Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
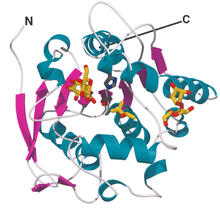
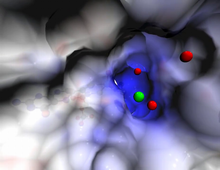
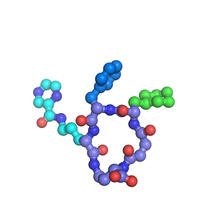
Most abundant protein in M. tuberculosis
2378
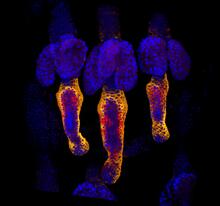
Model of a protein, antigen 85B, that is the most abundant protein exported by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaConfocal microscopy image of two Drosophila ovarioles
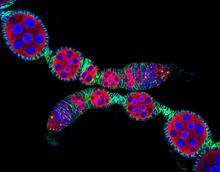
5772
Ovarioles in female insects are tubes in which egg cells (called oocytes) form at one end and complete their development as they reach the other end of the tube. 2004 Olympus BioScapes Competition View MediaStructure of heme, side view
3540
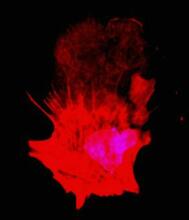
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaARTS triggers apoptosis
2432
Cell showing overproduction of the ARTS protein (red). ARTS triggers apoptosis, as shown by the activation of caspase-3 (green) a key tool in the cell's destruction. The nucleus is shown in blue. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaSimulation of uncontrolled avian flu outbreak
2574
This video simulation shows what an uncontrolled outbreak of transmissible avian flu among people living in Thailand might look like. Neil M. Ferguson, Imperial College London View MediaActive site of sulfite oxidase
2746
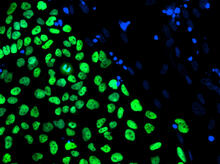
Sulfite oxidase is an enzyme that is essential for normal neurological development in children. John Enemark, University of Arizona View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
3275
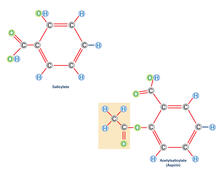
The nuclei stained green highlight human embryonic stem cells grown under controlled conditions in a laboratory. Blue represents the DNA of surrounding, supportive feeder cells. Julie Baker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaAspirin (with labels)
2530
Acetylsalicylate (bottom) is the aspirin of today. Crabtree + Company View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
5874
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
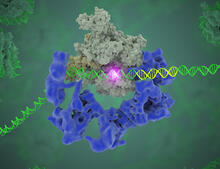
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaMitosis - prometaphase
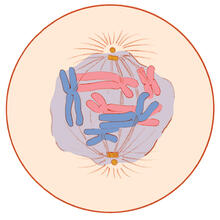
1331
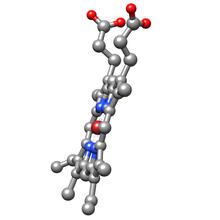
A cell in prometaphase during mitosis: The nuclear membrane breaks apart, and the spindle starts to interact with the chromosomes. Judith Stoffer View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 03
2796
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaMaster clock of the mouse brain
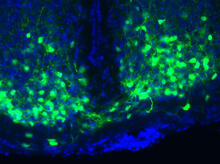
3547
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis View MediaBiopixels
3266
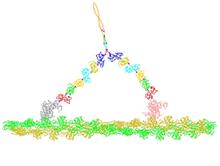
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. This image shows a small chip with about 500 blinking bacterial colonies or biopixels. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 7
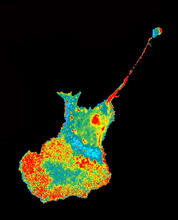
3419
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaChromatin in human tenocyte
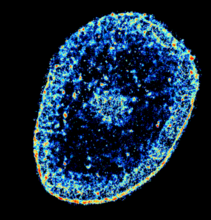
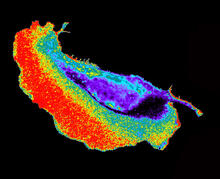
6893
The nucleus of a degenerating human tendon cell, also known as a tenocyte. It has been color-coded based on the density of chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaFocal adhesions (with labels)
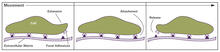
2503
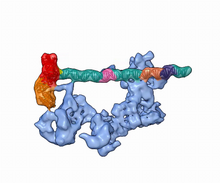
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaTFIID complex binds DNA to start gene transcription
3766
Gene transcription is a process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaMolecular interactions at the astrocyte nuclear membrane
3734
These ripples of color represent the outer membrane of the nucleus inside an astrocyte, a star-shaped cell inside the brain. Katerina Akassoglou, Gladstone Institute for Neurological Disease & UCSF View MediaMotion in the brain
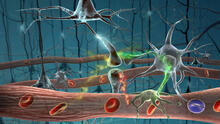
2323
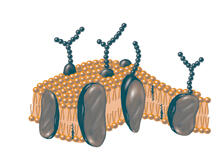
Amid a network of blood vessels and star-shaped support cells, neurons in the brain signal each other. The mists of color show the flow of important molecules like glucose and oxygen. Kim Hager and Neal Prakash, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaPlasma membrane
2523
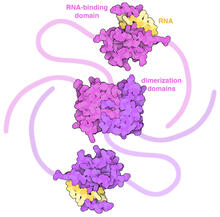
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2524 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaSARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
6991
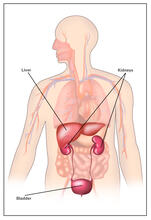
In SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, nucleocapsid is a complex molecule with many functional parts. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaBody toxins (with labels)
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaNetwork diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (unlabeled)
3436
This image shows the hierarchical ontology of genes, cellular components and processes derived from large genomic datasets. From Dutkowski et al. Janusz Dutkowski and Trey Ideker View MediaDrugs enter skin
2531
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2532 for a labeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaSimulation of controlled avian flu outbreak
2573
This video shows a controlled outbreak of transmissible avian flu among people living in Thailand. Neil M. Ferguson, Imperial College London View MediaCell division and cell death
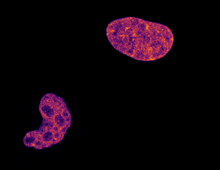
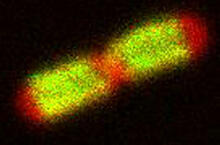
6790
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaiPS cell facility at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research
2723
This lab space was designed for work on the induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell collection, part of the NIGMS Human Genetic Cell Repository at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research. Courtney Sill, Coriell Institute for Medical Research View MediaHistones in chromatin (with labels)
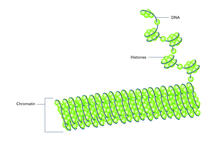
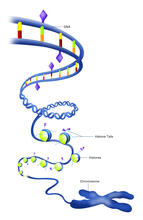
2561
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaEar hair cells derived from embryonic stem cells
3272
Mouse embryonic stem cells matured into this bundle of hair cells similar to the ones that transmit sound in the ear. Stefen Heller, Stanford University, via CIRM View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 3
5767
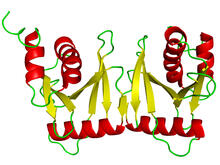
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaTonB protein in gram-negative bacteria
3549
The green in this image highlights a protein called TonB, which is produced by many gram-negative bacteria, including those that cause typhoid fever, meningitis and dysentery. Phillip Klebba, Kansas State University View MediaFruit fly ovaries
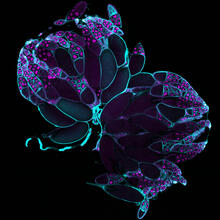
6807
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media
Fused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaDeveloping Arabidopsis flower buds
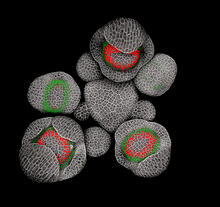
3743
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaGrowing hair follicle stem cells
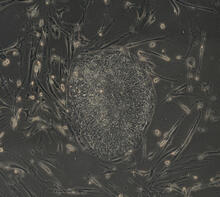
3499
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 04
2454
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaPolarized cells- 01
3332
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 02
2452
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaFrom DNA to Protein (labeled)
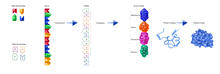
2510
The genetic code in DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into proteins with specific sequences. Crabtree + Company View MediaEpigenetic code (with labels)
2563
The "epigenetic code" controls gene activity with chemical tags that mark DNA (purple diamonds) and the "tails" of histone proteins (purple triangles). Crabtree + Company View MediatRNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans
2351
An NMR solution structure model of the transfer RNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans (subunit Sen15). This represents the first structure of a eukaryotic tRNA splicing endonuclease subunit. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaHeLa cells
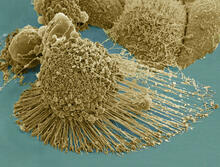
3519
Scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic HeLa cell. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaSponge
2728
Many of today's medicines come from products found in nature, such as this sponge found off the coast of Palau in the Pacific Ocean. Phil Baran, Scripps Research Institute View MediaHistone deacetylases
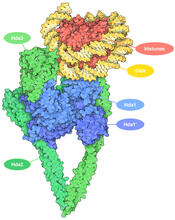
7001
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaFruit fly egg ooplasmic streaming
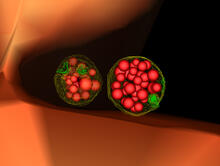
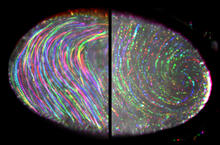
6809
Two fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg cells, one on each side of the central black line. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media