Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
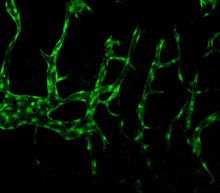
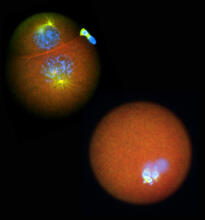
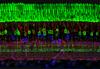
Normal vascular development in frog embryos
3404
In vivo vascular development in kdr:GFP frogs. Related to images 3403 and 3405. Hye Ji Cha, University of Texas at Austin View MediaBuilding blocks and folding of proteins
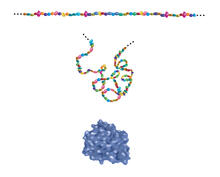
2508
Proteins are made of amino acids hooked end-to-end like beads on a necklace. To become active, proteins must twist and fold into their final, or "native," conformation. Crabtree + Company View MediaClathrin-mediated endocytosis
5753
Endocytosis is the process by which cells are able to take up membrane and extracellular materials through the formation of a small intracellular bubble, called a vesicle. Janet Iwasa, University of Utah View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 04
2454
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaTrp_RS - tryptophanyl tRNA-synthetase family of enzymes
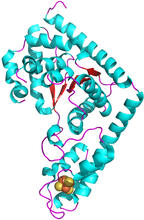
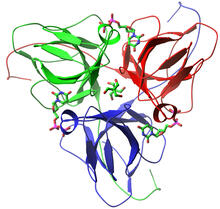
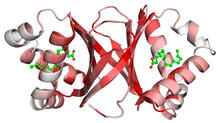
2483
This image represents the structure of TrpRS, a novel member of the tryptophanyl tRNA-synthetase family of enzymes. View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
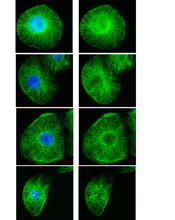
3443
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaMouse brain 3
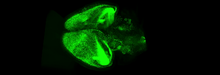
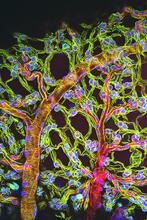
6931
Various views of a mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaFruit fly ovary
6522
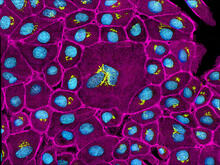
In this image of a stained fruit fly ovary, the ovary is packed with immature eggs (with DNA stained blue). The cytoskeleton (in pink) is a collection of fibers that gives a cell shape and support. Crystal D. Rogers, Ph.D., University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine; and Mariano A. Loza-Coll, Ph.D., California State University, Northridge. View MediaHIV Infected Cell
3386
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), shown here as tiny purple spheres, causes the disease known as AIDS (for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse embryo showing Smad4 protein
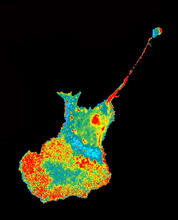
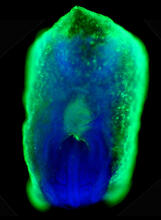
2607
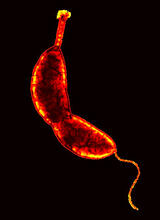
This eerily glowing blob isn't an alien or a creature from the deep sea--it's a mouse embryo just eight and a half days old. The green shell and core show a protein called Smad4. Kenneth Zaret, Fox Chase Cancer Center View MediaHydra 01
2437
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaHigh-throughput protein structure determination pipeline
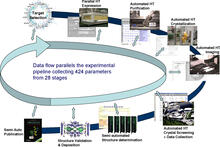
2364
This slide shows the technologies that the Joint Center for Structural Genomics developed for going from gene to structure and how the technologies have been integrated into a high-throughput pipeline Joint Center for Structural Genomics View MediaRNA interference
2558
RNA interference or RNAi is a gene-silencing process in which double-stranded RNAs trigger the destruction of specific RNAs. Crabtree + Company View MediadUTP pyrophosphatase from M. tuberculosis
2381
Model of an enzyme, dUTP pyrophosphatase, from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Drugs targeted to this enzyme might inhibit the replication of the bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
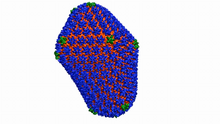
5874
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaPodocytes from a chronically diseased kidney
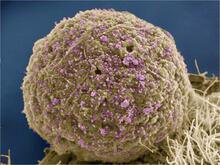
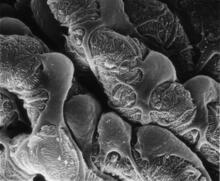
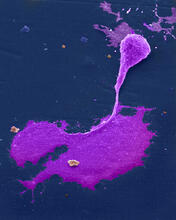
3565
This scanning electron microscope (SEM) image shows podocytes--cells in the kidney that play a vital role in filtering waste from the bloodstream--from a patient with chronic kidney disease. Olga Troyanskaya, Princeton University and Matthias Kretzler, University of Michigan View MediaHoneybee brain
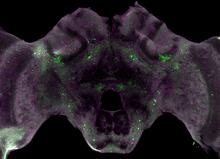
6755
Insect brains, like the honeybee brain shown here, are very different in shape from human brains. Gene Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaCytoskeleton
1272
The three fibers of the cytoskeleton--microtubules in blue, intermediate filaments in red, and actin in green--play countless roles in the cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaDimeric ferredoxin-like protein from an unidentified marine microbe
2340
This is the first structure of a protein derived from the metagenomic sequences collected during the Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling project. Joint Center for Structural Genomics View MediaHaplotypes
2566
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. Crabtree + Company View MediaFolding@Home
1276
Stanford University scientist Vijay Pande decided to couple the power of computers with the help of the public. Judith Stoffer View MediaPrecisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
3779
Moving protein or other molecules to specific cells to treat or examine them has been a major biological challenge. Nature Nanotechnology View MediaPurkinje cells are one of the main cell types in the brain
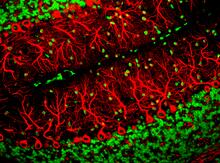
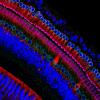
3637
This image captures Purkinje cells (red), one of the main types of nerve cell found in the brain. Yinghua Ma and Timothy Vartanian, Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y. View MediaFly by night
2417
This fruit fly expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the same pattern as the period gene, a gene that regulates circadian rhythm and is expressed in all sensory neurons on the surface of the fl Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
6789
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaPathways: What's the Connection? | Different Jobs in a Science Lab
6541
Learn about some of the different jobs in a scientific laboratory and how researchers work as a team to make discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaCoronavirus spike protein structure
3753
Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses responsible for 30 percent of mild respiratory infections and atypical deadly pneumonia in humans worldwide. Melody Campbell, UCSF View MediaSoft X-ray tomography of a pancreatic beta cell
6605
A color-coded, 3D model of a rat pancreatic β cell. This type of cell produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco. View MediaBlinking bacteria
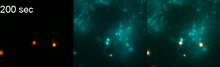
2724
Like a pulsing blue shower, E. coli cells flash in synchrony. Genes inserted into each cell turn a fluorescent protein on and off at regular intervals. Jeff Hasty, University of California, San Diego View MediaNucleolinus
2762
The nucleolinus is a cellular compartment that has been a lonely bystander in scientific endeavors. Mary Anne Alliegro, Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaEpithelial cells
3647
This image mostly shows normal cultured epithelial cells expressing green fluorescent protein targeted to the Golgi apparatus (yellow-green) and stained for actin (magenta) and DNA (cyan). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCaulobacter
3262
A study using Caulobacter crescentus showed that some bacteria use just-in-time processing, much like that used in industrial delivery, to make the glue that allows them to attach to surfaces, Yves Brun, Indiana University View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882
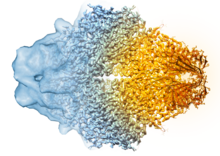
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaBacterial cells migrating through the tissues of the squid light organ
7015
Vibrio fischeri cells (~ 2 mm), labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP), passing through a very narrow bottleneck in the tissues (red) of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolope Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaAlternative splicing
2552
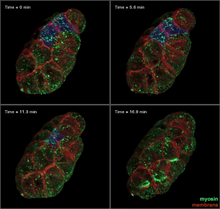
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Crabtree + Company View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3334
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaBacterial cells aggregating above the light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7018
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaFruit fly starvation leads to adipokine accumulation
6984
Adult Drosophila abdominal fat tissue showing cell nuclei labelled in magenta. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaCorrelative imaging by annotation with single molecules (CIASM) process
6568
These images illustrate a technique combining cryo-electron tomography and super-resolution fluorescence microscopy called correlative imaging by annotation with single molecules (CIASM). Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaHuman opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
3314
Opioid receptors on the surfaces of brain cells are involved in pleasure, pain, addiction, depression, psychosis, and other conditions. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaVesicle traffic
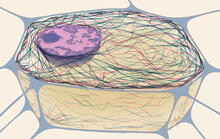
1283
This illustration shows vesicle traffic inside a cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaThree neurons and human ES cells
3290
The three neurons (red) visible in this image were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Undifferentiated stem cells are green here. Anirvan Ghosh lab, University of California, San Diego, via CIRM View MediaSheep hemoglobin crystal
2392
A crystal of sheep hemoglobin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 1
3413
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaAtomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
6601
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaCrab nerve cell
1247
Neuron from a crab showing the cell body (bottom), axon (rope-like extension), and growth cone (top right). Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaWeblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
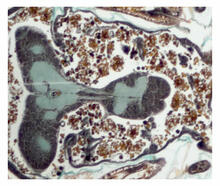
3616
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University. View MediaBacterial spore
2752
A spore from the bacterium Bacillus subtilis shows four outer layers that protect the cell from harsh environmental conditions. Patrick Eichenberger, New York University View Media