This page is historical material reflecting the Feedback Loop Blog as it existed on
July 19, 2010. This page is no longer updated and links to external websites
and some internal pages may not work.
July 19, 2010
Archived: More on Criterion Scores
In an earlier post, I presented an analysis of the relationship between the average significance criterion scores provided independently by individual reviewers and the overall impact scores determined at the end of the study section discussion for a sample of 360 NIGMS R01 grant applications reviewed during the October 2009 Council round. Based on the interest in this analysis reflected here and on other blogs, including DrugMonkey and Medical Writing, Editing & Grantsmanship, I want to provide some additional aspects of this analysis.
As I noted in the recent post, the criterion score most strongly correlated (0.74) with the overall impact score is approach. Here is a plot showing this correlation:
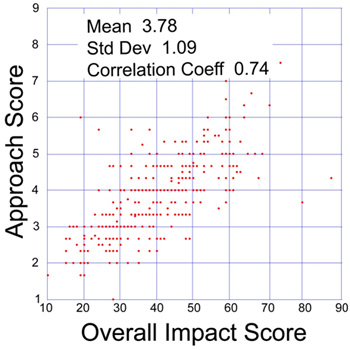 Similarly, here is a plot comparing the average innovation criterion score and the overall impact score:
Similarly, here is a plot comparing the average innovation criterion score and the overall impact score:
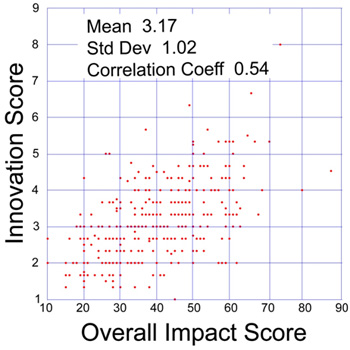 Note that the overall impact score is NOT derived by combining the individual criterion scores. This policy is based on several considerations, including:
Note that the overall impact score is NOT derived by combining the individual criterion scores. This policy is based on several considerations, including:

Plot of approach and overall impact scores in a sample of 360 NIGMS R01 applications reviewed during the October 2009 Council round.

Plot of innovation and overall impact scores in a sample of 360 NIGMS R01 applications reviewed during the October 2009 Council round.
- The effect of the individual criterion scores on the overall impact score is expected to depend on the nature of the project. For example, an application directed toward developing a community resource may not be highly innovative; indeed, a high level of innovation may be undesirable in this context. Nonetheless, such a project may receive a high overall impact score if the approach and significance are strong.
- The overall impact score is refined over the course of a study section discussion, whereas the individual criterion scores are not.
