Image Gallery: Dengue virus membrane protein structure
ID
3758
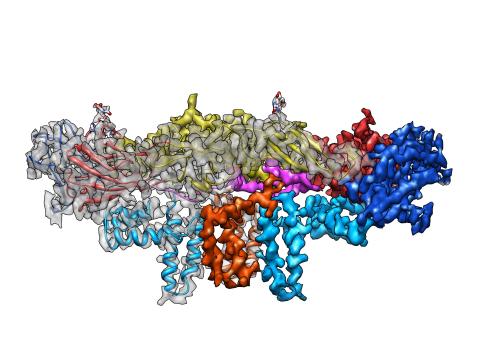
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. The proteins that span this membrane play an important role in the life cycle of the virus. Scientists used cryo-EM to determine the structure of a dengue virus at a 3.5-angstrom resolution to reveal how the membrane proteins undergo major structural changes as the virus matures and infects a host. The image shows a side view of the structure of a protein composed of two smaller proteins, called E and M. Each E and M contributes two molecules to the overall protein structure (called a heterotetramer), which is important for assembling and holding together the viral membrane, i.e., the shell that surrounds the genetic material of the dengue virus. The dengue protein's structure has revealed some portions in the protein that might be good targets for developing medications that could be used to combat dengue virus infections. For more on cryo-EM see the blog post Cryo-Electron Microscopy Reveals Molecules in Ever Greater Detail. You can watch a rotating view of the dengue virus surface structure in video 3748.
Source
Hong Zhou, UCLA