Image Gallery: Blood clots show their flex
Video file
ID
2450
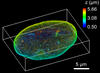
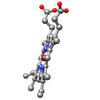
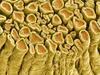
Blood clots stop bleeding, but they also can cause heart attacks and strokes. A team led by computational biophysicist Klaus Schulten of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign has revealed how a blood protein can give clots their lifesaving and life-threatening abilities. The researchers combined experimental and computational methods to animate fibrinogen, a protein that forms the elastic fibers that enable clots to withstand the force of blood pressure. This simulation shows that the protein, through a series of events, stretches up to three times its length. Adjusting this elasticity could improve how we manage healthful and harmful clots. NIH's National Center for Research Resources also supported this work. Featured in the March 19, 2008, issue of Biomedical Beat.
Source
Eric Lee, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Topics