Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
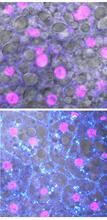
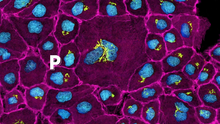
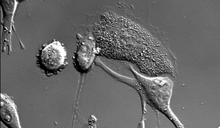
Fruit fly starvation leads to adipokine accumulation
6984
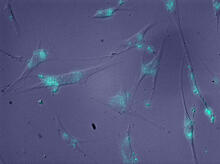
Adult Drosophila abdominal fat tissue showing cell nuclei labelled in magenta. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
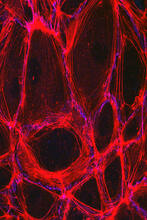
3739
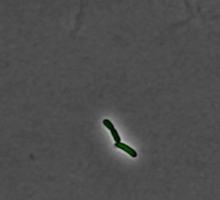
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria - video
3254
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaMitosis - interphase
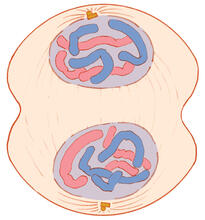
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaTrigonium diatom
6962
A Trigonium diatom imaged by a quantitative orientation-independent differential interference contrast (OI-DIC) microscope. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaMouse brain slice showing nerve cells
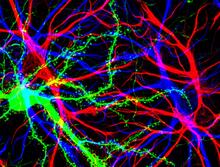
6901
A 20-µm thick section of mouse midbrain. The nerve cells are transparent and weren’t stained. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
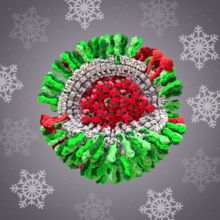
6355
CellPack image of the H1N1 influenza virus, with hemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins in green and red, respectively, on the outer envelope (white); matrix protein in gray, and ribonucleoprot Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaStress Response in Cells
6570
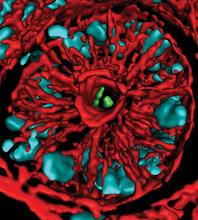
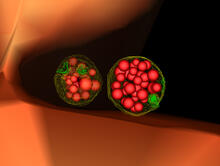
Two highly stressed osteosarcoma cells are shown with a set of green droplet-like structures followed by a second set of magenta droplets. Julia F. Riley and Carlos A. Castañeda, Syracuse University View MediaSoft X-ray tomography of a pancreatic beta cell
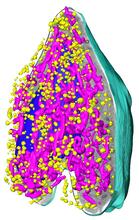
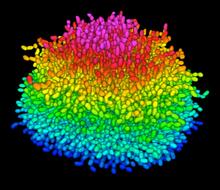
6605
A color-coded, 3D model of a rat pancreatic β cell. This type of cell produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco. View MediaMolecules blocking Huntington's protein production
2600
The molecules that glow blue in these cultured cells prevent the expression of the mutant proteins that cause Huntington's disease. Jiaxin Hu, David W. Dodd and Robert H. E. Hudson, UT Southwestern Medical Center View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
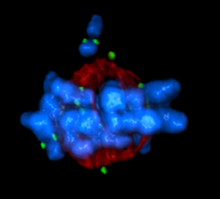
6352
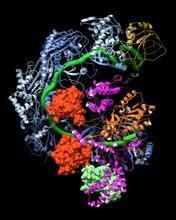
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaHydra 01
2437
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaMouse colon with gut bacteria
3566
A section of mouse colon with gut bacteria (center, in green) residing within a protective pocket. Sarkis K. Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology View MediaTelomeres on outer edge of nucleus during cell division
3484
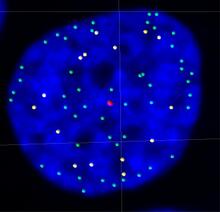
New research shows telomeres moving to the outer edge of the nucleus after cell division, suggesting these caps that protect chromosomes also may play a role in organizing DNA. Laure Crabbe, Jamie Kasuboski and James Fitzpatrick, Salk Institute for Biological Studies View MediaGenetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
2418
This delicate, birdlike projection is an immature seed of the Arabidopsis plant. The part in blue shows the cell that gives rise to the endosperm, the tissue that nourishes the embryo. Robert Fischer, University of California, Berkeley View MediaCryo-electron microscopy of the dengue virus showing protective membrane and membrane proteins
3748
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaRed blood cells
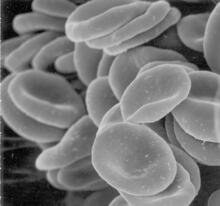
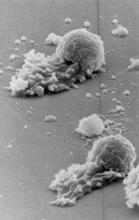
1101
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sa Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View MediaPathways: The Fascinating Cells of Research Organisms
6538
Learn how research organisms, such as fruit flies and mice, can help us understand and treat human diseases. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaMitosis - telophase
1332
Telophase during mitosis: Nuclear membranes form around each of the two sets of chromosomes, the chromosomes begin to spread out, and the spindle begins to break down. Judith Stoffer View MediaNerve and glial cells in fruit fly embryo
1091
Glial cells (stained green) in a fruit fly developing embryo have survived thanks to a signaling pathway initiated by neighboring nerve cells (stained red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
6902
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaBacillus anthracis being killed
3481
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. John Alumasa, Keiler Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University View MediaMovements of myosin
2324
Inside the fertilized egg cell of a fruit fly, we see a type of myosin (related to the protein that helps muscles contract) made to glow by attaching a fluorescent protein. Victoria Foe, University of Washington View MediaFruit fly embryo
2431
Cells in an early-stage fruit fly embryo, showing the DIAP1 protein (pink), an inhibitor of apoptosis. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaCalcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
3449
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaIon channels
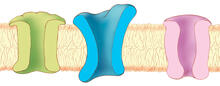
1284
The body uses a variety of ion channels to transport small molecules across cell membranes. Judith Stoffer View MediaGrowing hair follicle stem cells
3499
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaActin flow
2798
Speckle microscopy analysis of actin cytoskeleton force. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaZebrafish embryo
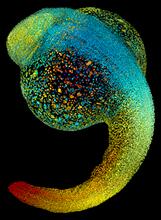
3644
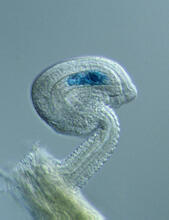
Just 22 hours after fertilization, this zebrafish embryo is already taking shape. By 36 hours, all of the major organs will have started to form. Philipp Keller, Bill Lemon, Yinan Wan, and Kristin Branson, Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Va. View MediaWorm sperm
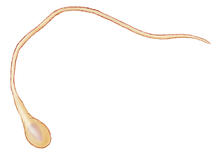
3489
To develop a system for studying cell motility in unnatrual conditions -- a microscope slide instead of the body -- Tom Roberts and Katsuya Shimabukuro at Florida State University disassembled and rec Tom Roberts, Florida State University View MediaMouse mammary cells lacking anti-cancer protein
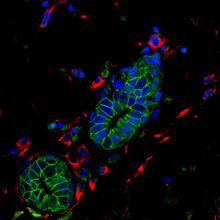
3432
Shortly after a pregnant woman gives birth, her breasts start to secrete milk. This process is triggered by hormonal and genetic cues, including the protein Elf5. Nature Cell Biology, November 2012, Volume 14 No 11 pp1113-1231 View MediaMitotic cell awaits chromosome alignment
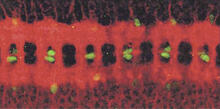
5765
During mitosis, spindle microtubules (red) attach to chromosome pairs (blue), directing them to the spindle equator. View MediaProteasome
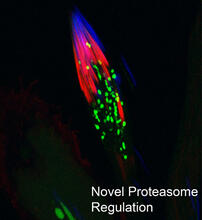
3451
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaThree muscle fibers; the middle has a defect found in some neuromuscular diseases
3630
Of the three muscle fibers shown here, the one on the right and the one on the left are normal. The middle fiber is deficient a large protein called nebulin (blue). Christopher Pappas and Carol Gregorio, University of Arizona View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--gradient background
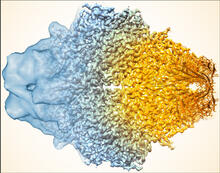
5883
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaGolgi theories
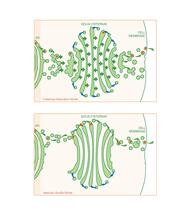
1278
Two models for how material passes through the Golgi apparatus: the vesicular shuttle model and the cisternae maturation model. Judith Stoffer View MediaMouse retina close-up
5872
Keunyoung ("Christine") Kim National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
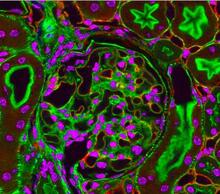
3725
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
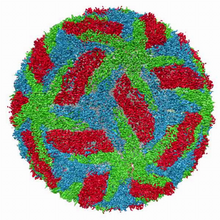
5874
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaA Growing Bacterial Biofilm
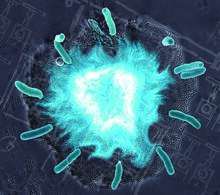
5825
A growing Vibrio cholerae (cholera) biofilm. Cholera bacteria form colonies called biofilms that enable them to resist antibiotic therapy within the body and other challenges to their growth. Jing Yan, Ph.D., and Bonnie Bassler, Ph.D., Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ. View MediaTiny strands of tubulin, a protein in a cell's skeleton
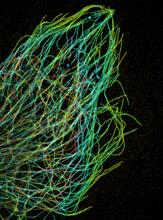
3611
Just as our bodies rely on bones for structural support, our cells rely on a cellular skeleton. Pakorn Kanchanawong, National University of Singapore and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health; and Clare Waterman, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaSupernova bacteria
2725
Bacteria engineered to act as genetic clocks flash in synchrony. Here, a "supernova" burst in a colony of coupled genetic clocks just after reaching critical cell density. Jeff Hasty, UCSD View MediaBrain cells in the hippocampus
3688
Hippocampal cells in culture with a neuron in green, showing hundreds of the small protrusions known as dendritic spines. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaCells lining the blood vessel walls
3633
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School. View MediaTracking cells in a gastrulating zebrafish embryo
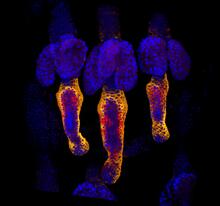
6776
During development, a zebrafish embryo is transformed from a ball of cells into a recognizable body plan by sweeping convergence and extension cell movements. This process is called gastrulation. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 3
5767
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View Media