Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
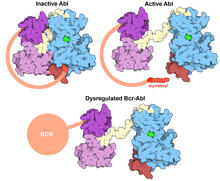
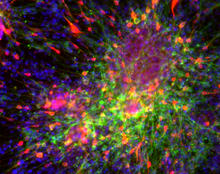
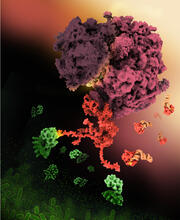
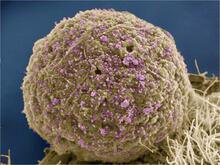
Protein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
7004
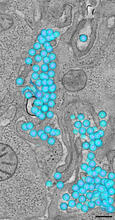
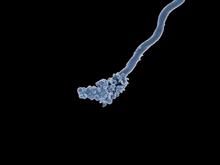
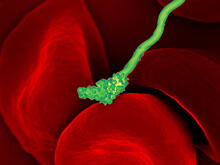
Protein kinases—enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules—are cancer chemotherapy targets because they play significant roles in almost all aspects of cell function, are tightly regulated, and co Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
3571
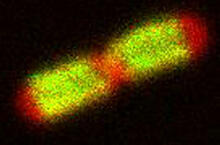
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaApoptosis reversed
3486
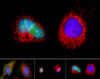
Two healthy cells (bottom, left) enter into apoptosis (bottom, center) but spring back to life after a fatal toxin is removed (bottom, right; top). Hogan Tang of the Denise Montell Lab, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 02
2791
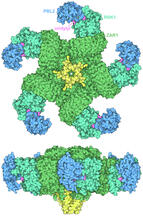
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaPlant resistosome
7002
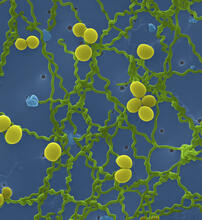
The research organism Arabidopsis thaliana forms a large molecular machine called a resistosome to fight off infections. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
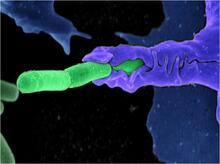
6805
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaBubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
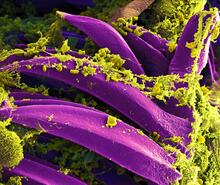
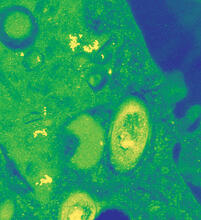
3576
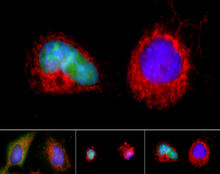
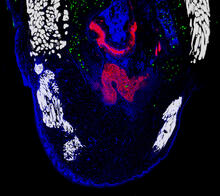
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. NIAID View MediaAbnormal, spiky fibroblast
3613
This is a fibroblast, a connective tissue cell that plays an important role in wound healing. Normal fibroblasts have smooth edges. Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, Mo. View MediaMyotonic dystrophy type 2 genetic defect
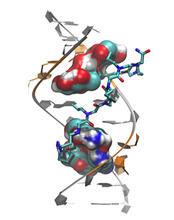
3573
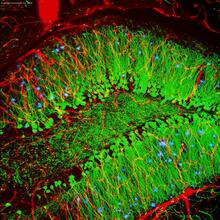
Scientists revealed a detailed image of the genetic defect that causes myotonic dystrophy type 2 and used that information to design drug candidates to counteract the disease. Matthew Disney, Scripps Research Institute and Ilyas Yildirim, Northwestern University View MediaDopaminergic neurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells
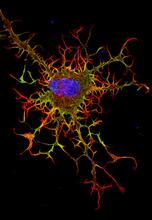
3271
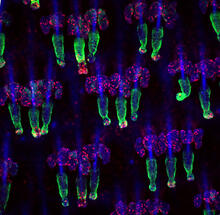
These neurons are derived from mouse embryonic stem cells. Red shows cells making a protein called TH that is characteristic of the neurons that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Yaping Sun, lab of Su Guo, University of California, San Francisco, via CIRM View MediaWound healing in process
3498
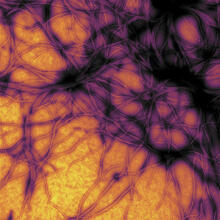
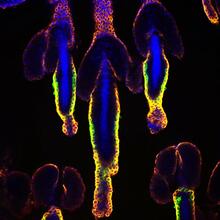
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaRegenerating lizard tail
6968
The interior of a regenerating lizard tail 14 days after the original tail was amputated. Thomas Lozito, University of Southern California. View MediaPrion protein fibrils 1
3460
Recombinant proteins such as the prion protein shown here are often used to model how proteins misfold and sometimes polymerize in neurodegenerative disorders. This prion protein was expressed in E. Ken Pekoc (public affairs officer) and Julie Marquardt, NIAID/ Rocky Mountain Laboratories View Media¿Qué es la sepsis? (Sepsis Infographic)
6551
La sepsis o septicemia es la respuesta fulminante y extrema del cuerpo a una infección. En los Estados Unidos, más de 1.7 millones de personas contraen sepsis cada año. Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas Generales View MediaShiga toxin
6997
E. coli bacteria normally live harmlessly in our intestines, but some cause disease by making toxins. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaSimulation of controlled avian flu outbreak
2573
This video shows a controlled outbreak of transmissible avian flu among people living in Thailand. Neil M. Ferguson, Imperial College London View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 01
2790
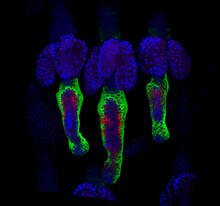
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
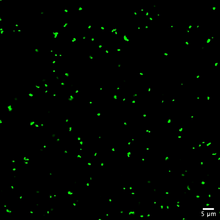
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaProtein clumping in zinc-deficient yeast cells
3550
The green spots in this image are clumps of protein inside yeast cells that are deficient in both zinc and a protein called Tsa1 that prevents clumping. Colin MacDiarmid and David Eide, University of Wisconsin--Madison View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaHIV Infected Cell
3386
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), shown here as tiny purple spheres, causes the disease known as AIDS (for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 03
2796
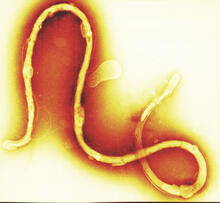
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaRelapsing fever bacterium (gray) and red blood cells
3585
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaTonB protein in gram-negative bacteria
3549
The green in this image highlights a protein called TonB, which is produced by many gram-negative bacteria, including those that cause typhoid fever, meningitis and dysentery. Phillip Klebba, Kansas State University View MediaWound healing in process
3497
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 01
2794
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 04
2793
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaWound healing in process
3500
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaBorrelia burgdorferi
1241
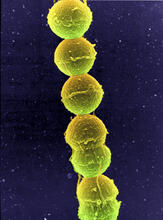
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete, a class of long, slender bacteria that typically take on a coiled shape. Infection with this bacterium causes Lyme disease. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaStreptococcus bacteria
1157
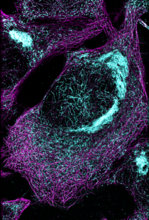
Image of Streptococcus, a type (genus) of spherical bacteria that can colonize the throat and back of the mouth. Stroptococci often occur in pairs or in chains, as shown here. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMicrotubules and tau aggregates
6892
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaLeptospira bacteria
1166
Leptospira, shown here in green, is a type (genus) of elongated, spiral-shaped bacteria. Infection can cause Weil's disease, a kind of jaundice, in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaSepsis Infographic
6536
Sepsis is the body’s overactive and extreme response to an infection. More than 1.7 million people get sepsis each year in the United States. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaHIV enzyme
6999
These images model the molecular structures of three enzymes with critical roles in the life cycle of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaVibrio bacteria
1160
Vibrio, a type (genus) of rod-shaped bacteria. Some Vibrio species cause cholera in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
6803
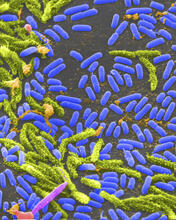
Groups of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) attached to a microstructured titanium surface (green) that mimics an orthopedic implant used in joint replacement. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaMeasles virus proteins
6996
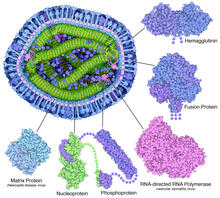
A cross section of the measles virus in which six proteins (enlarged on the outside of the virus) work together to infect cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMycobacterium tuberculosis
2716
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis, has infected one-quarter of the world's population and causes more than one million deaths each year, according to the Reuben Peters, Iowa State University View MediaVirtual snow world
2335
Glide across an icy canyon, where you see smiling snowmen and waddling penguins. Toss a snowball, hear it smash against an igloo, and then watch it explode in bright colors. David Patterson and Hunter Hoffmann, University of Washington View MediaAnthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
3612
Multiple anthrax bacteria (green) being enveloped by an immune system cell (purple). Anthrax bacteria live in soil and form dormant spores that can survive for decades. Camenzind G. Robinson, Sarah Guilman, and Arthur Friedlander, United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 04
2797
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaStaphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
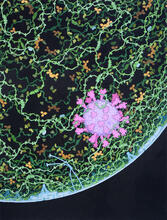
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaHungry, hungry macrophages
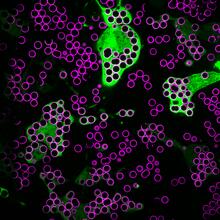
7009
Macrophages (green) are the professional eaters of our immune system. Meghan Morrissey, University of California, Santa Barbara. View MediaSARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
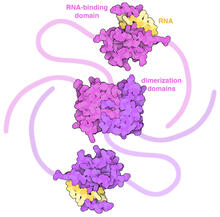
6991
In SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, nucleocapsid is a complex molecule with many functional parts. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHuman blood cells with Borrelia hermsii, a bacterium that causes relapsing fever
3586
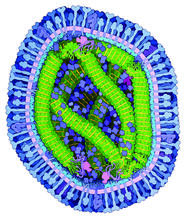
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaZika virus
6998
Zika virus is shown in cross section at center left. On the outside, it includes envelope protein (red) and membrane protein (magenta) embedded in a lipid membrane (light purple). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMeasles virus
6995
A cross section of the measles virus in which six proteins work together to infect cells. The measles virus is extremely infectious; 9 out of 10 people exposed will contract the disease. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaRespiratory droplet
6994
This painting shows a cross section of a small respiratory droplet, like the ones that are thought to transmit SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View Media