Image Gallery: Shiga toxin
ID
6997
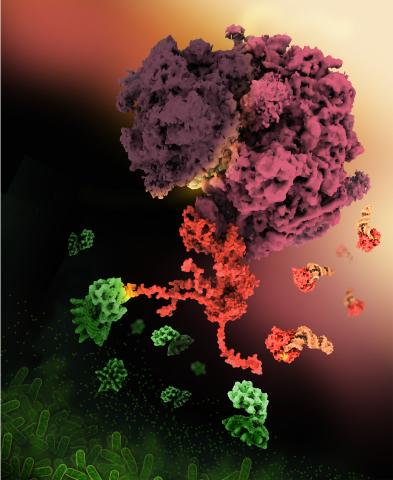
E. coli bacteria normally live harmlessly in our intestines, but some cause disease by making toxins. One of these toxins, called Shiga toxin (green), inactivates host ribosomes (purple) by mimicking their normal binding partners, the EF-Tu elongation factor (red) complexed with Phe-tRNAPhe (orange).
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: Shiga toxin 2 (PDB entry 7U6V) and Phe-tRNA (PDB entry 1TTT).
More information about this work can be found in the J. Biol. Chem. paper "Cryo-EM structure of Shiga toxin 2 in complex with the native ribosomal P-stalk reveals residues involved in the binding interaction" by Kulczyk et. al.
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: Shiga toxin 2 (PDB entry 7U6V) and Phe-tRNA (PDB entry 1TTT).
More information about this work can be found in the J. Biol. Chem. paper "Cryo-EM structure of Shiga toxin 2 in complex with the native ribosomal P-stalk reveals residues involved in the binding interaction" by Kulczyk et. al.
Source
Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank.