Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
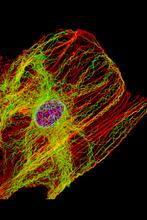
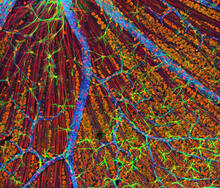
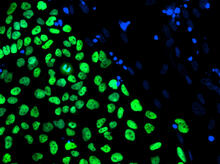
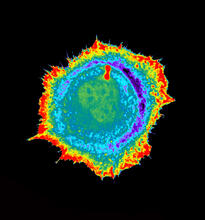
Cells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
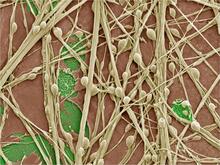
3617
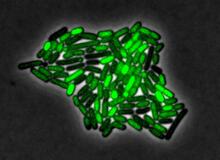
This image shows a normal fibroblast, a type of cell that is common in connective tissue and frequently studied in research labs. James J. Faust and David G. Capco, Arizona State University View MediaAnglerfish ovary cross-section
3620
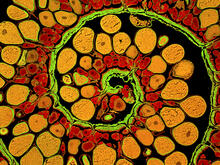
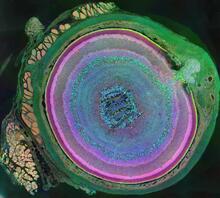
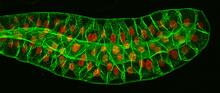
This image captures the spiral-shaped ovary of an anglerfish in cross-section. Once matured, these eggs will be released in a gelatinous, floating mass. James E. Hayden, The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, Pa. View MediaFruit fly nurse cells transporting their contents during egg development
6754
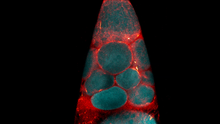
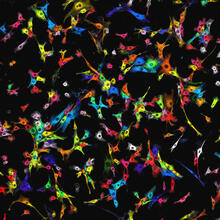
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
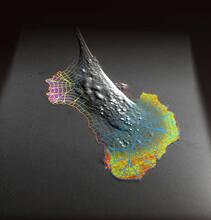
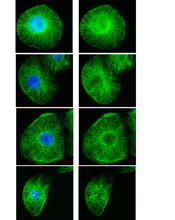
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
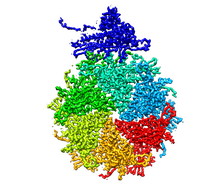
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaYeast art depicting the New York City skyline
6521
This skyline of New York City was created by “printing” nanodroplets containing yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) onto a large plate. Each dot is a separate yeast colony. Michael Shen, Ph.D., Jasmine Temple, Leslie Mitchell, Ph.D., and Jef Boeke, Ph.D., New York University School of Medicine; and Nick Phillips, James Chuang, Ph.D., and Jiarui Wang, Johns Hopkins University. View MediaFluorescent E. coli bacteria
3268
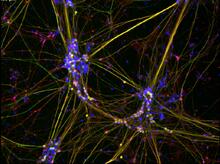
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. They called each blinking bacterial colony a biopixel. Thousands of fluorescent E. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaSynapses in culture
3399
Cultured hippocampal neurons grown on a substrate of glial cells (astrocytes). The glial cells form the pink/brown underlayment in this image. The tan threads are the neurons. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaBorrelia burgdorferi
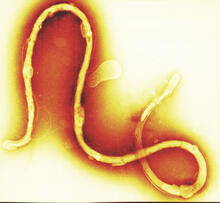
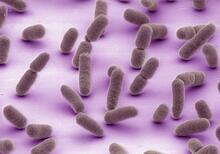
1241
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete, a class of long, slender bacteria that typically take on a coiled shape. Infection with this bacterium causes Lyme disease. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaQuartered torso
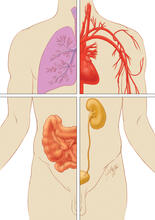
1280
Cells function within organs and tissues, such as the lungs, heart, intestines, and kidney. Judith Stoffer View MediaTongue 1
5810
Microscopy image of tongue. One in a series of two, see image 5811 National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse retina close-up
5872
Keunyoung ("Christine") Kim National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMotion in the brain
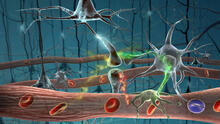
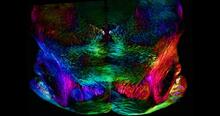
2323
Amid a network of blood vessels and star-shaped support cells, neurons in the brain signal each other. The mists of color show the flow of important molecules like glucose and oxygen. Kim Hager and Neal Prakash, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaVesicular shuttle model
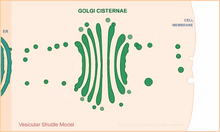
1306
Animation for the vesicular shuttle model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaNCMIR mouse tail
3395
Stained cross section of a mouse tail. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMicrotubules in hippocampal neurons
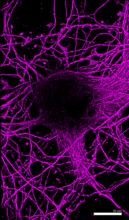
6890
Microtubules (magenta) in neurons of the hippocampus, a part of the brain involved in learning and memory. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide structural support to cells. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaMouse brain slice showing nerve cells
6901
A 20-µm thick section of mouse midbrain. The nerve cells are transparent and weren’t stained. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaLily mitosis 07
1017
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaFly cells
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaMouse Retina
3309
A genetic disorder of the nervous system, neurofibromatosis causes tumors to form on nerves throughout the body, including a type of tumor called an optic nerve glioma that can result in childhood bli Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaA mammalian eye has approximately 70 different cell types
3641
The incredible complexity of a mammalian eye (in this case from a mouse) is captured here. Each color represents a different type of cell. Bryan William Jones and Robert E. Marc, University of Utah View MediaSingle-cell “radios” image
7021
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaNeutrophil-like cells migrating in a microfluidic chip
6886
Neutrophil-like cells (blue) in a microfluidic chip preferentially migrating toward LTB4 over fMLP. Caroline Jones, University of Texas at Dallas. View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
3443
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria
3253
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaCryo-ET cell cross-section visualizing insulin vesicles
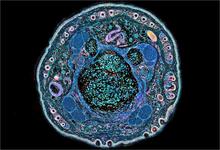
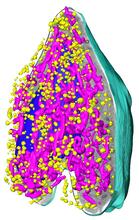
6607
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a color-coded, 3D version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaNCMIR Intestine-2
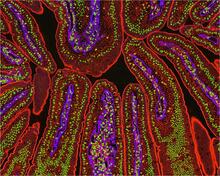
3390
The small intestine is where most of our nutrients from the food we eat are absorbed into the bloodstream. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaProteins related to myotonic dystrophy
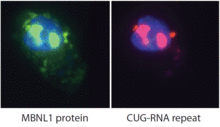
2727
Myotonic dystrophy is thought to be caused by the binding of a protein called Mbnl1 to abnormal RNA repeats. Manuel Ares, University of California, Santa Cruz View MediaHeLa cell undergoing division into two daughter cells
6520
Here, a human HeLa cell (a type of immortal cell line used in laboratory experiments) is undergoing cell division. Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaDynamin structure
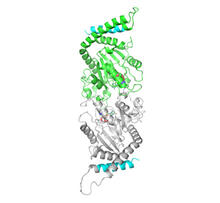
2744
When a molecule arrives at a cell's outer membrane, the membrane creates a pouch around the molecule that protrudes inward. Josh Chappie, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
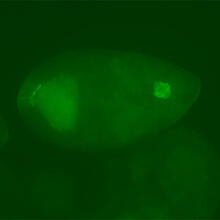
3275
The nuclei stained green highlight human embryonic stem cells grown under controlled conditions in a laboratory. Blue represents the DNA of surrounding, supportive feeder cells. Julie Baker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaPeripheral nerve cells derived from ES cells
3263
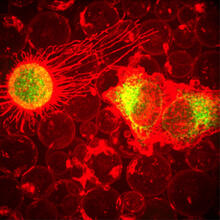
Peripheral nerve cells made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaPlasma-Derived Membrane Vesicles
5887
This fiery image doesn’t come from inside a bubbling volcano. Instead, it shows animal cells caught in the act of making bubbles, or blebbing. Jeanne Stachowiak, University of Texas at Austin View MediaInfluenza virus attaches to host membrane (with labels)
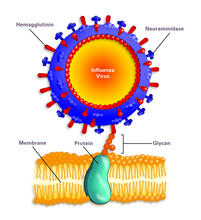
2505
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View MediaMitosis - metaphase
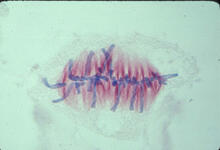
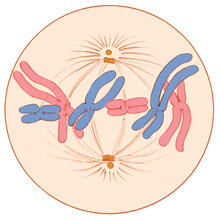
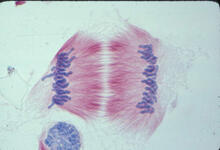
1329
A cell in metaphase during mitosis: The copied chromosomes align in the middle of the spindle. Judith Stoffer View MediaHuman skeletal muscle
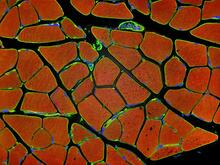
3677
Cross section of human skeletal muscle. Image taken with a confocal fluorescent light microscope. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaActin flow
2798
Speckle microscopy analysis of actin cytoskeleton force. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaSoft X-ray tomography of a pancreatic beta cell
6605
A color-coded, 3D model of a rat pancreatic β cell. This type of cell produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco. View MediaSalivary gland in the developing fruit fly
3603
For fruit flies, the salivary gland is used to secrete materials for making the pupal case, the protective enclosure in which a larva transforms into an adult fly. Richard Fehon, University of Chicago View MediaLily mitosis 11
1011
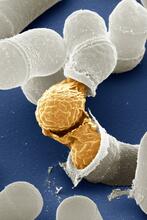
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaBirth of a yeast cell
3614
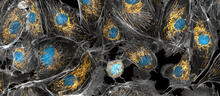
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany View MediaPanorama view of golden mitochondria
5762
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cells, generating the energy the cells need to do their tasks and to stay alive. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaHydra 02
2438
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaHuman fibroblast undergoing cell division
6519
During cell division, cells physically divide after separating their genetic material to create two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Nilay Taneja, Vanderbilt University, and Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
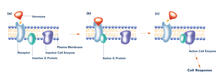
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaEarly life of a protein
2740
This illustration represents the early life of a protein—specifically, apomyoglobin—as it is synthesized by a ribosome and emerges from the ribosomal tunnel, which contains the newly formed protein's Silvia Cavagnero, University of Wisconsin, Madison View MediaDrosophila
6344
Two adult fruit flies (Drosophila) Dr. Vicki Losick, MDI Biological Laboratory, www.mdibl.org View MediaHydra 04
2440
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View Media