Image Gallery: Influenza virus attaches to host membrane
ID
2425
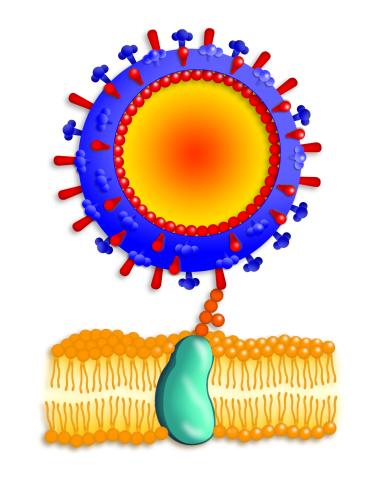
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Neuraminidase, an enzyme that chews sugars, helps newly made virus particles detach so they can infect other cells. Related to 213. Featured in the March 2006, issue of Findings in "Viral Voyages."
Source
Crabtree + Company
Topics