Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
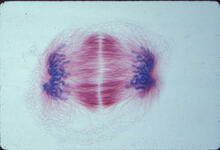
Lily mitosis 01
1058
A light microscope image shows the chromosomes, stained dark blue, in a dividing cell of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaStaphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 2
5778
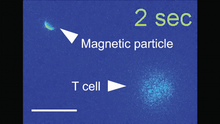
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View MediaMagnetic Janus particle activating a T cell
6800
A Janus particle being used to activate a T cell, a type of immune cell. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaNeurons from human ES cells 02
3285
These neurons were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The neural cell bodies with axonal projections are visible in red, and the nuclei in blue. Xianmin Zeng lab, Buck Institute for Age Research, via CIRM View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria - video
3254
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaPathways: What is It? | Why Scientists Study Cells
6540
Learn how curiosity about the world and our cells is key to scientific discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaZebrafish pigment cell
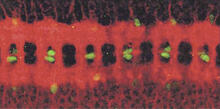
5754
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaBubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
3576
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. NIAID View MediaProtein map
2423
Network diagram showing a map of protein-protein interactions in a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell. This cluster includes 78 percent of the proteins in the yeast proteome. Hawoong Jeong, KAIST, Korea View MediaDeveloping nerve cells
3632
These developing mouse nerve cells have a nucleus (yellow) surrounded by a cell body, with long extensions called axons and thin branching structures called dendrites. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaMouse retina close-up
5872
Keunyoung ("Christine") Kim National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
6774
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. After an experimental intervention, they are expressing a nonfunctional version of FIT2, shown in green. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaMitotic cell awaits chromosome alignment
5765
During mitosis, spindle microtubules (red) attach to chromosome pairs (blue), directing them to the spindle equator. View MediaStretch detectors
2714
Muscles stretch and contract when we walk, and skin splits open and knits back together when we get a paper cut. Christopher Chen, University of Pennsylvania View MediaLily mitosis 12
1018
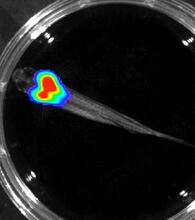
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
3557
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaFruit fly embryo
2431
Cells in an early-stage fruit fly embryo, showing the DIAP1 protein (pink), an inhibitor of apoptosis. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaFruit fly retina 02
2434
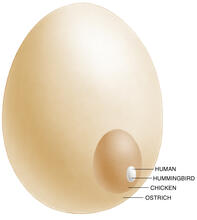
Section of a fruit fly retina showing the light-sensing molecules rhodopsin-5 (blue) and rhodopsin-6 (red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaEgg comparison
1339
The largest human cell (by volume) is the egg. Human eggs are 150 micrometers in diameter and you can just barely see one with a naked eye. In comparison, consider the eggs of chickens...or ostriches! Judith Stoffer View MediaYeast cells with accumulated cell wall material
6797
Yeast cells that abnormally accumulate cell wall material (blue) at their ends and, when preparing to divide, in their middles. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaHeLa cells
3522
Multiphoton fluorescence image of cultured HeLa cells with a fluorescent protein targeted to the Golgi apparatus (orange), microtubules (green) and counterstained for DNA (cyan). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaLily mitosis 03
1013
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaMouse cerebellum
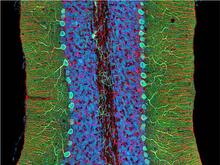
5795
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse cerebellum close-up
3371
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaScanning electron microscopy of collagen fibers
3735
This image shows collagen, a fibrous protein that's the main component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen is a strong, ropelike molecule that forms stretch-resistant fibers. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
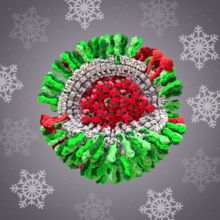
6355
CellPack image of the H1N1 influenza virus, with hemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins in green and red, respectively, on the outer envelope (white); matrix protein in gray, and ribonucleoprot Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 1
5855
Superresolution microscopy work on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the peripheral areas of the cell showing details of the structure and arrangement in a complex web of tubes. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaProteasome
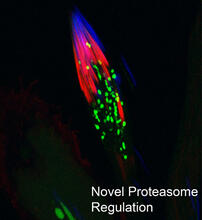
3451
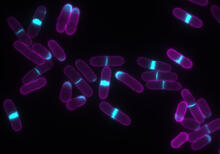
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaDrosophila
6344
Two adult fruit flies (Drosophila) Dr. Vicki Losick, MDI Biological Laboratory, www.mdibl.org View MediaYeast art depicting the New York City skyline
6521
This skyline of New York City was created by “printing” nanodroplets containing yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) onto a large plate. Each dot is a separate yeast colony. Michael Shen, Ph.D., Jasmine Temple, Leslie Mitchell, Ph.D., and Jef Boeke, Ph.D., New York University School of Medicine; and Nick Phillips, James Chuang, Ph.D., and Jiarui Wang, Johns Hopkins University. View MediaIntracellular forces
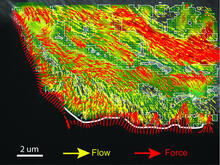
2799
Force vectors computed from actin cytoskeleton flow. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaFly cells live
2315
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaFlower-forming cells in a small plant related to cabbage (Arabidopsis)
3606
In plants, as in animals, stem cells can transform into a variety of different cell types. The stem cells at the growing tip of this Arabidopsis plant will soon become flowers. Arun Sampathkumar and Elliot Meyerowitz, California Institute of Technology View MediaMitosis - interphase
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaDividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
3631
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell_2
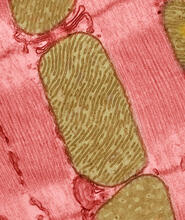
3664
These mitochondria (brown) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell
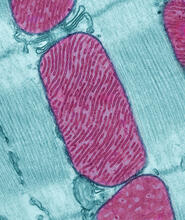
3661
These mitochondria (red) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6888
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
6803
Groups of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) attached to a microstructured titanium surface (green) that mimics an orthopedic implant used in joint replacement. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaZebrafish embryo
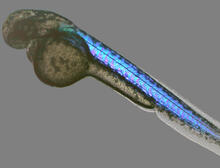
6897
A zebrafish embryo showing its natural colors. Zebrafish have see-through eggs and embryos, making them ideal research organisms for studying the earliest stages of development. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaNerve and glial cells in fruit fly embryo
1091
Glial cells (stained green) in a fruit fly developing embryo have survived thanks to a signaling pathway initiated by neighboring nerve cells (stained red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaDeveloping Arabidopsis flower buds
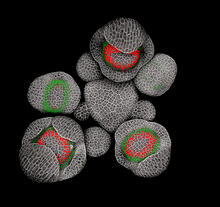
3743
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaBirth of a yeast cell
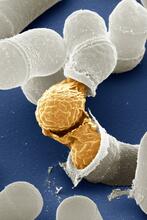
3614
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany View MediaHydra 02
2438
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaRegenerating lizard tail
6968
The interior of a regenerating lizard tail 14 days after the original tail was amputated. Thomas Lozito, University of Southern California. View MediaPeripheral nerve cell derived from ES cells
3264
A peripheral nerve cell made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View Media