Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
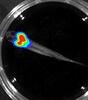
Bioluminescence in a Tube
5895
Details about the basic biology and chemistry of the ingredients that produce bioluminescence are allowing scientists to harness it as an imaging tool. Credit: Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute. Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute View MediaNetwork diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (unlabeled)
3436
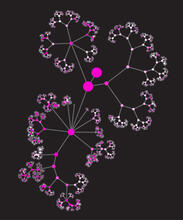
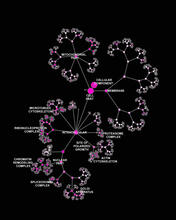
This image shows the hierarchical ontology of genes, cellular components and processes derived from large genomic datasets. From Dutkowski et al. Janusz Dutkowski and Trey Ideker View MediaTracking cells in a gastrulating zebrafish embryo
6776
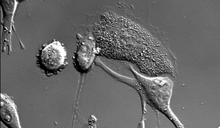
During development, a zebrafish embryo is transformed from a ball of cells into a recognizable body plan by sweeping convergence and extension cell movements. This process is called gastrulation. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaSnowflake yeast 3
6971
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaStudent overseeing protein cloning robot
2356
Student Christina Hueneke of the Midwest Center for Structural Genomics is overseeing a protein cloning robot. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaTEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
5759
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 2
6585
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaElectrostatic map of the adeno-associated virus
3374
The new highly efficient parallelized DelPhi software was used to calculate the potential map distribution of an entire virus, the adeno-associated virus, which is made up of more than 484,000 atoms. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 3
3415
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaAutomated Worm Sorter - 4
3475
Georgia Tech associate professor Hang Lu holds a microfluidic chip that is part of a system that uses artificial intelligence and cutting-edge image processing to automatically examine large number of Georgia Tech/Gary Meek View MediaBacterial symbionts colonizing the crypts of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid light organ
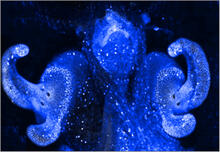
7020
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, stained blue. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaPores on the surface of the Hawaiian bobtail squid light organ
7016
The light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, stained blue. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaCrystals of CCD-1 in complex with cefotaxime
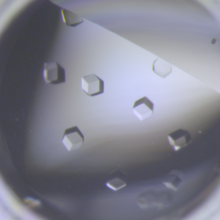
6764
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaHeLa cells
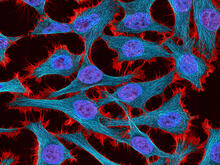
3521
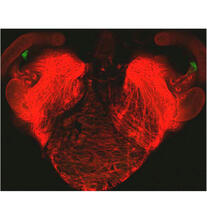
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse brain 3
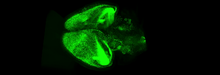
6931
Various views of a mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaCone snail shell
2576
A shell from the venomous cone snail Conus omaria, which lives in the Pacific and Indian oceans and eats other snails. Kerry Matz, University of Utah View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
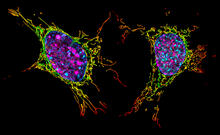
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaYeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
6772
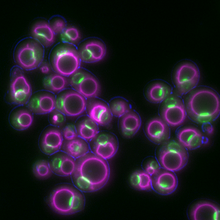
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaChromium X-ray source
2361
In the determination of protein structures by X-ray crystallography, this unique soft (l = 2.29Å) X-ray source is used to collect anomalous scattering data from protein crystals containing light atoms The Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaBreast cancer cells change migration phenotypes
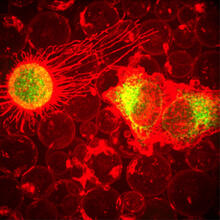
6986
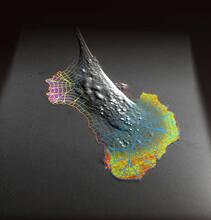
Cancer cells can change their migration phenotype, which includes their shape and the way that they move to invade different tissues. Bo Sun, Oregon State University. View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
6902
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaComputer algorithm
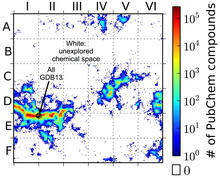
3458
This computer algorithm plots all feasible small carbon-based molecules as though they were cities on a map and identifies huge, unexplored spaces that may help fuel research into new drug therapies. Aaron Virshup, Julia Contreras-Garcia, Peter Wipf, Weitao Yang and David Beratan, University of Pittsburgh Center for Chemical Methodologies and Library Development View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
6591
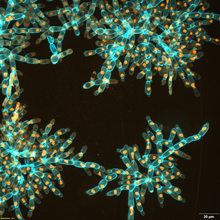
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaFruit fly ovarioles
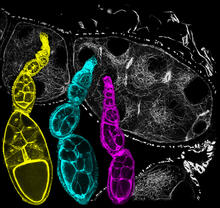
6810
Three fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovarioles (yellow, blue, and magenta) with egg cells visible inside them. Ovarioles are tubes in the reproductive systems of female insects. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6771
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR swimming in water. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--gradient background
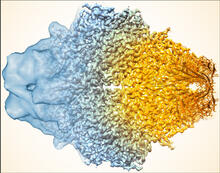
5883
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaMouse retina
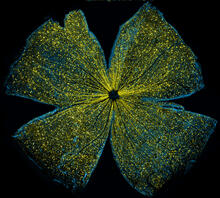
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaColorful communication
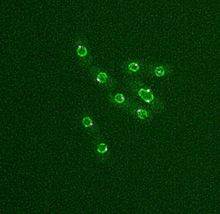
2313
The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi glows when near its kind. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaNeutrophil-like cells migrating in a microfluidic chip
6886
Neutrophil-like cells (blue) in a microfluidic chip preferentially migrating toward LTB4 over fMLP. Caroline Jones, University of Texas at Dallas. View MediaCas9 protein involved in the CRISPR gene-editing technology
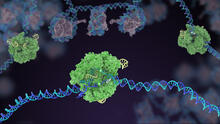
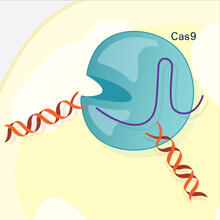
5816
In the gene-editing tool CRISPR, a small strand of RNA identifies a specific chunk of DNA. Janet Iwasa View MediaNetwork diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (labeled)
3437
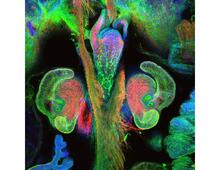
This image shows the hierarchical ontology of genes, cellular components and processes derived from large genomic datasets. From Dutkowski et al. Janusz Dutkowski and Trey Ideker, University of California, San Diego View MediaMouse Retina
3309
A genetic disorder of the nervous system, neurofibromatosis causes tumors to form on nerves throughout the body, including a type of tumor called an optic nerve glioma that can result in childhood bli Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
6789
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaScientists display X-ray diffraction pattern obtained with split X-ray beamline
2384
Scientists from Argonne National Laboratory's Advanced Photon Source (APS) display the first X-ray diffraction pattern obtained from a protein crystal using a split X-ray beam, the first of its kind a GM/CA Collaborative Access Team View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
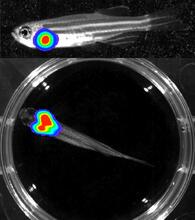
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 5
6489
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the fifthframe in a series of five. View MediaHIV Capsid
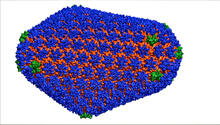
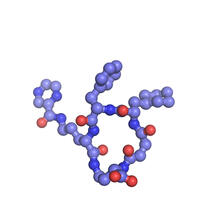
3477
This image is a computer-generated model of the approximately 4.2 million atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that contains the virus' genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaPlasma-Derived Membrane Vesicles
5887
This fiery image doesn’t come from inside a bubbling volcano. Instead, it shows animal cells caught in the act of making bubbles, or blebbing. Jeanne Stachowiak, University of Texas at Austin View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaEnzyme transition states
3429
The molecule on the left is an electrostatic potential map of the van der Waals surface of the transition state for human purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Vern Schramm, Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University View MediaDividing yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and spindle pole bodies
6795
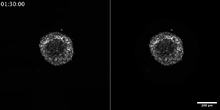
Time-lapse video of yeast cells undergoing cell division. Nuclear envelopes are shown in green, and spindle pole bodies, which help pull apart copied genetic information, are shown in magenta. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaFinding one bug
2314
A nanometer-sized biosensor can detect a single deadly bacterium in tainted ground beef. How? Weihong Tan, University of Florida in Gainesville View MediaMounting of protein crystals
2368
Automated methods using micromachined silicon are used at the Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics to mount protein crystals for X-ray crystallography. The Northeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 3
6487
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
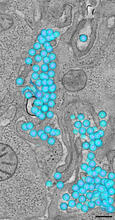
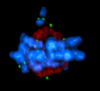
3571
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaBacterial cells aggregating above the light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7018
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaThe nascent juvenile light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7017
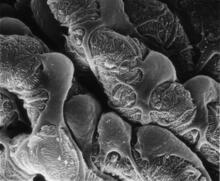
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, with different tissues are stained various colors. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaPodocytes from a chronically diseased kidney
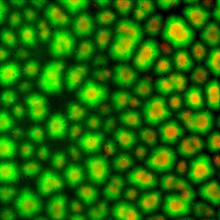
3565
This scanning electron microscope (SEM) image shows podocytes--cells in the kidney that play a vital role in filtering waste from the bloodstream--from a patient with chronic kidney disease. Olga Troyanskaya, Princeton University and Matthias Kretzler, University of Michigan View Media