Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
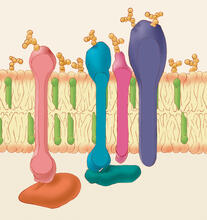
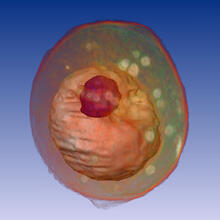
Animal cell membrane
1286
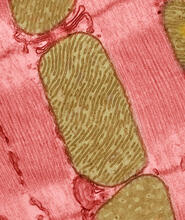
The membrane that surrounds a cell is made up of proteins and lipids. Judith Stoffer View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell_2
3664
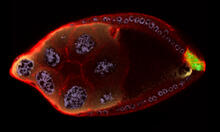
These mitochondria (brown) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaCellular polarity
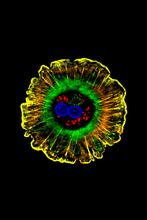
2309
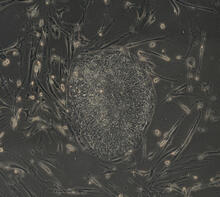
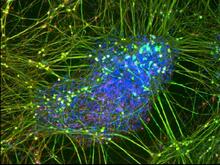
As an egg cell develops, a process called polarization controls what parts ultimately become the embryo's head and tail. This picture shows an egg of the fruit fly Drosophila. Wu-Min Deng, Florida State University View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaFly cells live
2315
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaLipid raft
1285
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. Judith Stoffer View MediaCryo-electron microscopy of the dengue virus showing protective membrane and membrane proteins
3748
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaTaste buds signal different tastes through ATP release
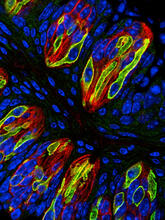
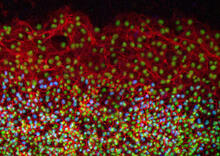
3444
Taste buds in a mouse tongue epithelium with types I, II, and III taste cells visualized by cell-type-specific fluorescent antibodies. Aki Taruno, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaHIV Capsid
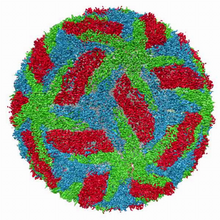
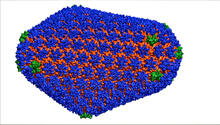
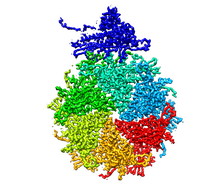
3477
This image is a computer-generated model of the approximately 4.2 million atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that contains the virus' genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaHuman skeletal muscle
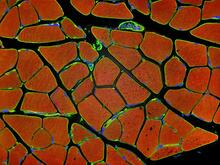
3677
Cross section of human skeletal muscle. Image taken with a confocal fluorescent light microscope. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse heart muscle cells 02
3283
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaCell proliferation in a quail embryo
2808
Image showing that the edge zone (top of image) of the quail embryo shows no proliferating cells (cyan), unlike the interior zone (bottom of image). Non-proliferating cell nuclei are labeled green. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaFluorescent E. coli bacteria
3268
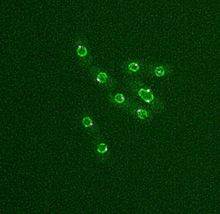
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. They called each blinking bacterial colony a biopixel. Thousands of fluorescent E. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaNCMIR Tongue 2
5811
Microscopy image of a tongue. One in a series of two, see image 5810 National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586
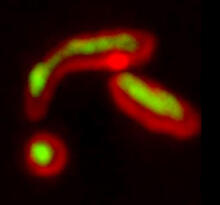
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaDividing cell
6965
As this cell was undergoing cell division, it was imaged with two microscopy techniques: differential interference contrast (DIC) and confocal. The DIC view appears in blue and shows the entire cell. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaInfluenza virus attaches to host membrane
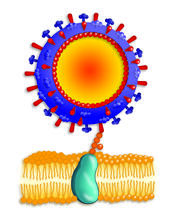
2425
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View Media3D reconstruction of the Golgi apparatus in a pancreas cell
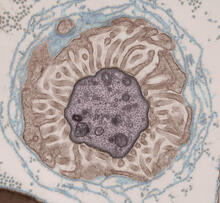
6609
Researchers used cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) to capture images of a rat pancreas cell that were then compiled and color-coded to produce a 3D reconstruction. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaHuman retinal organoid
6748
A replica of a human retina grown from stem cells. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaTransmission electron microscopy showing cross-section of the node of Ranvier
3740
Nodes of Ranvier are short gaps in the myelin sheath surrounding myelinated nerve cells (axons). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCell division with late aligning chromosomes
2747
This video shows an instance of abnormal mitosis where chromosomes are late to align. Gary Gorbsky, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation View MediaLily mitosis 04
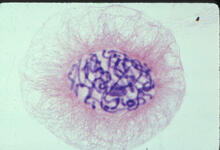
1014
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaYeast cell
1092
A whole yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell viewed by X-ray microscopy. Inside, the nucleus and a large vacuole (red) are visible. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
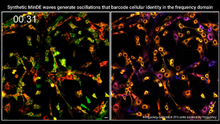
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaDraper, shown in the fatbody of a Drosophila melanogaster larva
2757
The fly fatbody is a nutrient storage and mobilization organ akin to the mammalian liver. The engulfment receptor Draper (green) is located at the cell surface of fatbody cells. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
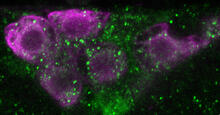
6982
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaLysosomes
1282
Lysosomes have powerful enzymes and acids to digest and recycle cell materials. Judith Stoffer View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaSea urchin embryo 05
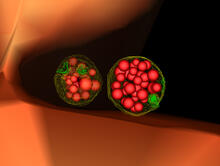
1051
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaMouse Brain Cross Section
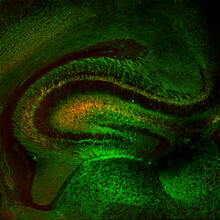
5886
The brain sections are treated with fluorescent antibodies specific to a particular protein and visualized using serial electron microscopy (SEM). Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared
1333
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaFruit fly brain responds to adipokines
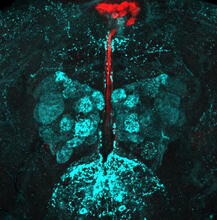
6985
Drosophila adult brain showing that an adipokine (fat hormone) generates a response from neurons (aqua) and regulates insulin-producing neurons (red).Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View Media
Cell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaSnowflake yeast 2
6970
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
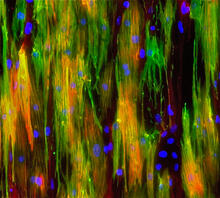
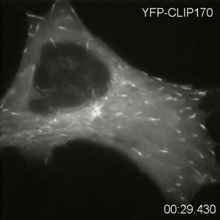
2784
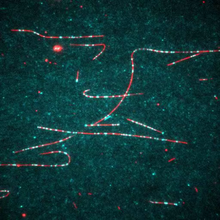
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaCell toxins
1312
A number of environmental factors cause DNA mutations that can lead to cancer: toxins in cigarette smoke, sunlight and other radiation, and some viruses. Judith Stoffer View MediaNeutrophil-like cells migrating in a microfluidic chip
6886
Neutrophil-like cells (blue) in a microfluidic chip preferentially migrating toward LTB4 over fMLP. Caroline Jones, University of Texas at Dallas. View MediaCryo-ET cross-section of the Golgi apparatus
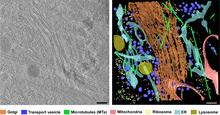
6606
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a 3D, color-coded version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaSnowflake yeast 1
6969
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaPeripheral nerve cell derived from ES cells
3264
A peripheral nerve cell made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaDividing yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and spindle pole bodies
6795
Time-lapse video of yeast cells undergoing cell division. Nuclear envelopes are shown in green, and spindle pole bodies, which help pull apart copied genetic information, are shown in magenta. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaFruit fly ovary
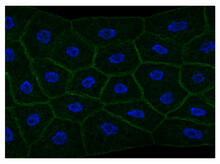
6522
In this image of a stained fruit fly ovary, the ovary is packed with immature eggs (with DNA stained blue). The cytoskeleton (in pink) is a collection of fibers that gives a cell shape and support. Crystal D. Rogers, Ph.D., University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine; and Mariano A. Loza-Coll, Ph.D., California State University, Northridge. View MediaMisfolded proteins within in the mitochondria
5878
Misfolded proteins (green) within mitochondria (red). Related to video 5877. Rong Li rong@jhu.edu Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland 21218, USA. View MediaDynein moving along microtubules
7023
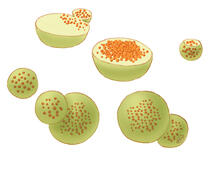
Dynein (green) is a motor protein that “walks” along microtubules (red, part of the cytoskeleton) and carries its cargo along with it. This video was captured through fluorescence microscopy. Morgan DeSantis, University of Michigan. View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 3
5767
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaBacteria shapes
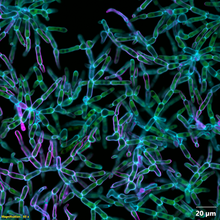
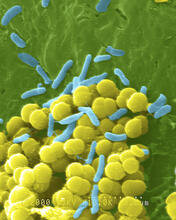
1158
A colorized scanning electron micrograph of bacteria. Scanning electron microscopes allow scientists to see the three-dimensional surface of their samples. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View MediaHuman liver cell (hepatocyte)
3610
Hepatocytes, like the one shown here, are the most abundant type of cell in the human liver. Donna Beer Stolz, University of Pittsburgh View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 01
2603
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (White Background)
6534
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View Media