Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
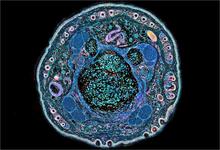
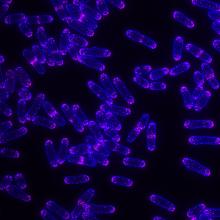
NCMIR mouse tail
3395
Stained cross section of a mouse tail. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria
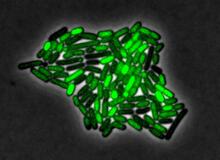
3253
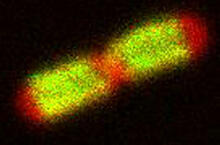
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
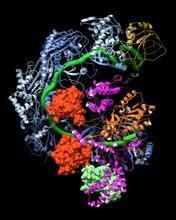
3597
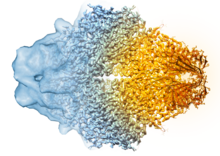
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaMitosis - metaphase
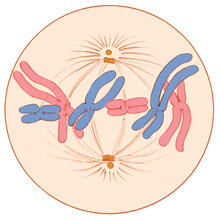
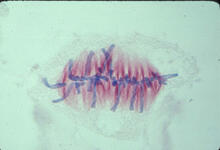
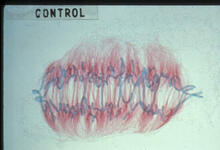
1329
A cell in metaphase during mitosis: The copied chromosomes align in the middle of the spindle. Judith Stoffer View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 1
5751
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaBeta 2-adrenergic receptor
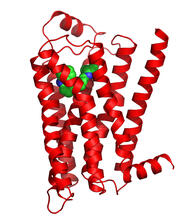
3358
The receptor is shown bound to a partial inverse agonist, carazolol. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaElectrostatic map of the adeno-associated virus with scale
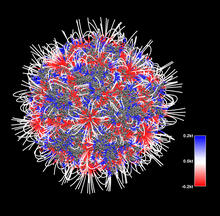
3375
The new highly efficient parallelized DelPhi software was used to calculate the potential map distribution of an entire virus, the adeno-associated virus, which is made up of more than 484,000 atoms. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaMounting of protein crystals
2368
Automated methods using micromachined silicon are used at the Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics to mount protein crystals for X-ray crystallography. The Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated
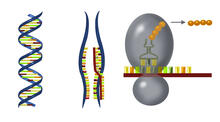
2547
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaDisease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
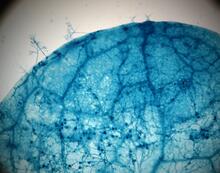
2782
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
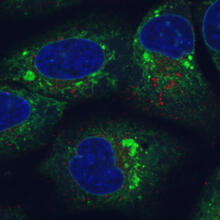
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaCarbon building blocks (with examples)
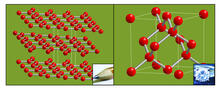
2507
The arrangement of identical molecular components can make a dramatic difference. For example, carbon atoms can be arranged into dull graphite (left) or sparkly diamonds (right). Crabtree + Company View MediaFocal adhesions (with labels)
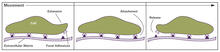
2503
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaA panorama view of cells
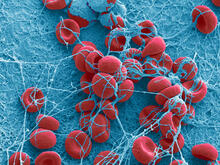
5761
This photograph shows a panoramic view of HeLa cells, a cell line many researchers use to study a large variety of important research questions. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaDose response curves
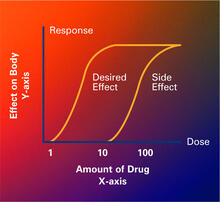
2533
Dose-response curves determine how much of a drug (X-axis) causes a particular effect, or a side effect, in the body (Y-axis). Featured in Medicines By Design. Crabtree + Company View MediaYeast cells with Fimbrin Fim1
6794
Yeast cells with the protein Fimbrin Fim1 shown in magenta. This protein plays a role in cell division. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View Media
Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University. View MediaLily mitosis 07
1017
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaLily mitosis 10
1010
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaMapping disease spread
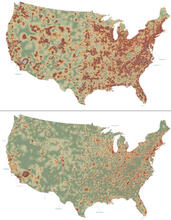
2320
How far and fast an infectious disease spreads across a community depends on many factors, including transportation. These U.S. David Chrest, RTI International View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
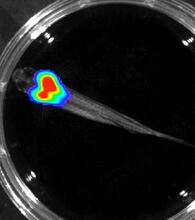
3557
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaSuperconducting magnet
1120
Superconducting magnet for NMR research, from the February 2003 profile of Dorothee Kern in Findings. Mike Lovett View MediaFruit fly brain responds to adipokines
6985
Drosophila adult brain showing that an adipokine (fat hormone) generates a response from neurons (aqua) and regulates insulin-producing neurons (red).Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View Media
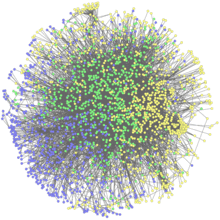
Network Map
2735
This network map shows the overlap (green) between the long QT syndrome (yellow) and epilepsy (blue) protein-interaction neighborhoods located within the human interactome. Seth Berger, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaTonB protein in gram-negative bacteria
3549
The green in this image highlights a protein called TonB, which is produced by many gram-negative bacteria, including those that cause typhoid fever, meningitis and dysentery. Phillip Klebba, Kansas State University View MediaRecombinant DNA (with labels)
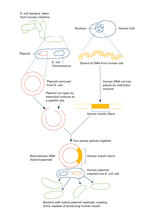
2565
To splice a human gene (in this case, the one for insulin) into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. Crabtree + Company View MediaStretch detectors
2714
Muscles stretch and contract when we walk, and skin splits open and knits back together when we get a paper cut. Christopher Chen, University of Pennsylvania View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaProtein clumping in zinc-deficient yeast cells
3550
The green spots in this image are clumps of protein inside yeast cells that are deficient in both zinc and a protein called Tsa1 that prevents clumping. Colin MacDiarmid and David Eide, University of Wisconsin--Madison View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaStructure of heme, side view
3540
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
6661
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaHow a microtubule builds and deconstructs
3650
A microtubule, part of the cell's skeleton, builds and deconstructs. View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 72 hour
6556
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface from a small i L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaMolecular view of glutamatergic synapse
6992
This illustration highlights spherical pre-synaptic vesicles that carry the neurotransmitter glutamate. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHuman retinal organoid
6748
A replica of a human retina grown from stem cells. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaAutofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
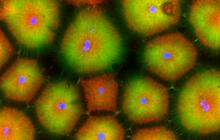
5755
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaSkin cell (keratinocyte)
3599
This normal human skin cell was treated with a growth factor that triggered the formation of specialized protein structures that enable the cell to move. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaNCMIR Kidney Glomeruli
3392
Stained glomeruli in the kidney. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaNucleotides make up DNA
2541
DNA consists of two long, twisted chains made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains one base, one phosphate molecule, and the sugar molecule deoxyribose. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 09
1022
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaFly cells
3594
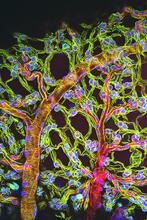
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 1
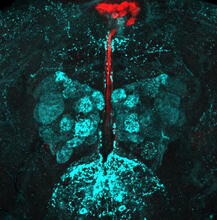
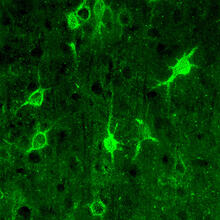
3741
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaHuman skeletal muscle
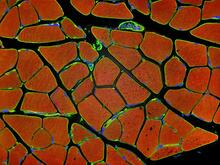
3677
Cross section of human skeletal muscle. Image taken with a confocal fluorescent light microscope. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaAminopeptidase N from N. meningitidis
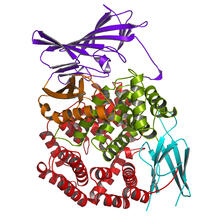
2341
Model of the enzyme aminopeptidase N from the human pathogen Neisseria meningitidis, which can cause meningitis epidemics. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaHeLa cells
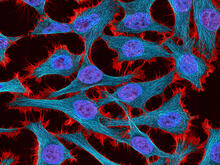
3521
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View Media