a protein derived from the metagenomic sequences collected during the Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling project. Joint Center for Structural Genomics View MediaMicrofluidic chip
3265
Microfluidic chips have many uses in biology labs. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
3414
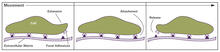
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaFocal adhesions (with labels)
2503
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View Media