Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
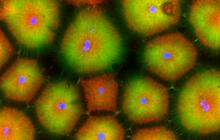
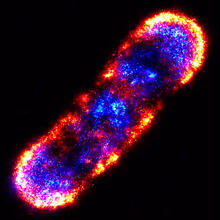
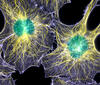
Crab larva eye
1251
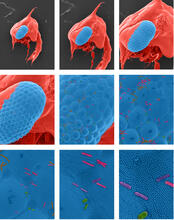
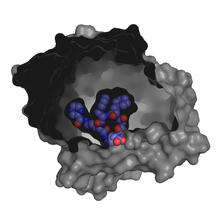
Colorized scanning electron micrographs progressively zoom in on the eye of a crab larva. In the higher-resolution frames, bacteria are visible on the eye. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaSpace-filling model of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
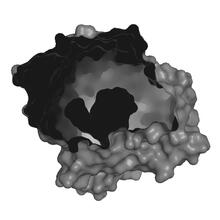
6767
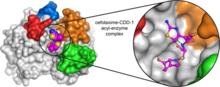
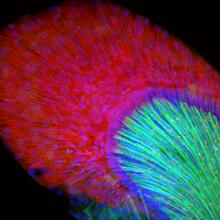
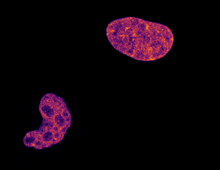
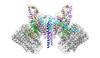
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
6774
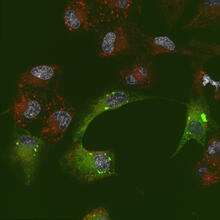
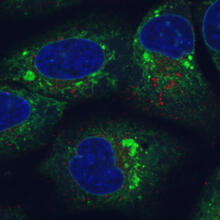
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. After an experimental intervention, they are expressing a nonfunctional version of FIT2, shown in green. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaEpithelial cell migration
6899
High-resolution time lapse of epithelial (skin) cell migration and wound healing. It shows an image taken every 13 seconds over the course of almost 14 minutes. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
6902
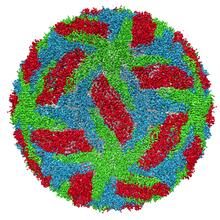
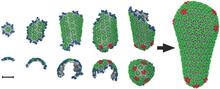
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
5874
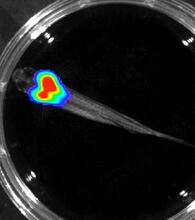
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
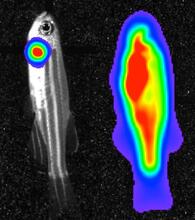
3557
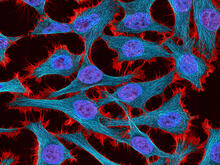
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaHeLa cells
3521
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCytonemes in developing fruit fly cells
3574
Scientists have long known that multicellular organisms use biological molecules produced by one cell and sensed by another to transmit messages that, for instance, guide proper development of organs Sougata Roy, University of California, San Francisco View MediaProtective membrane and membrane proteins of the dengue virus visualized with cryo-EM
3756
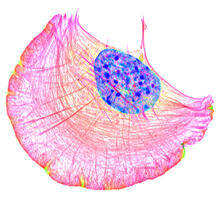
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
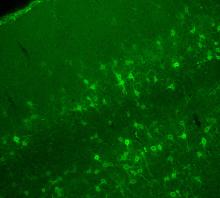
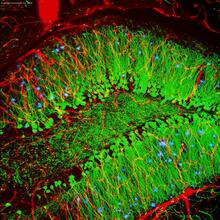
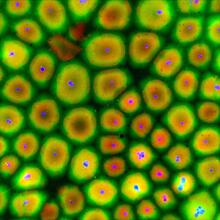
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 2
3742
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaPig trypsin crystal
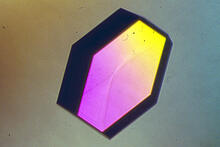
2403
A crystal of pig trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaThermotoga maritima and its metabolic network
2702
A combination of protein structures determined experimentally and computationally shows us the complete metabolic network of a heat-loving bacterium. View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 1
5855
Superresolution microscopy work on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the peripheral areas of the cell showing details of the structure and arrangement in a complex web of tubes. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaDNase
2410
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaMounting of protein crystals
2368
Automated methods using micromachined silicon are used at the Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics to mount protein crystals for X-ray crystallography. The Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaHawaiian bobtail squid
7011
An adult Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, swimming next to a submerged hand. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaC. elegans trapped by carnivorous fungus
6963
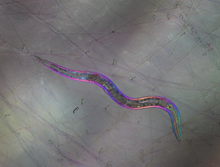
Real-time footage of Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm, trapped by a carnivorous fungus, Arthrobotrys dactyloides. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
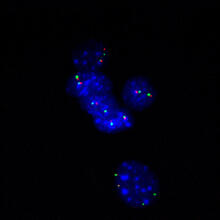
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaRelapsing fever bacterium (gray) and red blood cells
3585
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaResearch mentor and student
2767
A research mentor (Lori Eidson) and student (Nina Waldron, on the microscope) were 2009 members of the BRAIN (Behavioral Research Advancements In Neuroscience) program at Georgia State University in A Elizabeth Weaver, Georgia State University View MediaCrawling cell
6964
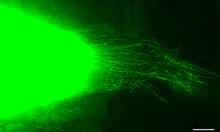
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaColorful communication
2313
The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi glows when near its kind. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaMapping brain differences
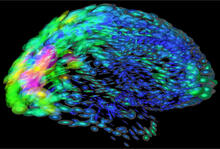
2419
This image of the human brain uses colors and shapes to show neurological differences between two people. Arthur Toga, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaCell division and cell death
6790
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaYeast cells with endocytic actin patches
6793
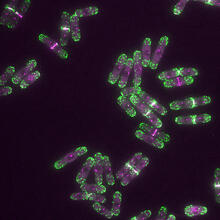
Yeast cells with endocytic actin patches (green). These patches help cells take in outside material. When a cell is in interphase, patches concentrate at its ends. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaBovine trypsin
2408
A crystal of bovine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaIntroduction to Genome Editing Using CRISPR/Cas9
5815
Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9 is a rapidly expanding field of scientific research with emerging applications in disease treatment, medical therapeutics and bioenergy, just to name a few. Janet Iwasa View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586
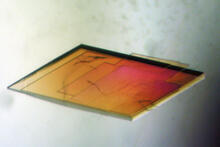
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMicrofluidic chip
3265
Microfluidic chips have many uses in biology labs. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaSelf-organizing proteins
2771
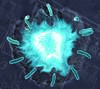
Under the microscope, an E. coli cell lights up like a fireball. Each bright dot marks a surface protein that tells the bacteria to move toward or away from nearby food and toxins. View MediaAntibiotic-surviving bacteria
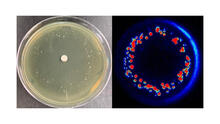
6802
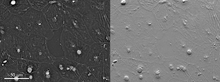
Colonies of bacteria growing despite high concentrations of antibiotics. These colonies are visible both by eye, as seen on the left, and by bioluminescence imaging, as seen on the right. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaAssembly of the HIV capsid
5729
The HIV capsid is a pear-shaped structure that is made of proteins the virus needs to mature and become infective. John Grime and Gregory Voth, The University of Chicago View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
3414
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
2406
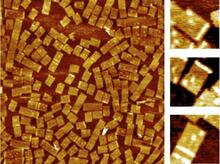
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaGolden gene chips
2455
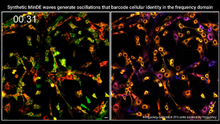
A team of chemists and physicists used nanotechnology and DNA's ability to self-assemble with matching RNA to create a new kind of chip for measuring gene activity. Hao Yan and Yonggang Ke, Arizona State University View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaSuperconducting magnet
1120
Superconducting magnet for NMR research, from the February 2003 profile of Dorothee Kern in Findings. Mike Lovett View MediaC. elegans showing internal structures
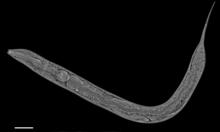
6961
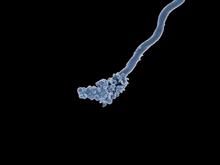
An image of Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm, showing internal structures including the intestine, pharynx, and body wall muscle. C. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs
6584
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMath from the heart
3592
Watch a cell ripple toward a beam of light that turns on a movement-related protein. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 3
3415
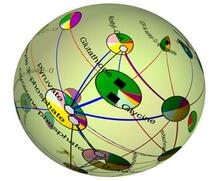
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaStatistical cartography
2331
Like a world of its own, this sphere represents all the known chemical reactions in the E. coli bacterium. Luis A. Nunes Amaral, Northwestern University View Media