Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
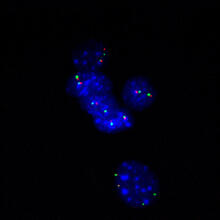
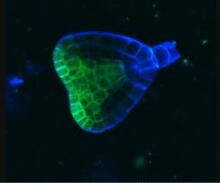
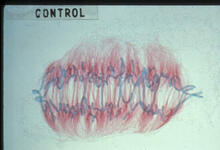
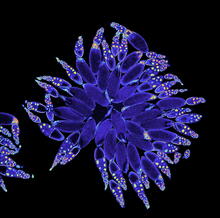
Telomeres on outer edge of nucleus during cell division
3484
New research shows telomeres moving to the outer edge of the nucleus after cell division, suggesting these caps that protect chromosomes also may play a role in organizing DNA. Laure Crabbe, Jamie Kasuboski and James Fitzpatrick, Salk Institute for Biological Studies View MediaLily mitosis 12
1018
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaMeiosis illustration
2545
Meiosis is the process whereby a cell reduces its chromosomes from diploid to haploid in creating eggs or sperm. Crabtree + Company View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaChromosome inside nucleus (with labels)
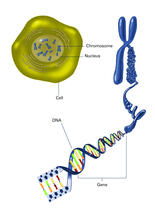
2540
The long, stringy DNA that makes up genes is spooled within chromosomes inside the nucleus of a cell. Crabtree + Company View MediaDinosaur evolutionary tree
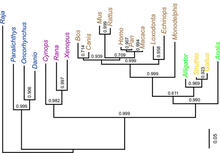
2474
Analysis of 68 million-year-old collagen molecule fragments preserved in a T. Chris Organ, Harvard University View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
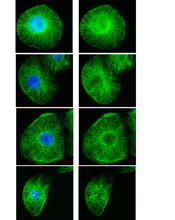
3443
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria
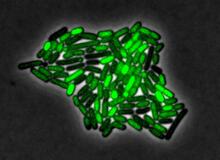
3253
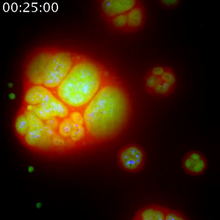
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6771
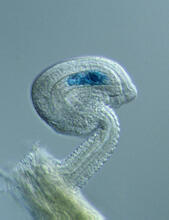
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR swimming in water. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaEarly development in Arabidopsis
2733
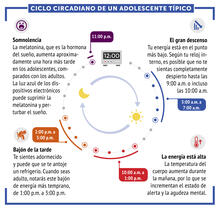
Early on, this Arabidopsis plant embryo picks sides: While one end will form the shoot, the other will take root underground. Zachery R. Smith, Jeff Long lab at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies View MediaCiclo circadiano de un adolescente típico
6612
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y conductuales que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaCircadian rhythm (with labels)
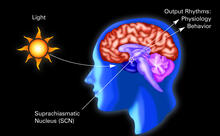
2569
The human body keeps time with a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. Crabtree + Company View MediaHoneybee brain
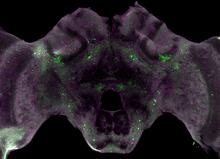
6755
Insect brains, like the honeybee brain shown here, are very different in shape from human brains. Gene Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. View MediaDisease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
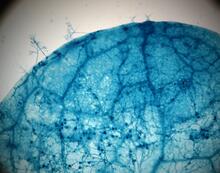
2782
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaRSV-Infected Cell
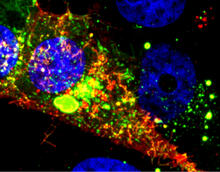
3567
Viral RNA (red) in an RSV-infected cell. Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University View MediaFrom DNA to Protein
2509
Nucleotides in DNA are copied into RNA, where they are read three at a time to encode the amino acids in a protein. Many parts of a protein fold as the amino acids are strung together. Crabtree + Company View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaDicer generates microRNAs
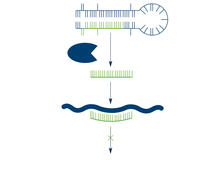
2556
The enzyme Dicer generates microRNAs by chopping larger RNA molecules into tiny Velcro®-like pieces. MicroRNAs stick to mRNA molecules and prevent the mRNAs from being made into proteins. Crabtree + Company View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 2
3732
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaTelomeres
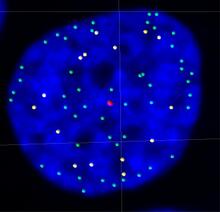
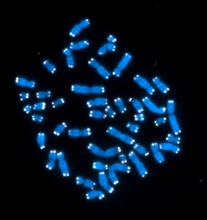
2626
The 46 human chromosomes are shown in blue, with the telomeres appearing as white pinpoints. Hesed Padilla-Nash and Thomas Ried, the National Cancer Institute, a part of NIH View MediaHistones in chromatin
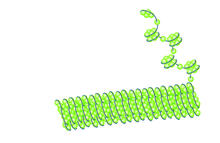
2560
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaZebrafish larva
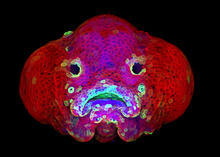
5881
You are face to face with a 6-day-old zebrafish larva. What look like eyes will become nostrils, and the bulges on either side will become eyes. Oscar Ruiz and George Eisenhoffer, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston View MediaHistones in chromatin (with labels)
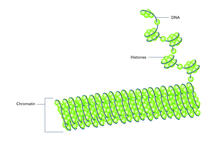
2561
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 09
1022
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaGenetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
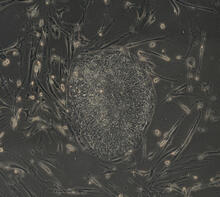
2418
This delicate, birdlike projection is an immature seed of the Arabidopsis plant. The part in blue shows the cell that gives rise to the endosperm, the tissue that nourishes the embryo. Robert Fischer, University of California, Berkeley View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 1
3730
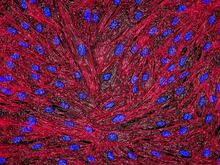
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaDNA and actin in cultured fibroblast cells
3670
DNA (blue) and actin (red) in cultured fibroblast cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 1
5751
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
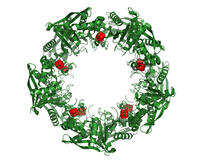
3720
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 3
3792
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaHighlighted cells
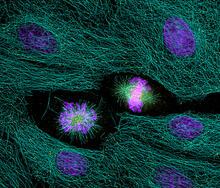
2429
The cytoskeleton (green) and DNA (purple) are highlighed in these cells by immunofluorescence. Torsten Wittmann, Scripps Research Institute View MediaDolly the sheep
2690
Scientists in Scotland were the first to clone an animal, this sheep named Dolly. She later gave birth to Bonnie, the lamb next to her. View MediaLily mitosis 13
1019
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
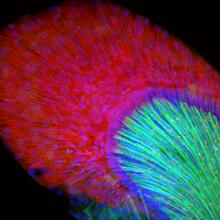
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaFruit fly ovary
3607
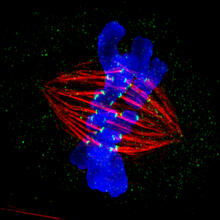
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
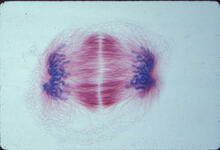
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaCRISPR illustration
3719
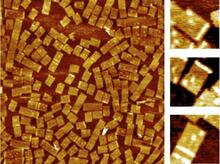
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaGolden gene chips
2455
A team of chemists and physicists used nanotechnology and DNA's ability to self-assemble with matching RNA to create a new kind of chip for measuring gene activity. Hao Yan and Yonggang Ke, Arizona State University View MediaChromosomes after crossing over
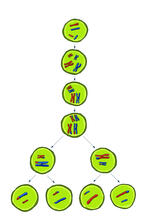
1314
Duplicated pair of chromosomes have exchanged material. Judith Stoffer View MediaFly by night
2417
This fruit fly expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the same pattern as the period gene, a gene that regulates circadian rhythm and is expressed in all sensory neurons on the surface of the fl Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia View MediaSponge
2728
Many of today's medicines come from products found in nature, such as this sponge found off the coast of Palau in the Pacific Ocean. Phil Baran, Scripps Research Institute View MediaZinc finger
2426
The structure of a gene-regulating zinc finger protein bound to DNA. Jeremy M. Berg, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaHost infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. View MediaNucleotides make up DNA
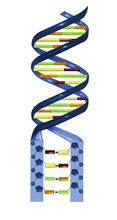
2541
DNA consists of two long, twisted chains made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains one base, one phosphate molecule, and the sugar molecule deoxyribose. Crabtree + Company View MediaAutomated Worm Sorter - 4
3475
Georgia Tech associate professor Hang Lu holds a microfluidic chip that is part of a system that uses artificial intelligence and cutting-edge image processing to automatically examine large number of Georgia Tech/Gary Meek View MediaRNA interference (with labels)
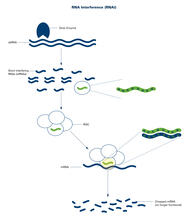
2559
RNA interference or RNAi is a gene-silencing process in which double-stranded RNAs trigger the destruction of specific RNAs. Crabtree + Company View MediaRNA strand (with labels)
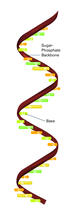
2555
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) has a sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). Featured in The New Genetics. Crabtree + Company View Media