Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
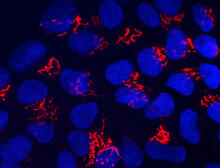
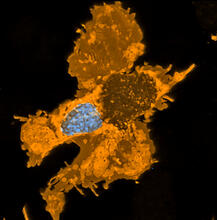
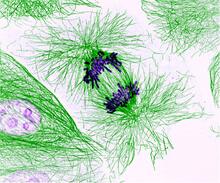
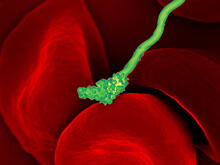
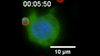
Suicidal Stem Cells
3341
Embryonic stem cells store pre-activated Bax (red) in the Golgi, near the nucleus (blue). Featured in the June 21, 2012, issue of Biomedical Beat. Mohanish Deshmukh View MediaYeast cells with endocytic actin patches
6793
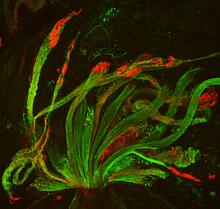
Yeast cells with endocytic actin patches (green). These patches help cells take in outside material. When a cell is in interphase, patches concentrate at its ends. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria - video
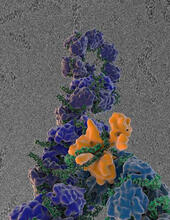
3254
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaYeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
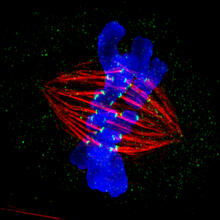
6798
Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes shown in magenta and tubulin shown in light blue. The nuclear envelope defines the borders of the nucleus, which houses DNA. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaZebrafish pigment cell
5754
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaSea urchin embryo 01
1047
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaMolecules blocking Huntington's protein production
2600
The molecules that glow blue in these cultured cells prevent the expression of the mutant proteins that cause Huntington's disease. Jiaxin Hu, David W. Dodd and Robert H. E. Hudson, UT Southwestern Medical Center View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 1
5777
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View MediaBacteria shapes
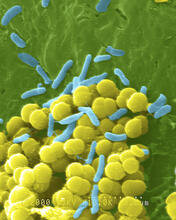
1158
A colorized scanning electron micrograph of bacteria. Scanning electron microscopes allow scientists to see the three-dimensional surface of their samples. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3334
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell_2
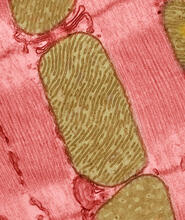
3664
These mitochondria (brown) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaZ rings in bacterial division
2456
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). Masaki Osawa, Duke University View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaHydra 05
2441
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
6661
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaRed blood cells
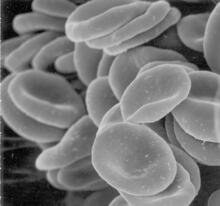
1101
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sa Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaDrugs enter skin (with labels)
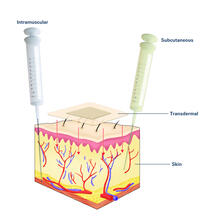
2532
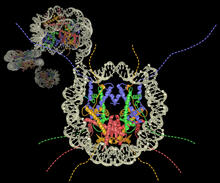
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2531 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaAtomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
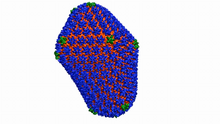
6601
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaTelomerase illustration
1335
Reactivating telomerase in our cells does not appear to be a good way to extend the human lifespan. Cancer cells reactivate telomerase. Judith Stoffer View MediaA multicolored fish scale 1
3782
Each of the colored specs in this image is a cell on the surface of a fish scale. Chen-Hui Chen and Kenneth Poss, Duke University View Media“Two-faced” Janus particle activating a macrophage
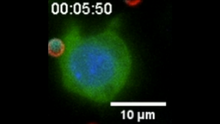
6801
A macrophage—a type of immune cell that engulfs invaders—“eats” and is activated by a “two-faced” Janus particle. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaIsolated Planarian Pharynx
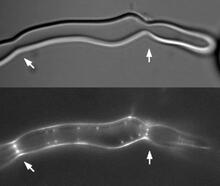
3593
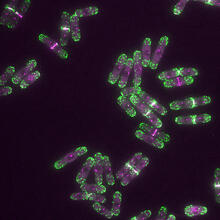
The feeding tube, or pharynx, of a planarian worm with cilia shown in red and muscle fibers shown in green View MediaDividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
3631
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaFlu virus proteins during self-replication
3434
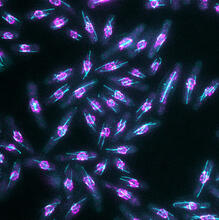
Influenza (flu) virus proteins in the act of self-replication. Viral nucleoprotein (blue) encapsidates [encapsulates] the RNA genome (green). Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, CA View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaHydra 06
2442
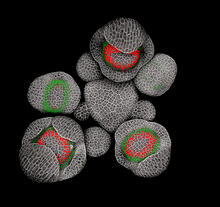
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaDeveloping Arabidopsis flower buds
3743
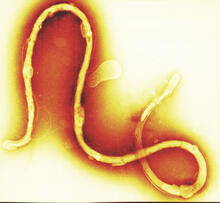
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaBorrelia burgdorferi
1241
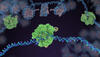
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete, a class of long, slender bacteria that typically take on a coiled shape. Infection with this bacterium causes Lyme disease. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaNucleosome
2741
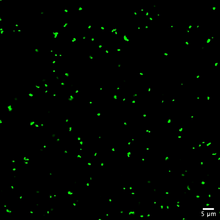
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaFruit fly spermatids
3590
Developing spermatids (precursors of mature sperm cells) begin as small, round cells and mature into long-tailed, tadpole-shaped ones. Lacramioara Fabian, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada View MediaBrain cells in the hippocampus
3688
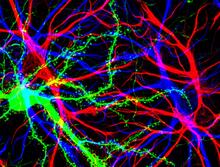
Hippocampal cells in culture with a neuron in green, showing hundreds of the small protrusions known as dendritic spines. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaSnowflake yeast 1
6969
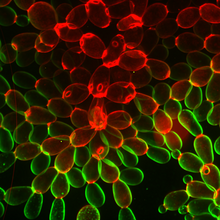
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaZinc levels in a plant leaf
3727
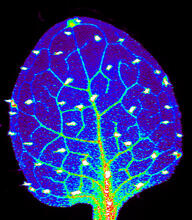
Zinc is required for the function of more than 300 enzymes, including those that help regulate gene expression, in various organisms including humans. Suzana Car, Dartmouth College View MediaBlinking bacteria
2724
Like a pulsing blue shower, E. coli cells flash in synchrony. Genes inserted into each cell turn a fluorescent protein on and off at regular intervals. Jeff Hasty, University of California, San Diego View MediaCellular metropolis
2308
Like a major city, a cell teems with specialized workers that carry out its daily operations--making energy, moving proteins, or helping with other tasks. Kathryn Howell, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared
1333
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaGlowing fish
2667
Professor Marc Zimmer's family pets, including these fish, glow in the dark in response to blue light. Featured in the September 2009 issue of Findings. View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 2
6585
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaRAC1 activation in motile fibroblast
2457
Novel biosensor system maps the timing and location of Rac protein activation in a living mouse embryo fibroblast. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaHuman liver cell (hepatocyte)
3610
Hepatocytes, like the one shown here, are the most abundant type of cell in the human liver. Donna Beer Stolz, University of Pittsburgh View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - video
5843
This video results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
5838
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaNeural tube development
2328
Proteins in the neural tissues of this zebrafish embryo direct cells to line up and form the neural tube, which will become the spinal cord and brain. Alexander Schier, Harvard University View MediaHuman blood cells with Borrelia hermsii, a bacterium that causes relapsing fever
3586
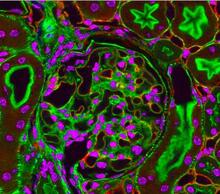
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
3725
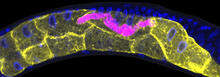
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaTracking cells in a gastrulating zebrafish embryo
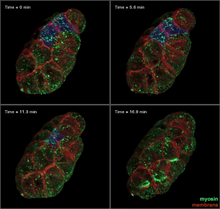
6776
During development, a zebrafish embryo is transformed from a ball of cells into a recognizable body plan by sweeping convergence and extension cell movements. This process is called gastrulation. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View Media