Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
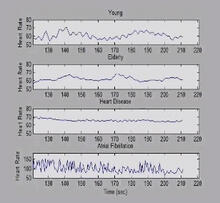
Heart rates time series image
3596
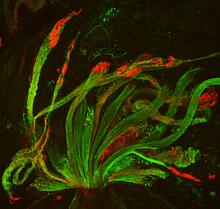
These time series show the heart rates of four different individuals. Madalena Costa and Ary Goldberger, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
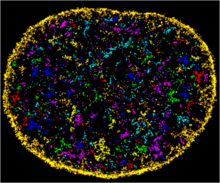
6888
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaHuman Adenovirus
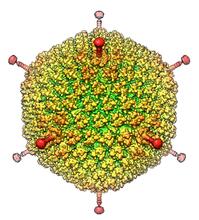
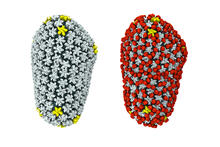
6347
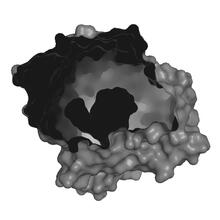
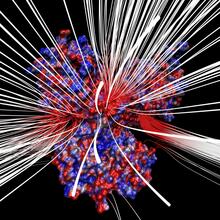
The cryo-EM structure of human adenovirus D26 (HAdV-D26) at near atomic resolution (3.7 Å), determined in collaboration with the NRAMM facility*. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaRat Hippocampus
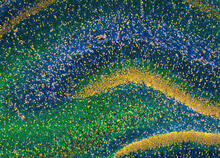
3308
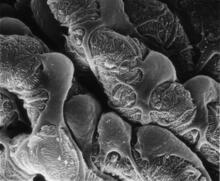
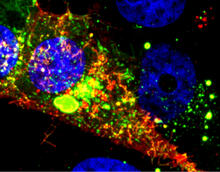
This image of the hippocampus was taken with an ultra-widefield high-speed multiphoton laser microscope. Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells
3286
This color-enhanced image is a scanning electron microscope image of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. David Hinton lab, University of Southern California, via CIRM View MediaMicroscopy image of bird-and-flower DNA origami
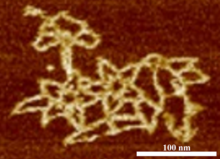
3690
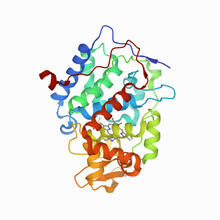
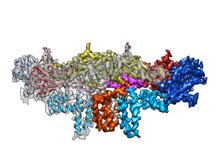
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaRibbon diagram of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
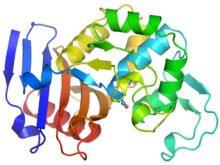
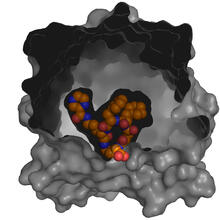
6766
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaCryo-EM reveals how the HIV capsid attaches to a human protein to evade immune detection
3755
The illustration shows the capsid of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) whose molecular features were resolved with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Juan R. Perilla, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
3414
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaPores on the surface of the Hawaiian bobtail squid light organ
7016
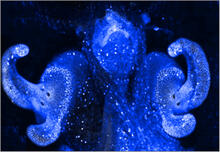
The light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, stained blue. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaMouse brain slice showing nerve cells
6901
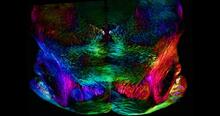
A 20-µm thick section of mouse midbrain. The nerve cells are transparent and weren’t stained. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaBacterial cells aggregating above the light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7018
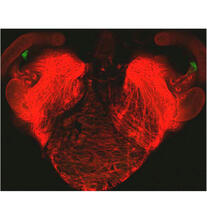
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaMicrofluidic chip
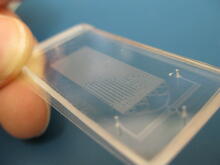
3265
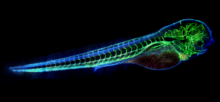
Microfluidic chips have many uses in biology labs. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaX-ray diffraction pattern from a crystallized cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
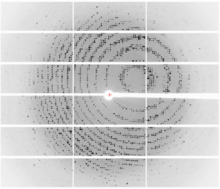
6765
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaBreast cancer cells change migration phenotypes
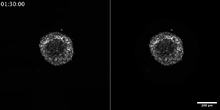
6986
Cancer cells can change their migration phenotype, which includes their shape and the way that they move to invade different tissues. Bo Sun, Oregon State University. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaX-ray crystallography (with labels)
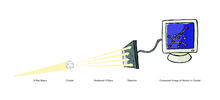
2512
X-ray crystallography allows researchers to see structures too small to be seen by even the most powerful microscopes. Crabtree + Company View MediaJack bean concanavalin A
2407
Crystals of jack bean concanavalin A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCytoscape network wiring diagram 2
2749
This image integrates the thousands of known molecular and genetic interactions happening inside our bodies using a computer program called Cytoscape. Trey Ideker, University of California, San Diego View MediaBacterial cells aggregated above a light-organ pore of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7019
The beating of cilia on the outside of the Hawaiian bobtail squid’s light organ concentrates Vibrio fischeri cells (green) present in the seawater into aggregates near the pore-containing tis Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View Media3D image of actin in a cell
3749
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaCCP enzyme
6762
The enzyme CCP is found in the mitochondria of baker’s yeast. Scientists study the chemical reactions that CCP triggers, which involve a water molecule, iron, and oxygen. Protein Data Bank. View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMapping metabolic activity
2319
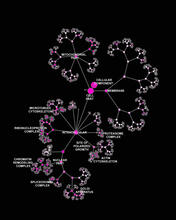
Like a map showing heavily traveled roads, this mathematical model of metabolic activity inside an E. coli cell shows the busiest pathway in white. Albert-László Barabási, University of Notre Dame View MediaNetwork diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (labeled)
3437
This image shows the hierarchical ontology of genes, cellular components and processes derived from large genomic datasets. From Dutkowski et al. Janusz Dutkowski and Trey Ideker, University of California, San Diego View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
6661
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaDengue virus membrane protein structure
3758
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
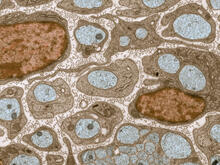
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of myelinated axons with ECM between the axons
3736
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells, as shown here. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaResearch mentor and student
2767
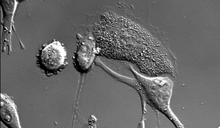
A research mentor (Lori Eidson) and student (Nina Waldron, on the microscope) were 2009 members of the BRAIN (Behavioral Research Advancements In Neuroscience) program at Georgia State University in A Elizabeth Weaver, Georgia State University View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 2
6588
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCluster analysis of mysterious protein
3295
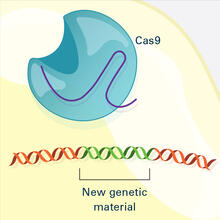
Researchers use cluster analysis to study protein shape and function. Each green circle represents one potential shape of the protein mitoNEET. Patricia Jennings and Elizabeth Baxter, University of California, San Diego View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 4
6488
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaIntroduction to Genome Editing Using CRISPR/Cas9
5815
Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9 is a rapidly expanding field of scientific research with emerging applications in disease treatment, medical therapeutics and bioenergy, just to name a few. Janet Iwasa View MediaPig trypsin (2)
2413
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaCRISPR illustration
3719
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaPodocytes from a chronically diseased kidney
3565
This scanning electron microscope (SEM) image shows podocytes--cells in the kidney that play a vital role in filtering waste from the bloodstream--from a patient with chronic kidney disease. Olga Troyanskaya, Princeton University and Matthias Kretzler, University of Michigan View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
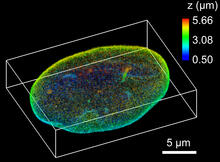
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaNuclear Lamina
6572
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 7
3419
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaBacterial glucose isomerase
2409
A crystal of bacterial glucose isomerase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaHeLa cells
3518
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaFruit fly spermatids
3590
Developing spermatids (precursors of mature sperm cells) begin as small, round cells and mature into long-tailed, tadpole-shaped ones. Lacramioara Fabian, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada View MediaDividing yeast cells with spindle pole bodies and contractile rings
6796
During cell division, spindle pole bodies (glowing dots) move toward the ends of yeast cells to separate copied genetic information. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaElectrostatic map of human spermine synthase
3658
From PDB entry 3c6k, Crystal structure of human spermine synthase in complex with spermidine and 5-methylthioadenosine. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaSuperconducting magnet
1120
Superconducting magnet for NMR research, from the February 2003 profile of Dorothee Kern in Findings. Mike Lovett View MediaRSV-Infected Cell
3567
Viral RNA (red) in an RSV-infected cell. Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University View Media