Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
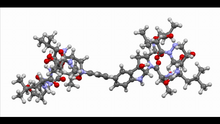
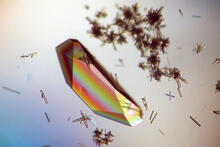
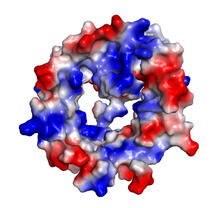
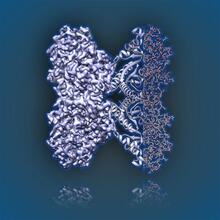
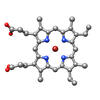
Himastatin, 360-degree view
6851
A 360-degree view of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaShiga toxin
6997
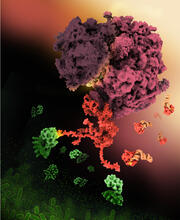
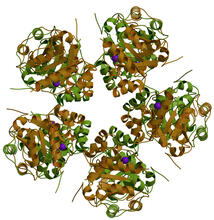
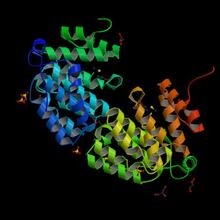
E. coli bacteria normally live harmlessly in our intestines, but some cause disease by making toxins. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaProtein involved in cell division from Mycoplasma pneumoniae
2377
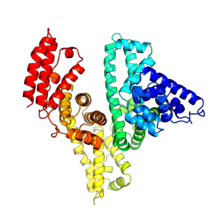
Model of a protein involved in cell division from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. This model, based on X-ray crystallography, revealed a structural domain not seen before. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaBacterial nanowire model
6580
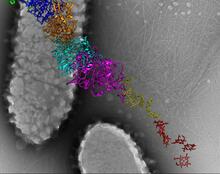
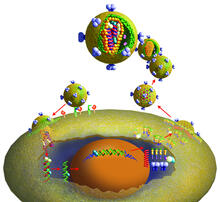
A model of a Geobacter sulfurreducens nanowire created from cryo-electron microscopy images. Edward Egelman, University of Virginia. View MediaHen egg lysozyme (1)
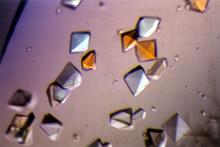
2396
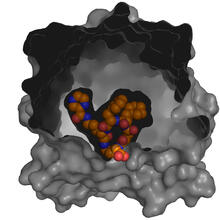
Crystals of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
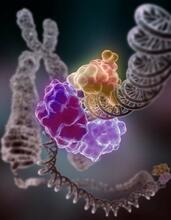
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaKinases (with labels)
2535
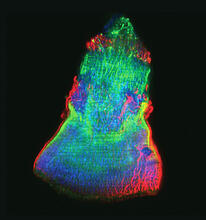
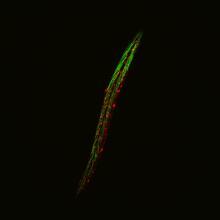
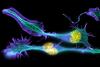
Kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups (red-yellow structures) to proteins (green), assigning the proteins a code. Crabtree + Company View MediaIsolated Planarian Pharynx
3593
The feeding tube, or pharynx, of a planarian worm with cilia shown in red and muscle fibers shown in green View MediaThe Structure of Cilia’s Doublet Microtubules
6549
Cilia (cilium in singular) are complex molecular machines found on many of our cells. Brown Lab, Harvard Medical School and Veronica Falconieri Hays View MediaPig alpha amylase
2412
Crystals of porcine alpha amylase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaSerum albumin structure 1
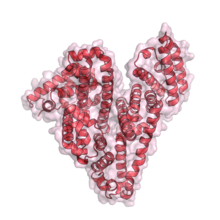
3744
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. Wladek Minor, University of Virginia View MediaA dynamic model of the DNA helicase protein complex
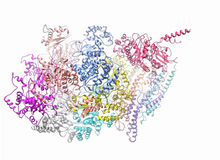
3750
This short video shows a model of the DNA helicase in yeast. This DNA helicase has 11 proteins that work together to unwind DNA during the process of copying it, called DNA replication. Huilin Li, Stony Brook University View MediaCellular aging
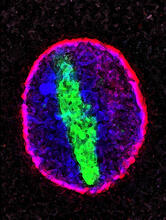
2578
A protein called tubulin (green) accumulates in the center of a nucleus (outlined in pink) from an aging cell. Maximiliano D'Angelo and Martin Hetzer, Salk Institute View MediaSection of an electron density map
2354
Electron density maps such as this one are generated from the diffraction patterns of X-rays passing through protein crystals. The Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaFluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
6581
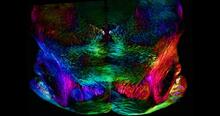
C. elegans, a tiny roundworm, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaMouse brain slice showing nerve cells
6901
A 20-µm thick section of mouse midbrain. The nerve cells are transparent and weren’t stained. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
6356
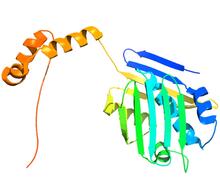
Related to image 6355. Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaVDAC-1 (4)
2495
The structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaRepairing DNA
3493
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine View MediaAldolase
6350
2.5Å resolution reconstruction of rabbit muscle aldolase collected on a FEI/Thermo Fisher Titan Krios with energy filter and image corrector. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaPanB from M. tuberculosis (1)
2380
Model of an enzyme, PanB, from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis. This enzyme is an attractive drug target. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaSerum albumin structure 2
3745
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. Wladek Minor, University of Virginia View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (2)
2404
Crystals of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaLife of an AIDS virus
2513
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaProtein from E. faecalis
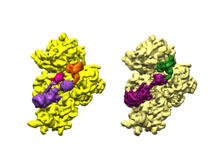
2342
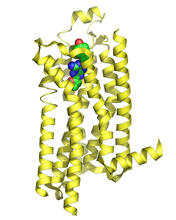
X-ray structure of a DNA repair enzyme superfamily representative from the human gastrointestinal bacterium Enterococcus faecalis. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaA2A adenosine receptor
3361
The receptor is shown bound to an inverse agonist, ZM241385. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaRNA folding in action
6625
An RNA molecule dynamically refolds itself as it is being synthesized. When the RNA is short, it ties itself into a “knot” (dark purple). Julius Lucks, Northwestern University View MediaDNase
2410
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaHsp33 figure 2
3355
Featured in the March 15, 2012 issue of Biomedical Beat. Related to Hsp33 Figure 1, image 3354. Ursula Jakob and Dana Reichmann, University of Michigan View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 04
2454
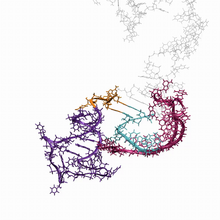
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaMyotonic dystrophy type 2 genetic defect
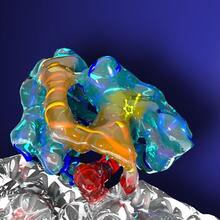
3573
Scientists revealed a detailed image of the genetic defect that causes myotonic dystrophy type 2 and used that information to design drug candidates to counteract the disease. Matthew Disney, Scripps Research Institute and Ilyas Yildirim, Northwestern University View MediaInsulin and protein interact in pancreatic beta cells
3546
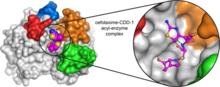
A large number of proteins interact with the hormone insulin as it is produced in and secreted from the beta cells of the pancreas. William E. Balch, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaSpace-filling model of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6767
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaIntracellular forces
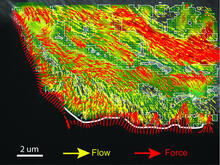
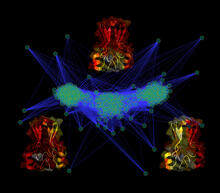
2799
Force vectors computed from actin cytoskeleton flow. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaCytonemes in developing fruit fly cells
3574
Scientists have long known that multicellular organisms use biological molecules produced by one cell and sensed by another to transmit messages that, for instance, guide proper development of organs Sougata Roy, University of California, San Francisco View MediaChang Shan
3483
For thousands of years, Chinese herbalists have treated malaria using Chang Shan, a root extract from a type of hydrangea that grows in Tibet and Nepal. Paul Schimmel Lab, Scripps Research Institute View MediaATP Synthase
6353
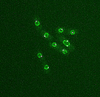
Atomic model of the membrane region of the mitochondrial ATP synthase built into a cryo-EM map at 3.6 Å resolution. ATP synthase is the primary producer of ATP in aerobic cells. Bridget Carragher, <a href="http://nramm.nysbc.org/">NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy</a> View MediaCluster analysis of mysterious protein
3295
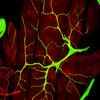
Researchers use cluster analysis to study protein shape and function. Each green circle represents one potential shape of the protein mitoNEET. Patricia Jennings and Elizabeth Baxter, University of California, San Diego View MediaMaster clock of the mouse brain
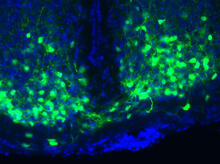
3547
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis View MediaBacterial ribosome assembly
6578
3D reconstructions of two stages in the assembly of the bacterial ribosome created from time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy images. Ribosomes translate genetic instructions into proteins. Joachim Frank, Columbia University. View MediaEarly life of a protein
2740
This illustration represents the early life of a protein—specifically, apomyoglobin—as it is synthesized by a ribosome and emerges from the ribosomal tunnel, which contains the newly formed protein's Silvia Cavagnero, University of Wisconsin, Madison View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaHuman endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex
6777
A 3D model of the human endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) that identifies its nine essential subunits. Rebecca Voorhees, California Institute of Technology. View MediaIon channel
3487
A special "messy" region of a potassium ion channel is important in its function. Yu Zhoi, Christopher Lingle Laboratory, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis View MediaZinc finger
2426
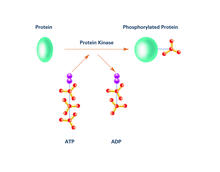
The structure of a gene-regulating zinc finger protein bound to DNA. Jeremy M. Berg, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaProtein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
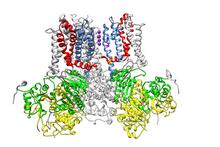
7004
Protein kinases—enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules—are cancer chemotherapy targets because they play significant roles in almost all aspects of cell function, are tightly regulated, and co Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHuman Adenovirus
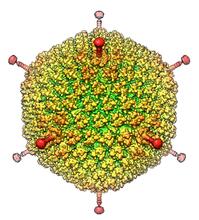
6347
The cryo-EM structure of human adenovirus D26 (HAdV-D26) at near atomic resolution (3.7 Å), determined in collaboration with the NRAMM facility*. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaNuclear Lamina – Three Views
6573
Three views of the entire nuclear lamina of a HeLa cell produced by tilted light sheet 3D single-molecule super-resolution imaging using a platform termed TILT3D. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaBacterial glucose isomerase
2409
A crystal of bacterial glucose isomerase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View Media