Image Gallery: Protein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
ID
7004
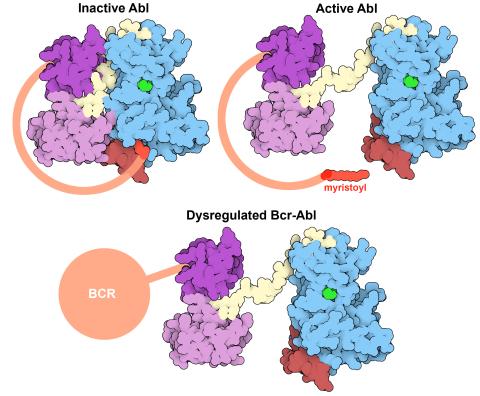
Protein kinases—enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules—are cancer chemotherapy targets because they play significant roles in almost all aspects of cell function, are tightly regulated, and contribute to the development of cancer and other diseases if any alterations to their regulation occur. Genetic abnormalities affecting the c-Abl tyrosine kinase are linked to chronic myelogenous leukemia, a cancer of immature cells in the bone marrow. In the noncancerous form of the protein, binding of a myristoyl group to the kinase domain inhibits the activity of the protein until it is needed (top left shows the inactive form, top right shows the open and active form). The cancerous variant of the protein, called Bcr-Abl, lacks this autoinhibitory myristoyl group and is continually active (bottom). ATP is shown in green bound in the active site of the kinase.
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: c-Abl tyrosine kinase and regulatory domains (PDB entry 1OPL) and F-actin binding domain (PDB entry 1ZZP).
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: c-Abl tyrosine kinase and regulatory domains (PDB entry 1OPL) and F-actin binding domain (PDB entry 1ZZP).
Source
Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank.