Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
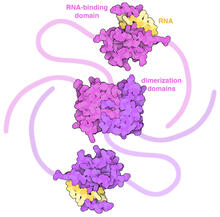
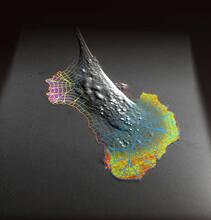
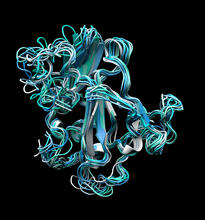
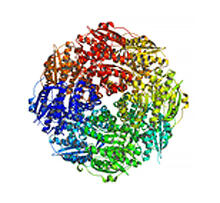
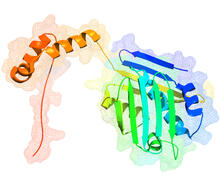
SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
6991
In SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, nucleocapsid is a complex molecule with many functional parts. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
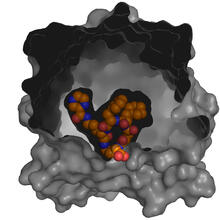
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaAtomic Structure of Poppy Enzyme
3422
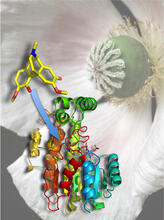
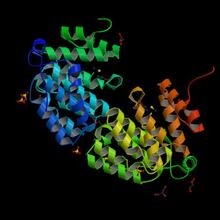
The atomic structure of the morphine biosynthetic enzyme salutaridine reductase bound to the cofactor NADPH. The substrate salutaridine is shown entering the active site. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (2)
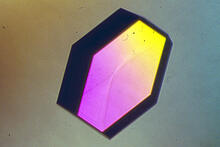
2404
Crystals of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaActive Site of E. coli response regulator PhoB
3412
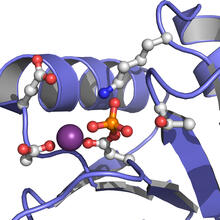
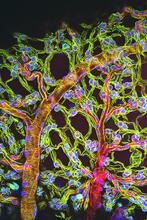
Active site of E. coli response regulator PhoB. Ann Stock, Rutgers University View MediaWeblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University. View MediaProtein from E. faecalis
2342
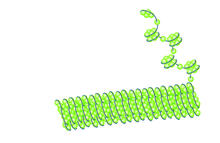
X-ray structure of a DNA repair enzyme superfamily representative from the human gastrointestinal bacterium Enterococcus faecalis. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaHistones in chromatin
2560
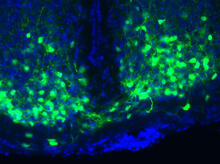
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaMaster clock of the mouse brain
3547
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
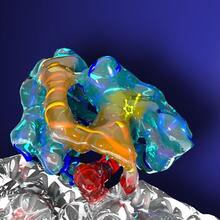
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaHimastatin and bacteria
6850
A model of the molecule himastatin overlaid on an image of Bacillus subtilis bacteria. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaDrosophila (fruit fly) myosin 1D motility assay
6562
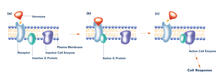
Actin gliding powered by myosin 1D. Note the counterclockwise motion of the gliding actin filaments. Serapion Pyrpassopoulos and E. Michael Ostap, University of Pennsylvania View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaStructure of amyloid-forming prion protein
3542
This structure from an amyloid-forming prion protein shows one way beta sheets can stack. Douglas Fowler, University of Washington View MediaClathrin-mediated endocytosis
5753
Endocytosis is the process by which cells are able to take up membrane and extracellular materials through the formation of a small intracellular bubble, called a vesicle. Janet Iwasa, University of Utah View MediaPlant resistosome
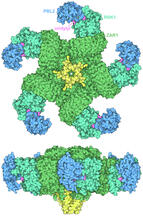
7002
The research organism Arabidopsis thaliana forms a large molecular machine called a resistosome to fight off infections. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaStructure of a key antigen protein involved with Hepatitis C Virus infection
5866
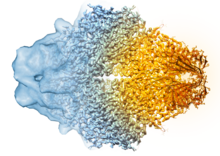
A three-dimensional representation of the structure of E2, a key antigen protein involved with hepatitis C virus infection. Mansun Law Associate Professor Department of Immunolgy and Microbial Science The Scripps Research Institute View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
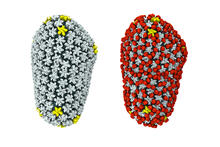
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
2406
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaRNA polymerase
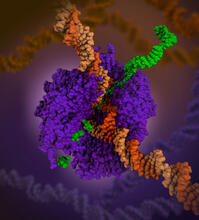
6993
RNA polymerase (purple) is a complex enzyme at the heart of transcription. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaVDAC video 01
2570
This video shows the structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
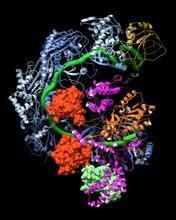
3597
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaSleep and the fly brain
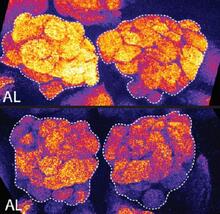
2596
In the top snapshots, the brain of a sleep-deprived fruit fly glows orange, marking high concentrations of a synaptic protein called Bruchpilot (BRP) involved in communication between neurons. Chiara Cirelli, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaStructure of telomerase
3459
Scientists recently discovered the full molecular structure of telomerase, an enzyme important to aging and cancer. Jiansen Jiang, Edward J. Miracco, Z. Hong Zhou and Juli Feigon, University of California, Los Angeles; Kathleen Collins, University of California, Berkeley View MediaCatalase diversity
7003
Catalases are some of the most efficient enzymes found in cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMandelate racemase from B. subtilis
2350
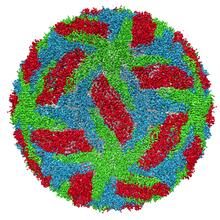
Model of the mandelate racemase enzyme from Bacillus subtilis, a bacterium commonly found in soil. New York Structural GenomiX Research Consortium, PSI View MediaRotavirus structure
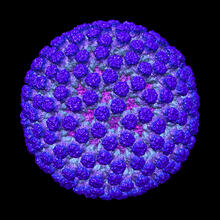
3584
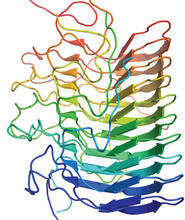
This image shows a computer-generated, three-dimensional map of the rotavirus structure. This virus infects humans and other animals and causes severe diarrhea in infants and young children. Bridget Carragher, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaEarly ribbon drawing of a protein
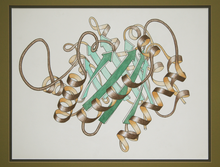
2748
This ribbon drawing of a protein hand drawn and colored by researcher Jane Richardson in 1981 helped originate the ribbon representation of proteins that is now ubiquitous in molecular graphics. Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaIntracellular forces
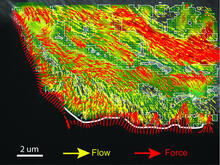
2799
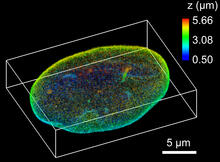
Force vectors computed from actin cytoskeleton flow. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaNuclear Lamina
6572
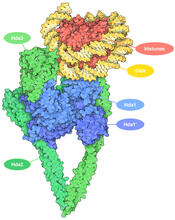
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaHistone deacetylases
7001
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaDiversity oriented synthesis: generating skeletal diversity using folding processes
3327
This 1 1/2-minute video animation was produced for chemical biologist Stuart Schreiber's lab page. The animation shows how diverse chemical structures can be produced in the lab. Eric Keller View MediaProtective membrane and membrane proteins of the dengue virus visualized with cryo-EM
3756
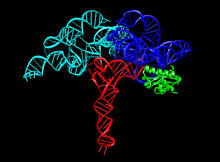
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaRibonuclease P structure
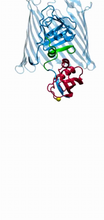
3660
Ribbon diagram showing the structure of Ribonuclease P with tRNA. PDB entry 3Q1Q, molecular modeling by Fred Friedman, NIGMS View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
6902
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaHsp33 figure 1
3354
Featured in the March 15, 2012 issue of Biomedical Beat. Related to Hsp33 Figure 2, image 3355. Ursula Jakob and Dana Reichmann, University of Michigan View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaWreath-shaped protein from X. campestris
2372
Crystal structure of a protein with unknown function from Xanthomonas campestris, a plant pathogen. Eight copies of the protein crystallized to form a ring. Ken Schwinn and Sonia Espejon-Reynes, New York SGX Research Center for Structural Genomics View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaProtein crystals
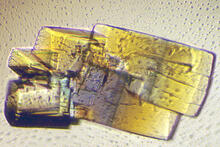
1060
Structural biologists create crystals of proteins, shown here, as a first step in a process called X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCryo-EM reveals how the HIV capsid attaches to a human protein to evade immune detection
3755
The illustration shows the capsid of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) whose molecular features were resolved with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Juan R. Perilla, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaDynamin Fission
3448
Time lapse series shows short dynamin assemblies (not visible) constricting a lipid tube to make a "beads on a string" appearance, then cutting off one of the beads i.e., catalyzing membrane fission). Ramachandran, Pucadyil et al. , The Scripps Research Institute View MediaKluyveromyces polysporus Argonaute bound to guide RNA
3408
A segment of siRNA, shown in red, guides a "slicer" protein called Argonaute (multi-colored twists and corkscrews) to the target RNA molecules. Kotaro Nakanishi and David Weinberg, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
2784
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaHsp33 Heat Shock Protein Inactive to Active
3402
When the heat shock protein hsp33 is folded, it is inactive and contains a zinc ion, stabilizing the redox sensitive domain (orange). Dana Reichmann, University of Michigan View MediaRNase A (2)
2402
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaBrains of sleep-deprived and well-rested fruit flies
3490
On top, the brain of a sleep-deprived fly glows orange because of Bruchpilot, a communication protein between brain cells. These bright orange brain areas are associated with learning. Chiara Cirelli, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaStructure of Glutamate Dehydrogenase
3421
Some children are born with a mutation in a regulatory site on this enzyme that causes them to over-secrete insulin when they consume protein. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaBacteria working to eat
2304
Gram-negative bacteria perform molecular acrobatics just to eat. Because they're encased by two membranes, they must haul nutrients across both. Emad Tajkhorshid, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View Media