Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
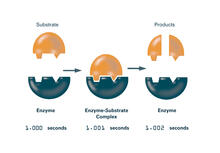
Enzymes convert subtrates into products (with labels)
2522
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2521 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaPathways: What's the Connection? | Different Jobs in a Science Lab
6541
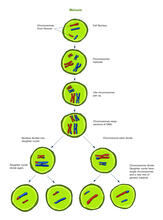
Learn about some of the different jobs in a scientific laboratory and how researchers work as a team to make discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaMeiosis illustration (with labels)
2546
Meiosis is the process whereby a cell reduces its chromosomes from diploid to haploid in creating eggs or sperm. Crabtree + Company View MediaMitosis - anaphase
1328
A cell in anaphase during mitosis: Chromosomes separate into two genetically identical groups and move to opposite ends of the spindle. Judith Stoffer View MediaTelomerase illustration
1335
Reactivating telomerase in our cells does not appear to be a good way to extend the human lifespan. Cancer cells reactivate telomerase. Judith Stoffer View MediaBioluminescence in a Tube
5895
Details about the basic biology and chemistry of the ingredients that produce bioluminescence are allowing scientists to harness it as an imaging tool. Credit: Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute. Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
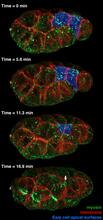
3297
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaAutomated crystal screening system
2362
Automated crystal screening systems such as the one shown here are becoming a common feature at synchrotron and other facilities where high-throughput crystal structure determination is being carried Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaMap of protein structures 01
2365
A global "map of the protein structure universe." The Berkeley Structural Genomics Center has developed a method to visualize the vast universe of protein structures in which proteins of similar struc Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaBacterial glucose isomerase
2409
A crystal of bacterial glucose isomerase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaInsulin and protein interact in pancreatic beta cells
3546
A large number of proteins interact with the hormone insulin as it is produced in and secreted from the beta cells of the pancreas. William E. Balch, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaNCMIR Kidney Glomeruli
3392
Stained glomeruli in the kidney. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaStaphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaLily mitosis 02
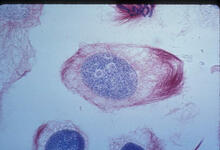
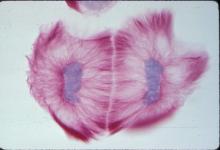
1012
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaRNA interference
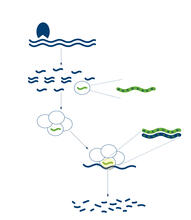
2558
RNA interference or RNAi is a gene-silencing process in which double-stranded RNAs trigger the destruction of specific RNAs. Crabtree + Company View MediaAssembly of the HIV capsid
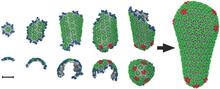
5729
The HIV capsid is a pear-shaped structure that is made of proteins the virus needs to mature and become infective. John Grime and Gregory Voth, The University of Chicago View MediaDynamin structure
2744
When a molecule arrives at a cell's outer membrane, the membrane creates a pouch around the molecule that protrudes inward. Josh Chappie, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of myelinated axons with ECM between the axons
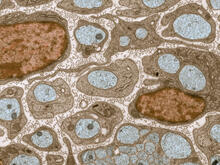
3736
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells, as shown here. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaBlinking bacteria
2724
Like a pulsing blue shower, E. coli cells flash in synchrony. Genes inserted into each cell turn a fluorescent protein on and off at regular intervals. Jeff Hasty, University of California, San Diego View MediaHistone deacetylases
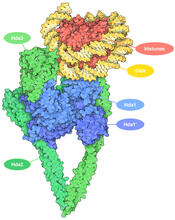
7001
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMouse brain 1
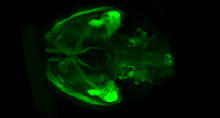
6929
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaPartial Model of a Cilium’s Doublet Microtubule
6548
Cilia (cilium in singular) are complex molecular machines found on many of our cells. Brown Lab, Harvard Medical School and Veronica Falconieri Hays. View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 1
5777
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaMeasles virus proteins
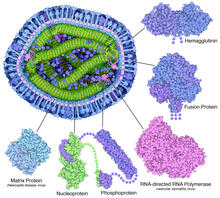
6996
A cross section of the measles virus in which six proteins (enlarged on the outside of the virus) work together to infect cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaFlagellated bacterial cells
7014
Vibrio fischeri (2 mm in length) is the exclusive symbiotic partner of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaWound healing in process
3500
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaSerum albumin structure 1
3744
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. Wladek Minor, University of Virginia View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaCryo-electron microscopy of the dengue virus showing protective membrane and membrane proteins
3748
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaSecreted protein from Mycobacteria
2379
Model of a major secreted protein of unknown function, which is only found in mycobacteria, the class of bacteria that causes tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaCultured cells
1178
This image of laboratory-grown cells was taken with the help of a scanning electron microscope, which yields detailed images of cell surfaces. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaPeripheral nerve cell derived from ES cells
3264
A peripheral nerve cell made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaSimulation of controlled avian flu outbreak
2573
This video shows a controlled outbreak of transmissible avian flu among people living in Thailand. Neil M. Ferguson, Imperial College London View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared
1333
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaMouse retina close-up
5872
Keunyoung ("Christine") Kim National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaChromium X-ray source
2361
In the determination of protein structures by X-ray crystallography, this unique soft (l = 2.29Å) X-ray source is used to collect anomalous scattering data from protein crystals containing light atoms The Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaAutomated Worm Sorter - 4
3475
Georgia Tech associate professor Hang Lu holds a microfluidic chip that is part of a system that uses artificial intelligence and cutting-edge image processing to automatically examine large number of Georgia Tech/Gary Meek View MediaSmall blood vessels in a mouse retina
3400
Blood vessels at the back of the eye (retina) are used to diagnose glaucoma and diabetic eye disease. They also display characteristic changes in people with high blood pressure. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaMitochondrion from insect flight muscle
3662
This is a tomographic reconstruction of a mitochondrion from an insect flight muscle. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaRhodopsin bound to visual arrestin
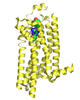
6768
Rhodopsin is a pigment in the rod cells of the retina (back of the eye). It is extremely light-sensitive, supporting vision in low-light conditions. Protein Data Bank. View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaFruitful dyes
2317
These colorful, computer-generated ribbons show the backbone of a molecule that glows a fluorescent red. Roger Y. Tsien, University of California, San Diego View MediaFruit fly ovaries
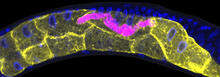
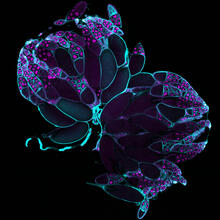
6807
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media
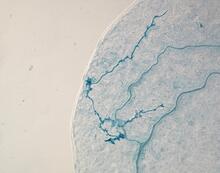
Arabidopsis leaf injected with a pathogen
2780
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf eight days after being infected with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis, which is closely related to crop pathogens that Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaLily mitosis 13
1019
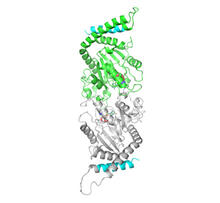
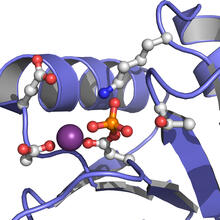
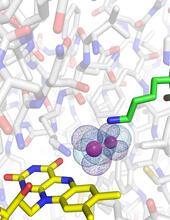
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaActive Site of E. coli response regulator PhoB
3412
Active site of E. coli response regulator PhoB. Ann Stock, Rutgers University View MediaMicrotubules and tau aggregates
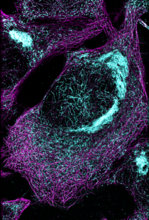
6892
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaO2 reacting with a flavin-dependent enzyme
3411
Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan View Media