Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
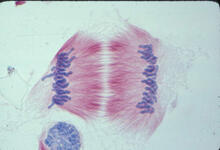
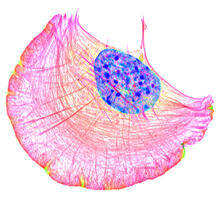
Lily mitosis 11
1011
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum
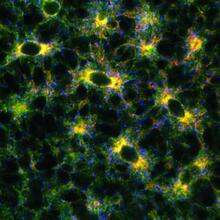
2649
Fluorescent markers show the interconnected web of tubes and compartments in the endoplasmic reticulum. The protein atlastin helps build and maintain this critical part of cells. Andrea Daga, Eugenio Medea Scientific Institute (Conegliano, Italy) View MediaZinc levels in a plant leaf
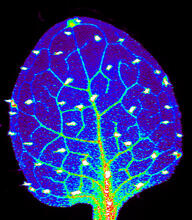
3727
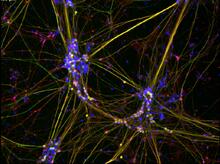
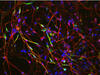
Zinc is required for the function of more than 300 enzymes, including those that help regulate gene expression, in various organisms including humans. Suzana Car, Dartmouth College View MediaNeurons from human ES cells
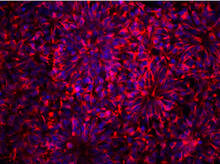
3284
These neural precursor cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The neural cell bodies are stained red, and the nuclei are blue. Xianmin Zeng lab, Buck Institute for Age Research, via CIRM View MediaEgg comparison
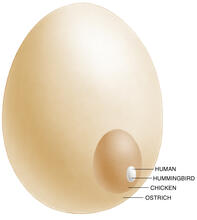
1339
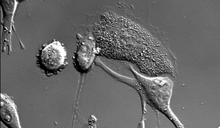
The largest human cell (by volume) is the egg. Human eggs are 150 micrometers in diameter and you can just barely see one with a naked eye. In comparison, consider the eggs of chickens...or ostriches! Judith Stoffer View MediaHydra 06
2442
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaMitosis - interphase
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaTracking embryonic zebrafish cells
6775
To better understand cell movements in developing embryos, researchers isolated cells from early zebrafish embryos and grew them as clusters. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
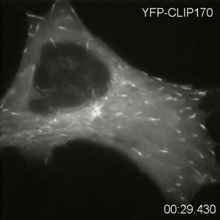
2784
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaSea urchin embryo 02
1048
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaMolecular model of freshly made Rous sarcoma virus (RSV)
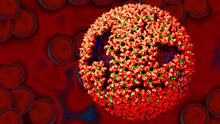
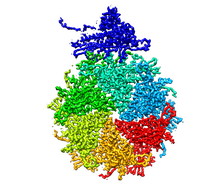
3771
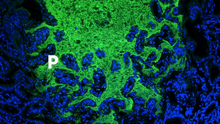
Viruses have been the foes of animals and other organisms for time immemorial. Boon Chong Goh, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
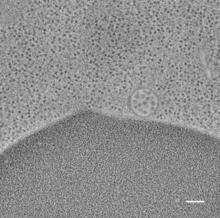
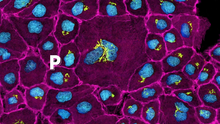
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaGenetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
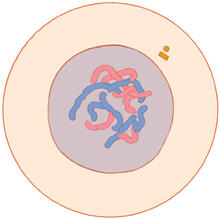
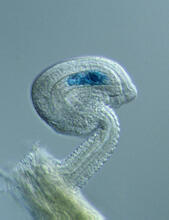
2418
This delicate, birdlike projection is an immature seed of the Arabidopsis plant. The part in blue shows the cell that gives rise to the endosperm, the tissue that nourishes the embryo. Robert Fischer, University of California, Berkeley View MediaImmune cell attacks cell infected with a retrovirus
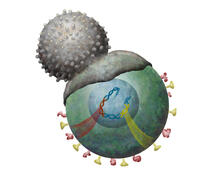
2489
T cells engulf and digest cells displaying markers (or antigens) for retroviruses, such as HIV. Kristy Whitehouse, science illustrator View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 2
5768
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaBiofilm blocking fluid flow
3446
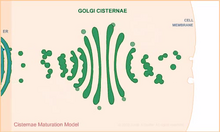
This time-lapse movie shows that bacterial communities called biofilms can create blockages that prevent fluid flow in devices such as stents and catheters over a period of about 56 hours. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaCisternae maturation model
1307
Animation for the cisternae maturation model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaDNA and actin in cultured fibroblast cells
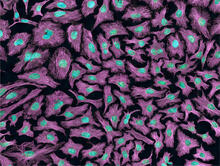
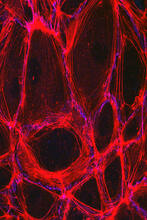
3670
DNA (blue) and actin (red) in cultured fibroblast cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediamDia1 antibody staining- 02
3331
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaPeripheral nerve cells derived from ES cells
3263
Peripheral nerve cells made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 1
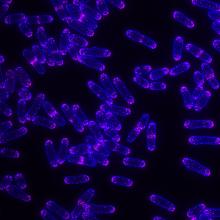
5751
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaYeast cells with endocytic actin patches
6793
Yeast cells with endocytic actin patches (green). These patches help cells take in outside material. When a cell is in interphase, patches concentrate at its ends. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaGlowing bacteria make a pretty postcard
3492
This tropical scene, reminiscent of a postcard from Key West, is actually a petri dish containing an artistic arrangement of genetically engineered bacteria. Nathan C. Shaner, The Scintillon Institute View MediaYeast cells with Fimbrin Fim1
6794
Yeast cells with the protein Fimbrin Fim1 shown in magenta. This protein plays a role in cell division. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View Media
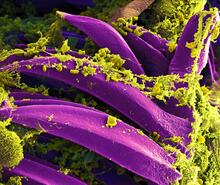
Bubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
3576
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. NIAID View MediaPathways: The Fascinating Cells of Research Organisms
6538
Learn how research organisms, such as fruit flies and mice, can help us understand and treat human diseases. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaLife in balance
1336
Mitosis creates cells, and apoptosis kills them. The processes often work together to keep us healthy. Judith Stoffer View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaEarly life of a protein
2740
This illustration represents the early life of a protein—specifically, apomyoglobin—as it is synthesized by a ribosome and emerges from the ribosomal tunnel, which contains the newly formed protein's Silvia Cavagnero, University of Wisconsin, Madison View MediaCalcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
3449
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaPigment cells in fish skin
5756
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaDividing yeast cells with spindle pole bodies and contractile rings
6796
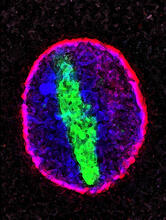
During cell division, spindle pole bodies (glowing dots) move toward the ends of yeast cells to separate copied genetic information. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaCellular aging
2578
A protein called tubulin (green) accumulates in the center of a nucleus (outlined in pink) from an aging cell. Maximiliano D'Angelo and Martin Hetzer, Salk Institute View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
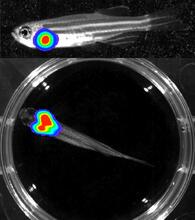
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaSymmetrically and asymmetrically elongating cells
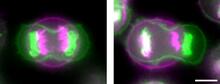
3648
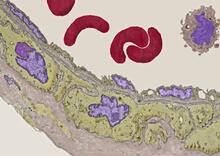
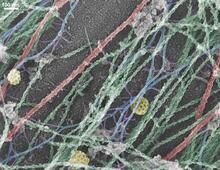
Merged fluorescent images of symmetrically (left) or asymmetrically (right) elongating HeLa cells at the end of early anaphase (magenta) and late anaphase (green). Tomomi Kiyomitsu and Iain M. Cheeseman, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
3738
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaHeLa cells
3520
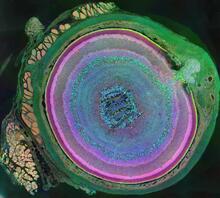
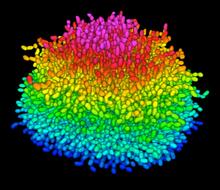
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells with cytoskeletal microtubules (magenta) and DNA (cyan). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaA mammalian eye has approximately 70 different cell types
3641
The incredible complexity of a mammalian eye (in this case from a mouse) is captured here. Each color represents a different type of cell. Bryan William Jones and Robert E. Marc, University of Utah View MediaAn insect tracheal cell delivers air to muscles
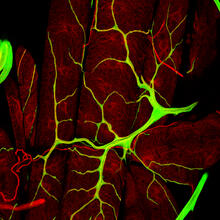
3615
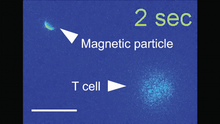
Insects like the fruit fly use an elaborate network of branching tubes called trachea (green) to transport oxygen throughout their bodies. Jayan Nair and Maria Leptin, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany View MediaMagnetic Janus particle activating a T cell
6800
A Janus particle being used to activate a T cell, a type of immune cell. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaCells use bubble-like structures called vesicles to transport cargo
3634
Cells use bubble-like structures called vesicles (yellow) to import, transport, and export cargo and in cellular communication. A single cell may be filled with thousands of moving vesicles.Tatyana Svitkina, University of Pennsylvania View Media
A Growing Bacterial Biofilm
5825
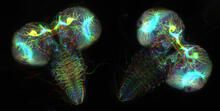
A growing Vibrio cholerae (cholera) biofilm. Cholera bacteria form colonies called biofilms that enable them to resist antibiotic therapy within the body and other challenges to their growth. Jing Yan, Ph.D., and Bonnie Bassler, Ph.D., Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ. View MediaFruit fly larvae brains showing tubulin
6808
Two fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) larvae brains with neurons expressing fluorescently tagged tubulin protein. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaTetrapolar mitosis
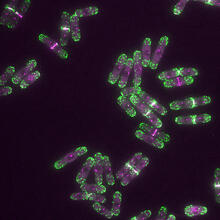
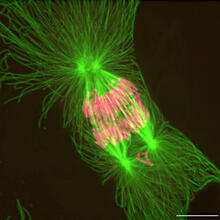
2739
This image shows an abnormal, tetrapolar mitosis. Chromosomes are highlighted pink. The cells shown are S3 tissue cultured cells from Xenopus laevis, African clawed frog. Gary Gorbsky, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation View MediaCells lining the blood vessel walls
3633
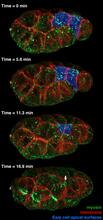
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School. View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3297
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaCrawling cell
6964
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaPathways: What is Basic Science?
6539
Learn about basic science, sometimes called “pure” or “fundamental” science, and how it contributes to the development of medical treatments. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View Media