Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
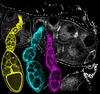
Genetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaARTS triggers apoptosis
2432
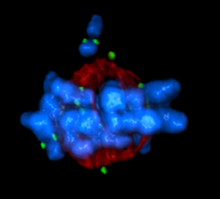
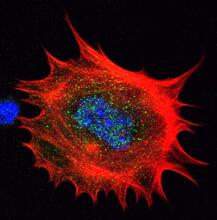
Cell showing overproduction of the ARTS protein (red). ARTS triggers apoptosis, as shown by the activation of caspase-3 (green) a key tool in the cell's destruction. The nucleus is shown in blue. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaMitotic cell awaits chromosome alignment
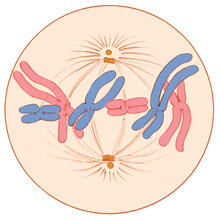
5765
During mitosis, spindle microtubules (red) attach to chromosome pairs (blue), directing them to the spindle equator. View MediaPulsating response to stress in bacteria - video
3254
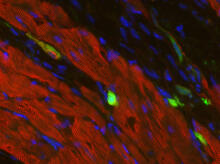
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaHeart muscle with reprogrammed skin cells
3273
Skins cells were reprogrammed into heart muscle cells. The cells highlighted in green are remaining skin cells. Red indicates a protein that is unique to heart muscle. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, via CIRM View MediaMitosis - metaphase
1329
A cell in metaphase during mitosis: The copied chromosomes align in the middle of the spindle. Judith Stoffer View MediaClathrin-mediated endocytosis
5753
Endocytosis is the process by which cells are able to take up membrane and extracellular materials through the formation of a small intracellular bubble, called a vesicle. Janet Iwasa, University of Utah View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 02
2604
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaHair cells: the sound-sensing cells in the ear
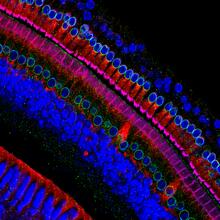
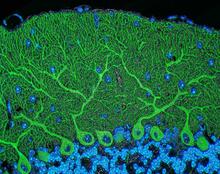
3618
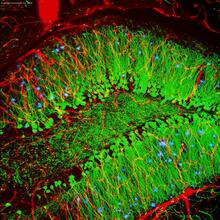
These cells get their name from the hairlike structures that extend from them into the fluid-filled tube of the inner ear. Henning Horn, Brian Burke, and Colin Stewart, Institute of Medical Biology, Agency for Science, Technology, and Research, Singapore View MediaCerebellum: the brain's locomotion control center
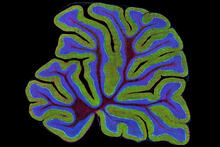
3639
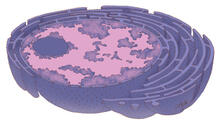
The cerebellum of a mouse is shown here in cross-section. The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Thomas Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, University of California, San Diego View MediaCultured cells
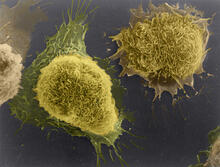
1178
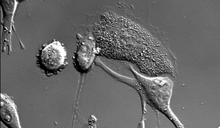
This image of laboratory-grown cells was taken with the help of a scanning electron microscope, which yields detailed images of cell surfaces. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMouse cerebellum
5795
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2807
Confocal image showing high levels of the protein vimentin (white) at the edge zone of a quail embryo. Cell nuclei are labeled green. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaV. Cholerae Biofilm
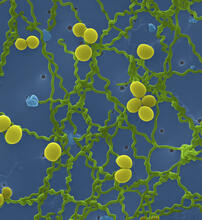
3580
Industrious V. cholerae bacteria (yellow) tend to thrive in denser biofilms (left) while moochers (red) thrive in weaker biofilms (right). View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaMyelinated axons 1
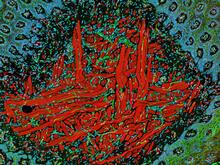
3396
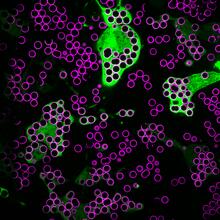
Myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaHungry, hungry macrophages
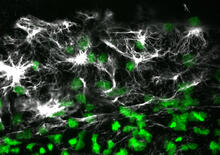
7009
Macrophages (green) are the professional eaters of our immune system. Meghan Morrissey, University of California, Santa Barbara. View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
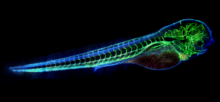
6661
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaNCMIR Tongue 2
5811
Microscopy image of a tongue. One in a series of two, see image 5810 National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaAutofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
5755
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaMouse Retina
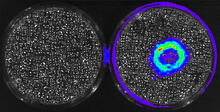
3309
A genetic disorder of the nervous system, neurofibromatosis causes tumors to form on nerves throughout the body, including a type of tumor called an optic nerve glioma that can result in childhood bli Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaCancer Cells Glowing from Luciferin
3480
The activator cancer cell culture, right, contains a chemical that causes the cells to emit light when in the presence of immune cells. Mark Sellmyer, Stanford University School of Medicine View MediaSpreading Cells- 02
3329
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaVesicle traffic
1283
This illustration shows vesicle traffic inside a cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaPlanarian stem cell colony
3306
Planarians are freshwater flatworms that have powerful abilities to regenerate their bodies, which would seem to make them natural model organisms in which to study stem cells. Peter Reddien, Whitehead Institute View MediaSea urchin embryo 06
1052
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View Media3D image of actin in a cell
3749
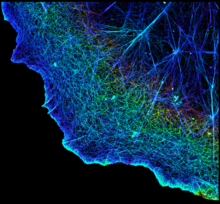
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2809
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaFruit fly nurse cells transporting their contents during egg development
6754
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaNucleus and rough ER
1290
The nucleus contains the DNA of eukaryotic cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
6891
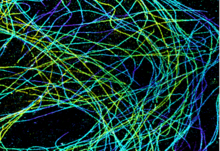
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
3725
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaDying melanoma cells
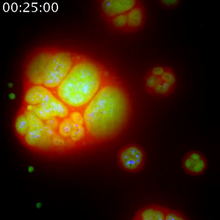
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaPainted chromosomes
2764
Like a paint-by-numbers picture, painted probes tint individual human chromosomes by targeting specific DNA sequences. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaActive site of sulfite oxidase
2746
Sulfite oxidase is an enzyme that is essential for normal neurological development in children. John Enemark, University of Arizona View MediaSkin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
3628
This image shows the uncontrolled growth of cells in squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. If caught early, squamous cell carcinoma is usually not life-threatening. Markus Schober and Elaine Fuchs, The Rockefeller University View MediaFocal adhesions (with labels)
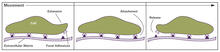
2503
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaAtomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
6601
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
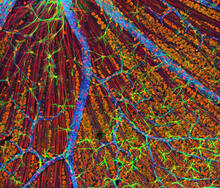
3739
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMouse liver labeled with fluorescent probe
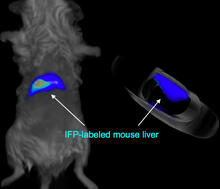
2601
A mouse liver glows after being tagged with specially designed infrared-fluorescent protein (IFP). Xiaokun Shu, University of California, San Diego View MediaLeptospira bacteria
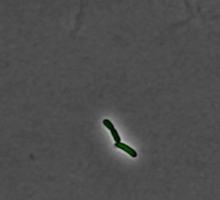
1166
Leptospira, shown here in green, is a type (genus) of elongated, spiral-shaped bacteria. Infection can cause Weil's disease, a kind of jaundice, in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
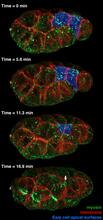
3297
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaNCMIR kidney-1
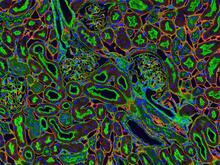
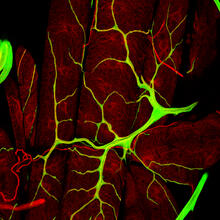
3675
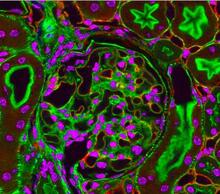
Stained kidney tissue. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaA panorama view of cells
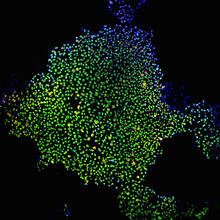
5761
This photograph shows a panoramic view of HeLa cells, a cell line many researchers use to study a large variety of important research questions. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaCell Nucleus and Lipid Droplets
6547
A cell nucleus (blue) surrounded by lipid droplets (yellow). James Olzmann, University of California, Berkeley View MediaLysosomes and microtubules
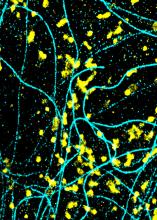
6889
Lysosomes (yellow) and detyrosinated microtubules (light blue). Lysosomes are bubblelike organelles that take in molecules and use enzymes to break them down. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaQuartered torso
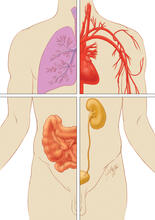
1280
Cells function within organs and tissues, such as the lungs, heart, intestines, and kidney. Judith Stoffer View MediaAn insect tracheal cell delivers air to muscles
3615
Insects like the fruit fly use an elaborate network of branching tubes called trachea (green) to transport oxygen throughout their bodies. Jayan Nair and Maria Leptin, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany View MediaHost infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. View Media