Image Gallery: Early development in Arabidopsis
ID
2733
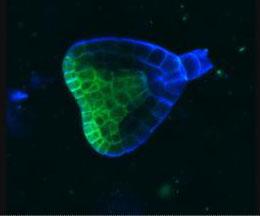
Early on, this Arabidopsis plant embryo picks sides: While one end will form the shoot, the other will take root underground. Short pieces of RNA in the bottom half (blue) make sure that shoot-forming genes are expressed only in the embryo's top half (green), eventually allowing a seedling to emerge with stems and leaves. Like animals, plants follow a carefully orchestrated polarization plan and errors can lead to major developmental defects, such as shoots above and below ground. Because the complex gene networks that coordinate this development in plants and animals share important similarities, studying polarity in Arabidopsis--a model organism--could also help us better understand human development.
Source
Zachery R. Smith, Jeff Long lab at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies
Topics