Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
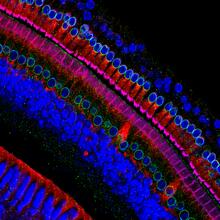
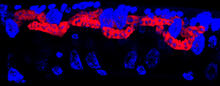
Hair cells: the sound-sensing cells in the ear
3618
These cells get their name from the hairlike structures that extend from them into the fluid-filled tube of the inner ear. Henning Horn, Brian Burke, and Colin Stewart, Institute of Medical Biology, Agency for Science, Technology, and Research, Singapore View MediaPlanarian stem cell colony
3306
Planarians are freshwater flatworms that have powerful abilities to regenerate their bodies, which would seem to make them natural model organisms in which to study stem cells. Peter Reddien, Whitehead Institute View MediaOptic nerve astrocytes
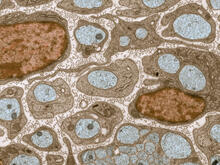
5852
Astrocytes in the cross section of a human optic nerve head Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaAnimal cell membrane
1286
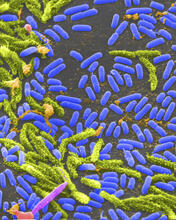
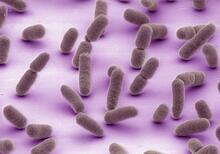
The membrane that surrounds a cell is made up of proteins and lipids. Judith Stoffer View MediaVibrio bacteria
1160
Vibrio, a type (genus) of rod-shaped bacteria. Some Vibrio species cause cholera in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaFruit fly sperm cells
2433
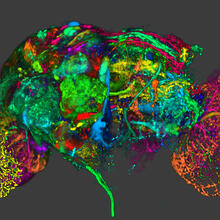
Developing fruit fly spermatids require caspase activity (green) for the elimination of unwanted organelles and cytoplasm via apoptosis. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
5838
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 2)
6555
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi (red) and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 48 hours on 1% agar surface from a sma L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaInduced pluripotent stem cells from skin 02
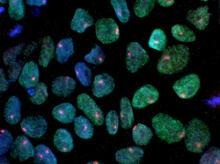
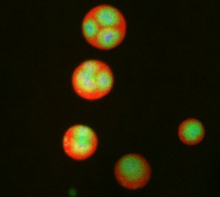
3279
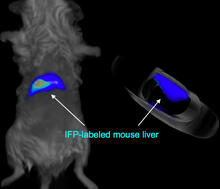
These induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) were derived from a woman's skin. Blue show nuclei. Green show a protein found in iPS cells but not in skin cells (NANOG). Kathrin Plath lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaMouse liver labeled with fluorescent probe
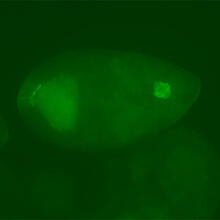
2601
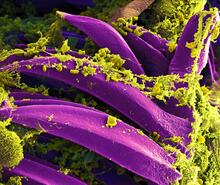
A mouse liver glows after being tagged with specially designed infrared-fluorescent protein (IFP). Xiaokun Shu, University of California, San Diego View MediaBubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
3576
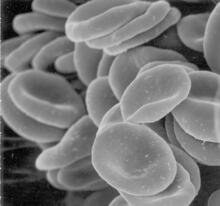
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. NIAID View MediaRed blood cells
1101
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sa Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaThermotoga maritima and its metabolic network
2702
A combination of protein structures determined experimentally and computationally shows us the complete metabolic network of a heat-loving bacterium. View MediaCells use bubble-like structures called vesicles to transport cargo
3634
Cells use bubble-like structures called vesicles (yellow) to import, transport, and export cargo and in cellular communication. A single cell may be filled with thousands of moving vesicles.Tatyana Svitkina, University of Pennsylvania View Media
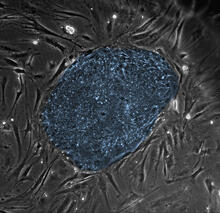
Human embryonic stem cells
2608
The center cluster of cells, colored blue, shows a colony of human embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaCentrioles anchor cilia in planaria
3292
Centrioles (green) anchor cilia (red), which project on the surface of pharynx cells of the freshwater planarian Schmidtea mediterranea. Juliette Azimzadeh, University of California, San Francisco View MediaSmooth ER
1292
The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two types: Rough ER is covered with ribosomes and prepares newly made proteins; smooth ER specializes in making lipids and breaking down toxic molecules. Judith Stoffer View MediaSnowflake yeast 1
6969
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaCell in two stages of division
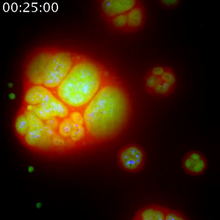
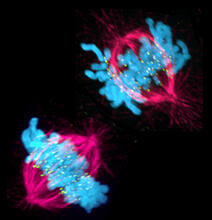
3541
This image shows a cell in two stages of division: prometaphase (top) and metaphase (bottom). Lilian Kabeche, Dartmouth View MediaLife in balance
1336
Mitosis creates cells, and apoptosis kills them. The processes often work together to keep us healthy. Judith Stoffer View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 3
5779
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View MediaDDR2 Receptors Attach to Collagen in Breast Tumor
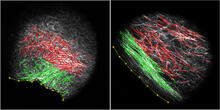
3478
On the left, the boundary of a breast tumor (yellow) attaches to collagen fibers that are closest to it (green) using DDR2. On the right, a tumor without DDR2 remains disconnected from the collagen. Callie Corsa and Suzanne Ponik, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis View MediaFly cells
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaSynapses in culture
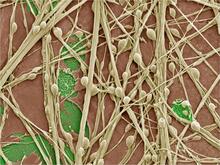
3399
Cultured hippocampal neurons grown on a substrate of glial cells (astrocytes). The glial cells form the pink/brown underlayment in this image. The tan threads are the neurons. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaDividing cell
6965
As this cell was undergoing cell division, it was imaged with two microscopy techniques: differential interference contrast (DIC) and confocal. The DIC view appears in blue and shows the entire cell. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaSimulation of leg muscles moving
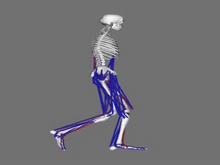
6598
When we walk, muscles and nerves interact in intricate ways. This simulation, which is based on data from a six-foot-tall man, shows these interactions. Chand John and Eran Guendelman, Stanford University View MediaHost infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. View MediaHuman Adenovirus
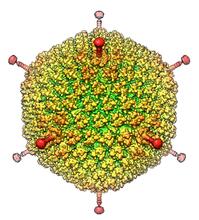
6347
The cryo-EM structure of human adenovirus D26 (HAdV-D26) at near atomic resolution (3.7 Å), determined in collaboration with the NRAMM facility*. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaEpithelial cells
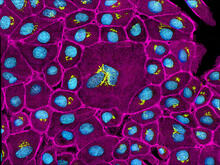
3647
This image mostly shows normal cultured epithelial cells expressing green fluorescent protein targeted to the Golgi apparatus (yellow-green) and stained for actin (magenta) and DNA (cyan). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of myelinated axons with ECM between the axons
3736
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells, as shown here. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 3
3792
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaEndothelial cell
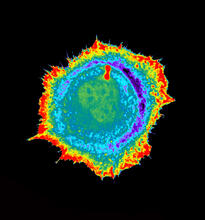
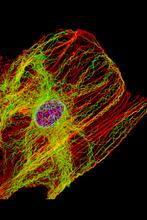
1102
This image shows two components of the cytoskeleton, microtubules (green) and actin filaments (red), in an endothelial cell derived from a cow lung. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaMolecular interactions at the astrocyte nuclear membrane
3734
These ripples of color represent the outer membrane of the nucleus inside an astrocyte, a star-shaped cell inside the brain. Katerina Akassoglou, Gladstone Institute for Neurological Disease & UCSF View MediaPurkinje cells are one of the main cell types in the brain
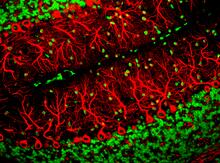
3637
This image captures Purkinje cells (red), one of the main types of nerve cell found in the brain. Yinghua Ma and Timothy Vartanian, Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y. View MediaHuman ES cells differentiating into neurons
3276
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaCells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
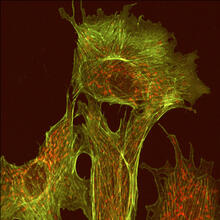
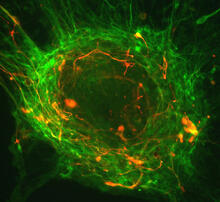
3617
This image shows a normal fibroblast, a type of cell that is common in connective tissue and frequently studied in research labs. James J. Faust and David G. Capco, Arizona State University View MediaCrab larva eye
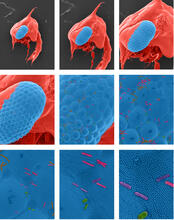
1251
Colorized scanning electron micrographs progressively zoom in on the eye of a crab larva. In the higher-resolution frames, bacteria are visible on the eye. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
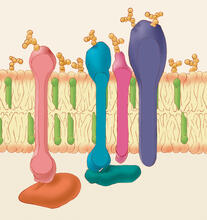
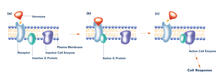
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaActin filaments bundled around the dynamin helical polymer
6571
Multiple actin filaments (magenta) are organized around a dynamin helical polymer (rainbow colored) in this model derived from cryo-electron tomography. Elizabeth Chen, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaTime-lapse video of floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 24 hours
6550
This time-lapse video shows the emergence of a flower-like pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), that are gr L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaTranslation
1281
Ribosomes manufacture proteins based on mRNA instructions. Each ribosome reads mRNA, recruits tRNA molecules to fetch amino acids, and assembles the amino acids in the proper order. Judith Stoffer View MediaCells lining the trachea
3646
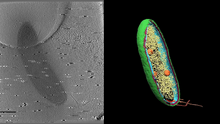
In this image, viewed with a ZEISS ORION NanoFab microscope, the community of cells lining a mouse airway is magnified more than 10,000 times. Eva Mutunga and Kate Klein, University of the District of Columbia and National Institute of Standards and Technology View MediaCryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
6569
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (White Background)
6534
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View Media