Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
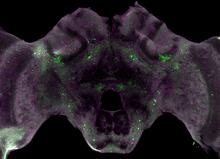
Honeybee brain
6755
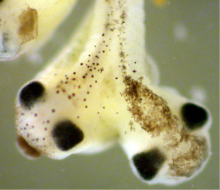
Insect brains, like the honeybee brain shown here, are very different in shape from human brains. Gene Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. View MediaTwo-headed Xenopus laevis tadpole
2755
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a research organism for studying embryonic development. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 5
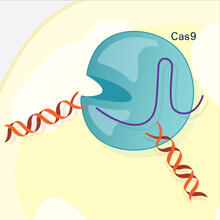
6489
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the fifthframe in a series of five. View MediaRNA strand (with labels)
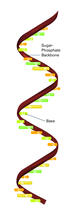
2555
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) has a sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). Featured in The New Genetics. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 06
1016
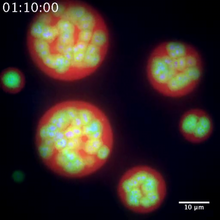
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
3791
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaChromosomes after crossing over
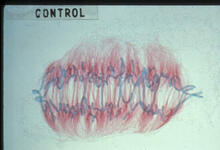
1314
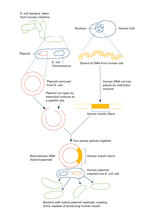
Duplicated pair of chromosomes have exchanged material. Judith Stoffer View MediaRecombinant DNA
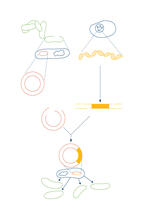
2564
To splice a human gene into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. coli bacterium, cut the plasmid with a restriction enzyme, and splice in human DNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaGenetic patchworks
2588
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University View MediaSponge
2728
Many of today's medicines come from products found in nature, such as this sponge found off the coast of Palau in the Pacific Ocean. Phil Baran, Scripps Research Institute View MediaFrom DNA to Protein
2509
Nucleotides in DNA are copied into RNA, where they are read three at a time to encode the amino acids in a protein. Many parts of a protein fold as the amino acids are strung together. Crabtree + Company View MediaComputer sketch of bird-and-flower DNA origami
3689
A computer-generated sketch of a DNA origami folded into a flower-and-bird structure. See also related image 3690. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaNucleosome
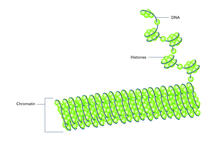
2741
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
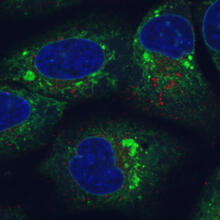
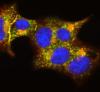
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
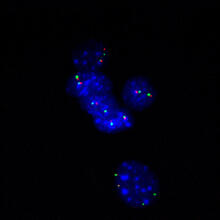
6983
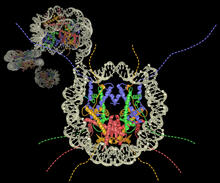
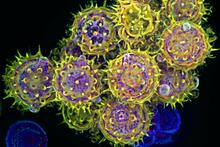
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
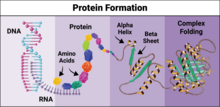
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaProtein formation
6603
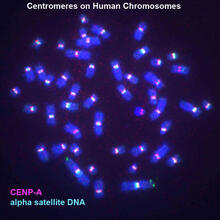
Proteins are 3D structures made up of smaller units. DNA is transcribed to RNA, which in turn is translated into amino acids. NIGMS, with the folded protein illustration adapted from Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaCentromeres on human chromosomes
3255
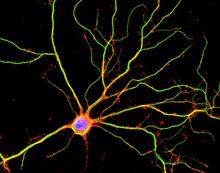
Human metaphase chromosomes are visible with fluorescence in vitro hybridization (FISH). Centromeric alpha satellite DNA (green) are found in the heterochromatin at each centromere. Peter Warburton, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaHippocampal neuron in culture
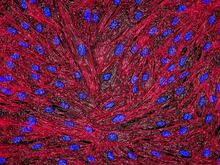
3687
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaLily mitosis 03
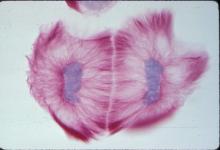
1013
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaHistones in chromatin (with labels)
2561
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaMature, flowering Arabidopsis
2779
This is an adult flowering Arabidopsis thaliana plant with the inbred designation L-er. Arabidopsis is the most widely used model organism for researchers who study plant genetics. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaPainted chromosomes
2764
Like a paint-by-numbers picture, painted probes tint individual human chromosomes by targeting specific DNA sequences. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaPlanarian stem cell colony
3306
Planarians are freshwater flatworms that have powerful abilities to regenerate their bodies, which would seem to make them natural model organisms in which to study stem cells. Peter Reddien, Whitehead Institute View MediaRSV-Infected Cell
3567
Viral RNA (red) in an RSV-infected cell. Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University View MediaDicty fruit
2684
Dictyostelium discoideum is a microscopic amoeba. A group of 100,000 form a mound as big as a grain of sand. Featured in The New Genetics. View MediaRecombinant DNA (with labels)
2565
To splice a human gene (in this case, the one for insulin) into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 13
1019
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaPollen grains: male germ cells in plants and a cause of seasonal allergies
3609
Those of us who get sneezy and itchy-eyed every spring or fall may have pollen grains, like those shown here, to blame. Edna, Gil, and Amit Cukierman, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pa. View MediaDNA and actin in cultured fibroblast cells
3670
DNA (blue) and actin (red) in cultured fibroblast cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaA multicolored fish scale 1
3782
Each of the colored specs in this image is a cell on the surface of a fish scale. Chen-Hui Chen and Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaIntrons (with labels)
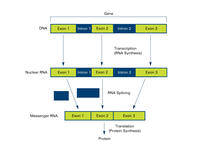
2551
Genes are often interrupted by stretches of DNA (introns, blue) that do not contain instructions for making a protein. Crabtree + Company View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
3443
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 3
6487
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (White Background)
6534
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
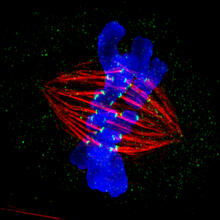
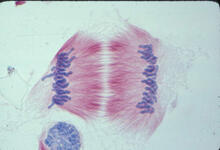
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaFly by night
2417
This fruit fly expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the same pattern as the period gene, a gene that regulates circadian rhythm and is expressed in all sensory neurons on the surface of the fl Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 01
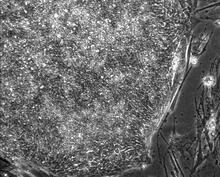
2603
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaAlternative splicing (with labels)
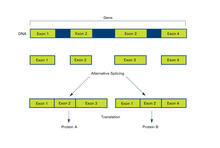
2553
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Featured in The New Genetics. Crabtree + Company View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 2
3732
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaChromosome fiber 01
2475
This microscopic image shows a chromatin fiber--a DNA molecule bound to naturally occurring proteins. Marc Green and Susan Forsburg, University of Southern California View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 1
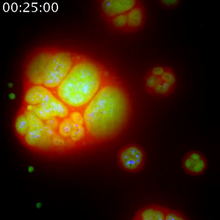
5751
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaGlowing bacteria make a pretty postcard
3492
This tropical scene, reminiscent of a postcard from Key West, is actually a petri dish containing an artistic arrangement of genetically engineered bacteria. Nathan C. Shaner, The Scintillon Institute View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaLily mitosis 09
1022
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaLily mitosis 11
1011
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaLos ritmos circadianos y el núcleo supraquiasmático
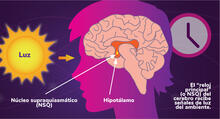
6614
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y de comportamiento que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaDisease-resistant Arabidopsis leaf
2781
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf a few days after being exposed to the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View Media