This page is historical material reflecting the Feedback Loop Blog as it existed on
August 25, 2014. This page is no longer updated and links to external websites
and some internal pages may not work.
August 25, 2014
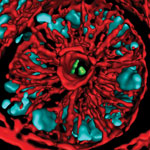
Receptor proteins bind to bacterial cell wall fragments, initiating an immune response to remove bad gut bacteria. Credit: S. Melanie Lee, Caltech; Zbigniew Mikulski and Klaus Ley, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology.
Our bodies depend on a set of immune receptors to remove harmful bacteria and control the growth of helpful bacteria in our guts. Genetic changes that alter the function of the receptors can have an adverse effect and result in chronic inflammatory diseases like Crohn’s disease. Catherine Leimkuhler Grimes and Vishnu Mohanan of the University of Delaware researched a Crohn’s-associated immune receptor, NOD
2, to figure out how it can lose the ability to respond properly to bacteria. In the process, they identified the involvement of a protective protein called HSP
70. Increasing HSP
70 levels in kidney, colon and white blood cells appeared to restore NOD
2 function. This work represents a first step toward developing drugs to treat Crohn’s disease.
This work was funded in part by an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) Network of Biomedical Research Excellence (INBRE) grant.