Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
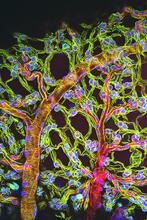
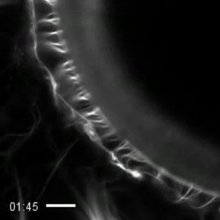
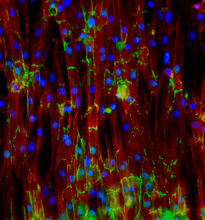
Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University. View MediaMitosis - prophase
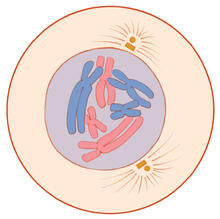
1330
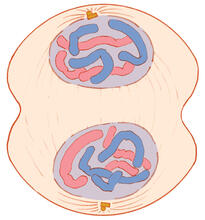
A cell in prophase, near the start of mitosis: In the nucleus, chromosomes condense and become visible. In the cytoplasm, the spindle forms. Judith Stoffer View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
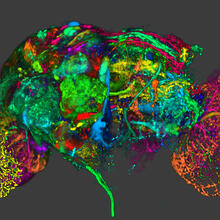
5838
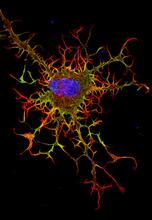
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaDeveloping nerve cells
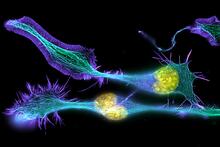
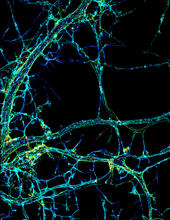
3632
These developing mouse nerve cells have a nucleus (yellow) surrounded by a cell body, with long extensions called axons and thin branching structures called dendrites. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaLysosomes
1282
Lysosomes have powerful enzymes and acids to digest and recycle cell materials. Judith Stoffer View MediaBacteria in the mouse colon
3527
Image of the colon of a mouse mono-colonized with Bacteroides fragilis (red) residing within the crypt channel. The red staining is due to an antibody to B. Sarkis K. Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology View MediaNerve and glial cells in fruit fly embryo
1091
Glial cells (stained green) in a fruit fly developing embryo have survived thanks to a signaling pathway initiated by neighboring nerve cells (stained red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaHow cilia do the wave
3494
Thin, hair-like biological structures called cilia are tiny but mighty. Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University View MediaMovements of myosin
2324
Inside the fertilized egg cell of a fruit fly, we see a type of myosin (related to the protein that helps muscles contract) made to glow by attaching a fluorescent protein. Victoria Foe, University of Washington View MediaMitosis - telophase
1332
Telophase during mitosis: Nuclear membranes form around each of the two sets of chromosomes, the chromosomes begin to spread out, and the spindle begins to break down. Judith Stoffer View MediaFly cells
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaTransmission electron microscopy showing cross-section of the node of Ranvier
3740
Nodes of Ranvier are short gaps in the myelin sheath surrounding myelinated nerve cells (axons). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View MediaRed blood cells
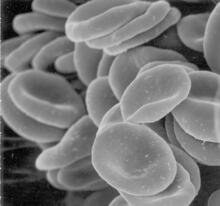
1101
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sa Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMouse cerebellum close-up
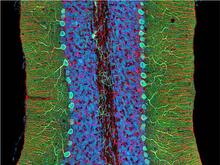
3371
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCryo-ET cross-section of the Golgi apparatus
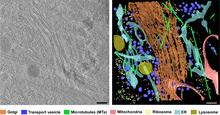
6606
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a 3D, color-coded version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
3678
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaMouse retina
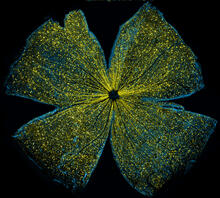
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaSea urchin embryo 03
1049
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaSnowflake yeast 3
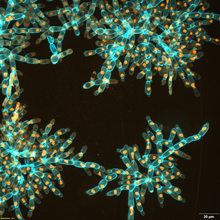
6971
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaVesicle traffic
1283
This illustration shows vesicle traffic inside a cell. Judith Stoffer View Media3D reconstruction of a tubular matrix in peripheral endoplasmic reticulum
5857
Detailed three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular matrix in a thin section of the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum between the plasma membranes of the cell. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaCerebellum: the brain's locomotion control center
3639
The cerebellum of a mouse is shown here in cross-section. The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Thomas Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, University of California, San Diego View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaCell curvature
2803
Rendering of the surface of an endothelial cell; membrane curvature is color coded. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria - video
3254
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
3738
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCisternae maturation model
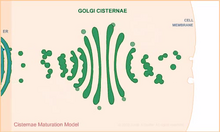
1307
Animation for the cisternae maturation model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaTiny strands of tubulin, a protein in a cell's skeleton
3611
Just as our bodies rely on bones for structural support, our cells rely on a cellular skeleton. Pakorn Kanchanawong, National University of Singapore and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health; and Clare Waterman, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaIntasome
6346
Salk researchers captured the structure of a protein complex called an intasome (center) that lets viruses similar to HIV establish permanent infection in their hosts. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaTracking embryonic zebrafish cells
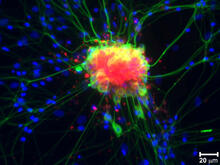
6775
To better understand cell movements in developing embryos, researchers isolated cells from early zebrafish embryos and grew them as clusters. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaMouse heart muscle cells
3282
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaWorms and human infertility
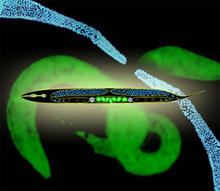
2333
This montage of tiny, transparent C. elegans--or roundworms--may offer insight into understanding human infertility. Abby Dernburg, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 3
6589
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Video created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaYeast cells with endocytic actin patches
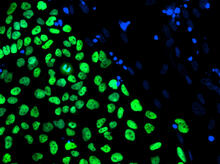
6793
Yeast cells with endocytic actin patches (green). These patches help cells take in outside material. When a cell is in interphase, patches concentrate at its ends. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
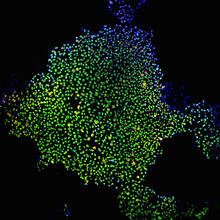
3275
The nuclei stained green highlight human embryonic stem cells grown under controlled conditions in a laboratory. Blue represents the DNA of surrounding, supportive feeder cells. Julie Baker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 02
2604
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaNCMIR kidney-1
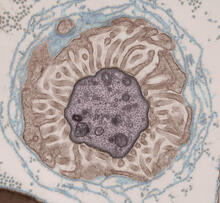
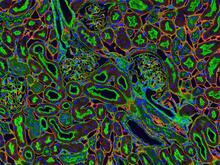
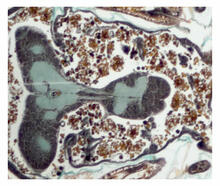
3675
Stained kidney tissue. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
3739
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaSpinal nerve cells
3251
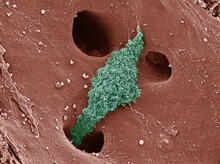
Neurons (green) and glial cells from isolated dorsal root ganglia express COX-2 (red) after exposure to an inflammatory stimulus (cell nuclei are blue). Lawrence Marnett, Vanderbilt University View MediaAbnormal, spiky fibroblast
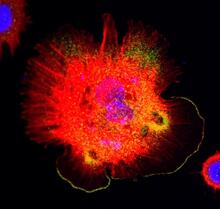
3613
This is a fibroblast, a connective tissue cell that plays an important role in wound healing. Normal fibroblasts have smooth edges. Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, Mo. View MediaPlasma membrane (with labels)
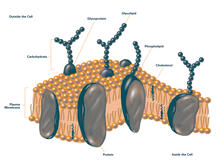
2524
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2523 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaKupffer cell residing in the liver
6535
Kupffer cells appear in the liver during the early stages of mammalian development and stay put throughout life to protect liver cells, clean up old red blood cells, and regulate iron levels. Thomas Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, University of California, San Diego. View MediaSmall blood vessels in a mouse retina
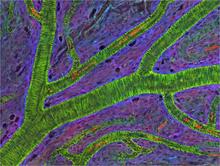
3400
Blood vessels at the back of the eye (retina) are used to diagnose glaucoma and diabetic eye disease. They also display characteristic changes in people with high blood pressure. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaMigrating pigment cells
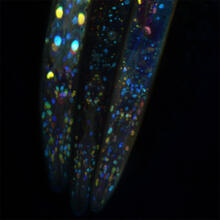
5758
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaSpreading Cells 01
3328
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
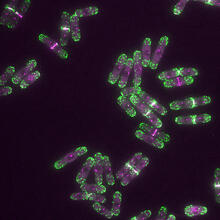
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View Media