Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
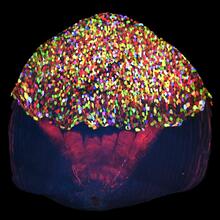
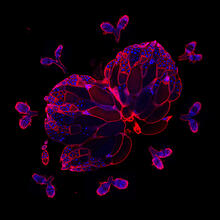
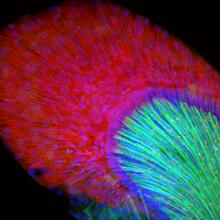
A multicolored fish scale 2
3783
Each of the tiny colored specs in this image is a cell on the surface of a fish scale. Chen-Hui Chen and Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaAlternative splicing
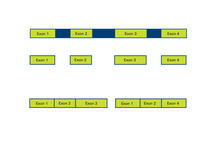
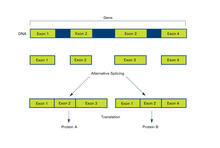
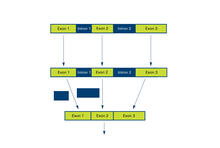
2552
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Crabtree + Company View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
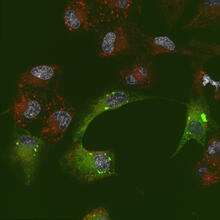
6774
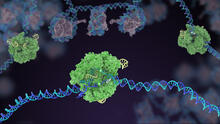
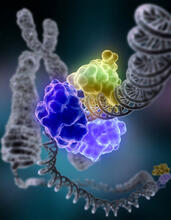
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. After an experimental intervention, they are expressing a nonfunctional version of FIT2, shown in green. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
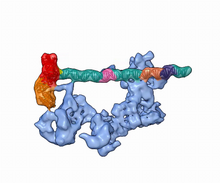
3597
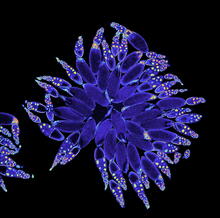
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 3
3792
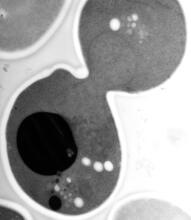
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
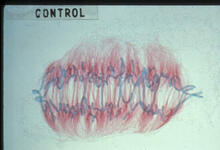
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaChromosomes before crossing over
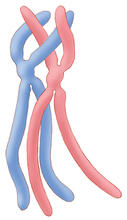
1315
Duplicated pair of chromosomes lined up and ready to cross over. Judith Stoffer View MediaLily mitosis 08
1021
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaSnowflake DNA origami
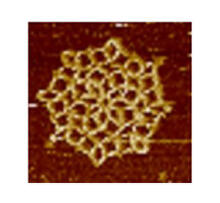
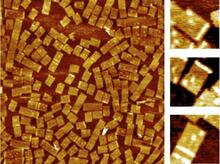
3724
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. The image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Images: A Holiday-Themed Collection. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaDolly the sheep
2690
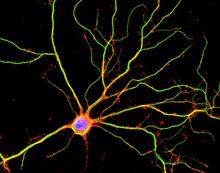
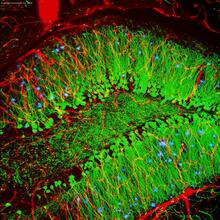
Scientists in Scotland were the first to clone an animal, this sheep named Dolly. She later gave birth to Bonnie, the lamb next to her. View MediaHippocampal neuron in culture
3687
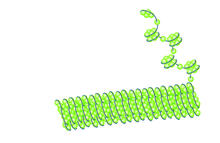
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaHistones in chromatin
2560
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaLife of an AIDS virus
2513
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria - video
3254
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaLily mitosis 13
1019
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaCircadian rhythm (with labels)
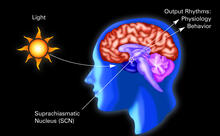
2569
The human body keeps time with a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. Crabtree + Company View MediaProtein formation
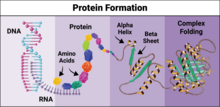
6603
Proteins are 3D structures made up of smaller units. DNA is transcribed to RNA, which in turn is translated into amino acids. NIGMS, with the folded protein illustration adapted from Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaSymmetrically and asymmetrically elongating cells
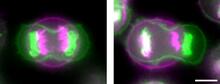
3648
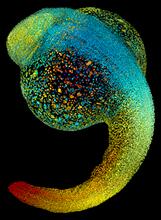
Merged fluorescent images of symmetrically (left) or asymmetrically (right) elongating HeLa cells at the end of early anaphase (magenta) and late anaphase (green). Tomomi Kiyomitsu and Iain M. Cheeseman, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research View MediaZebrafish embryo
3644
Just 22 hours after fertilization, this zebrafish embryo is already taking shape. By 36 hours, all of the major organs will have started to form. Philipp Keller, Bill Lemon, Yinan Wan, and Kristin Branson, Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Va. View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaChromosomes after crossing over
1314
Duplicated pair of chromosomes have exchanged material. Judith Stoffer View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
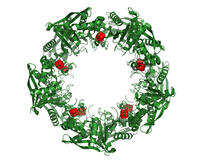
3720
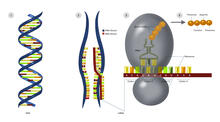
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaGolden gene chips
2455
A team of chemists and physicists used nanotechnology and DNA's ability to self-assemble with matching RNA to create a new kind of chip for measuring gene activity. Hao Yan and Yonggang Ke, Arizona State University View MediaWild-type and mutant fruit fly ovaries
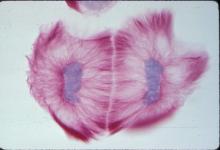
6806
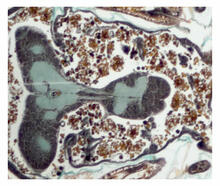
The two large, central, round shapes are ovaries from a typical fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaAlternative splicing (with labels)
2553
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Featured in The New Genetics. Crabtree + Company View MediaDividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
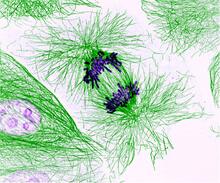
3631
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated
2547
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaIntrons
2550
Genes are often interrupted by stretches of DNA (introns, blue) that do not contain instructions for making a protein. Crabtree + Company View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated (with labels)
2548
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaFruit fly ovary_2
3656
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit--they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaTrypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
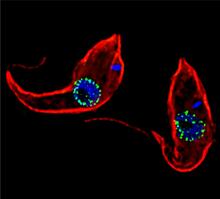
3765
Trypanosoma brucei is a single-cell parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans. Michael Rout, Rockefeller University View MediaBottles of warfarin
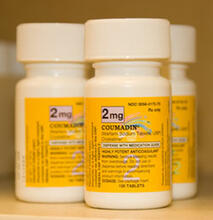
2579
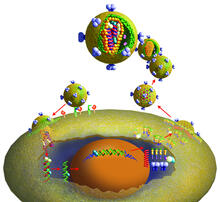
In 2007, the FDA modified warfarin's label to indicate that genetic makeup may affect patient response to the drug. The widely used blood thinner is sold under the brand name Coumadin®. Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH View MediaCRISPR illustration
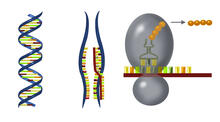
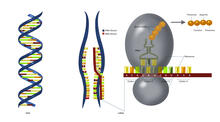
3719
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 2
3732
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
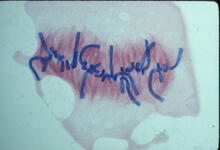
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated (with labels and numbers for stages)
2549
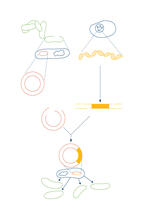
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaRecombinant DNA
2564
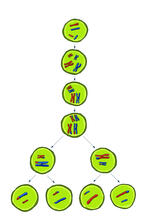
To splice a human gene into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. coli bacterium, cut the plasmid with a restriction enzyme, and splice in human DNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaMeiosis illustration
2545
Meiosis is the process whereby a cell reduces its chromosomes from diploid to haploid in creating eggs or sperm. Crabtree + Company View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaGenetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
2418
This delicate, birdlike projection is an immature seed of the Arabidopsis plant. The part in blue shows the cell that gives rise to the endosperm, the tissue that nourishes the embryo. Robert Fischer, University of California, Berkeley View MediaFruit fly ovary
3607
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaCas9 protein involved in the CRISPR gene-editing technology
5816
In the gene-editing tool CRISPR, a small strand of RNA identifies a specific chunk of DNA. Janet Iwasa View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaRepairing DNA
2330
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine View MediaLily mitosis 09
1022
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View Media