Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
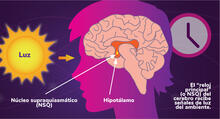
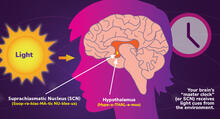
Los ritmos circadianos y el núcleo supraquiasmático
6614
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y de comportamiento que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
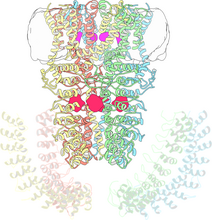
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaHIV Capsid
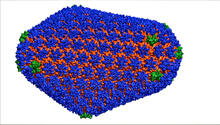
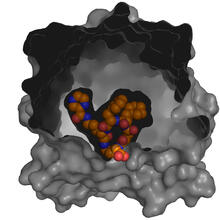
3477
This image is a computer-generated model of the approximately 4.2 million atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that contains the virus' genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaAspirin (with labels)
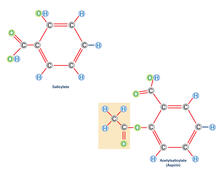
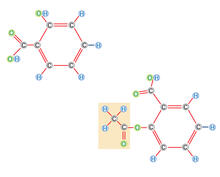
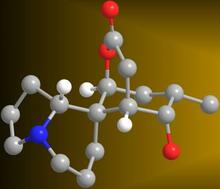
2530
Acetylsalicylate (bottom) is the aspirin of today. Crabtree + Company View MediaCryo-electron microscopy revealing the "wasabi receptor"
3747
The TRPA1 protein is responsible for the burn you feel when you taste a bite of sushi topped with wasabi. Jean-Paul Armache, UCSF View MediaZinc levels in a plant leaf
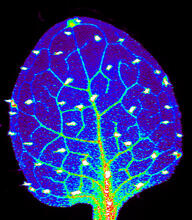
3727
Zinc is required for the function of more than 300 enzymes, including those that help regulate gene expression, in various organisms including humans. Suzana Car, Dartmouth College View MediaBrain waves of a patient anesthetized with propofol
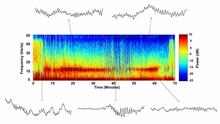
6779
A representation of a patient’s brain waves after receiving the anesthetic propofol. Emery N. Brown, M.D., Ph.D., Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
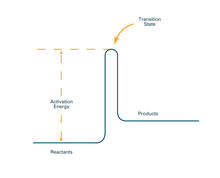
2526
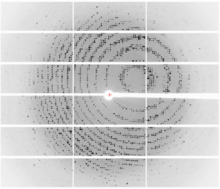
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaX-ray diffraction pattern from a crystallized cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6765
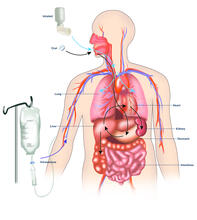
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaA drug's life in the body (with labels)
2528
A drug's life in the body. Medicines taken by mouth (oral) pass through the liver before they are absorbed into the bloodstream. Crabtree + Company View MediaFruit fly brain responds to adipokines
6985
Drosophila adult brain showing that an adipokine (fat hormone) generates a response from neurons (aqua) and regulates insulin-producing neurons (red).Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View Media
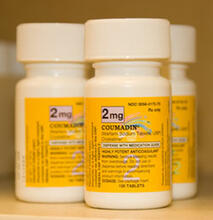
Bottles of warfarin
2579
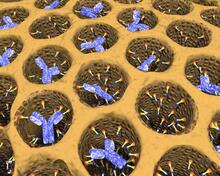
In 2007, the FDA modified warfarin's label to indicate that genetic makeup may affect patient response to the drug. The widely used blood thinner is sold under the brand name Coumadin®. Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH View MediaAntibodies in silica honeycomb
2750
Antibodies are among the most promising therapies for certain forms of cancer, but patients must take them intravenously, exposing healthy tissues to the drug and increasing the risk of side effects. Chenghong Lei, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory & Karl Erik Hellstrom, University of Washington View MediaHimastatin, 360-degree view
6851
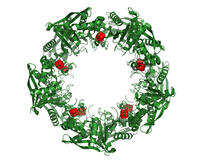
A 360-degree view of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
3720
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaBioluminescence in a Tube
5895
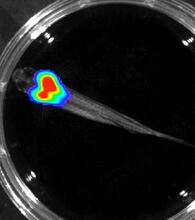
Details about the basic biology and chemistry of the ingredients that produce bioluminescence are allowing scientists to harness it as an imaging tool. Credit: Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute. Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
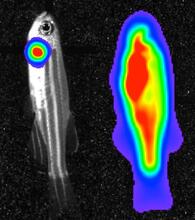
3557
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaIndependence Day
5888
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaBond types
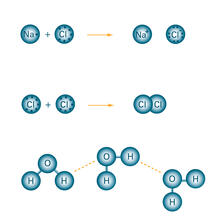
2519
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaActive site of sulfite oxidase
2746
Sulfite oxidase is an enzyme that is essential for normal neurological development in children. John Enemark, University of Arizona View MediaQuorum-sensing inhibitor limits bacterial growth
3728
To simulate the consequences of disrupting bacterial cell-to-cell communication, called quorum sensing, in the crypts (small chambers within the colon), the researchers experimented with an inhibitor Minyoung Kevin Kim and Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaCircadian rhythms and the SCN
6613
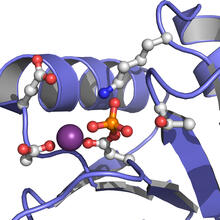
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. NIGMS View MediaActive Site of E. coli response regulator PhoB
3412
Active site of E. coli response regulator PhoB. Ann Stock, Rutgers University View MediaGlycan arrays
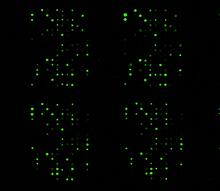
1265
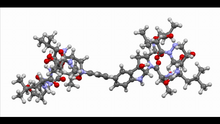
The signal is obtained by allowing proteins in human serum to interact with glycan (polysaccharide) arrays. The arrays are shown in replicate so the pattern is clear. Ola Blixt, Scripps Research Institute View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 02
2795
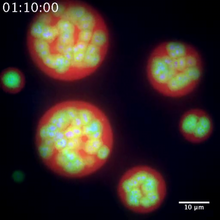
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaYeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
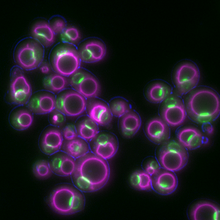
6772
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaActivation energy
2525
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2526 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 04
2797
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaA Bacillus subtilis biofilm grown in a Petri dish
3718
Bacterial biofilms are tightly knit communities of bacterial cells growing on, for example, solid surfaces, such as in water pipes or on teeth. Gürol Süel, UCSD View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaATP synthase
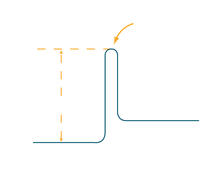
2517
The world's smallest motor, ATP synthase, generates energy for the cell. See image 2518 for a labeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaHuman opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
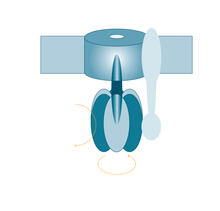
3314
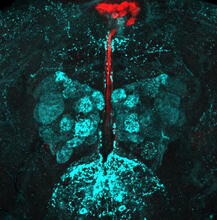
Opioid receptors on the surfaces of brain cells are involved in pleasure, pain, addiction, depression, psychosis, and other conditions. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaMaster clock of the mouse brain
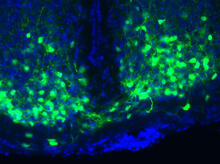
3547
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis View MediaAtomic Structure of Poppy Enzyme
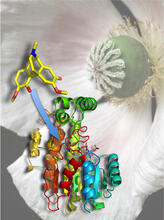
3422
The atomic structure of the morphine biosynthetic enzyme salutaridine reductase bound to the cofactor NADPH. The substrate salutaridine is shown entering the active site. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaNetwork Map
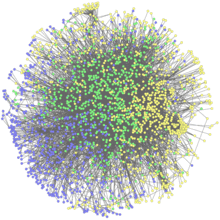
2735
This network map shows the overlap (green) between the long QT syndrome (yellow) and epilepsy (blue) protein-interaction neighborhoods located within the human interactome. Seth Berger, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaHimastatin and bacteria
6850
A model of the molecule himastatin overlaid on an image of Bacillus subtilis bacteria. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaFruit fly starvation leads to adipokine accumulation
6984
Adult Drosophila abdominal fat tissue showing cell nuclei labelled in magenta. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaCytochrome structure with anticancer drug
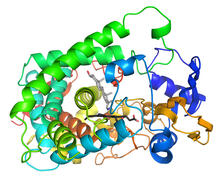
3326
This image shows the structure of the CYP17A1 enzyme (ribbons colored from blue N-terminus to red C-terminus), with the associated heme colored black. Emily Scott, University of Kansas View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 02
2791
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaSerratezomine A
2687
A 3-D model of the alkaloid serratezomine A shows the molecule's complex ring structure. View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
3791
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 01
2790
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaPrecisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
3779
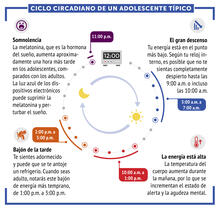
Moving protein or other molecules to specific cells to treat or examine them has been a major biological challenge. Nature Nanotechnology View MediaCiclo circadiano de un adolescente típico
6612
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y conductuales que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaHimastatin
6848
A model of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaCarbon building blocks
2506
The arrangement of identical molecular components can make a dramatic difference. For example, carbon atoms can be arranged into dull graphite (left) or sparkly diamonds (right). Crabtree + Company View Media